Interval Cascade Intelligent Control in Vaper-water Plate-type Heat Exchange Process
-
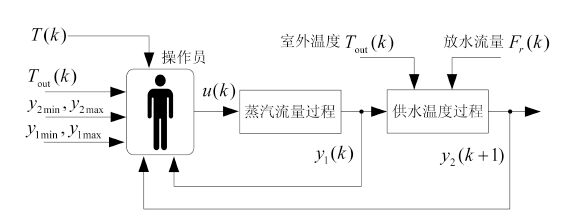
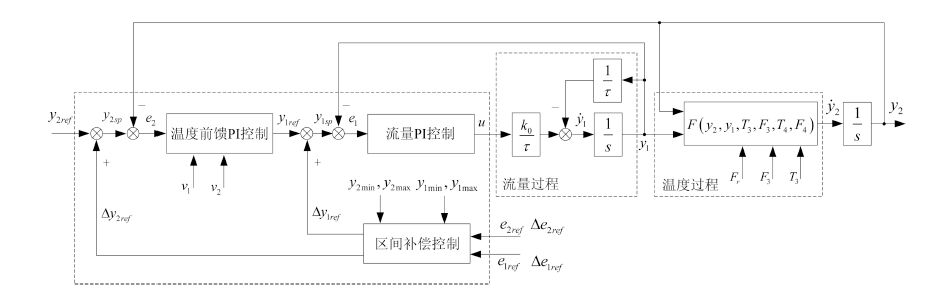
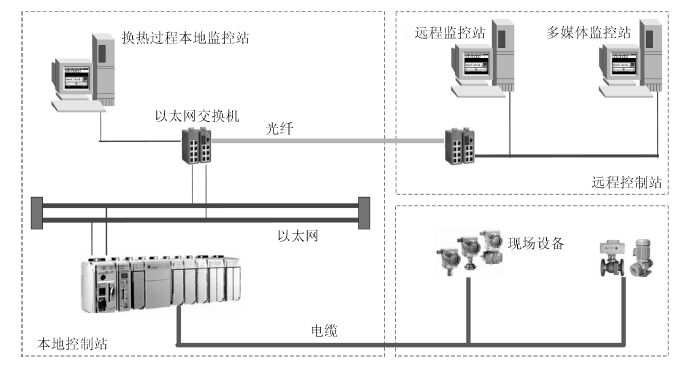
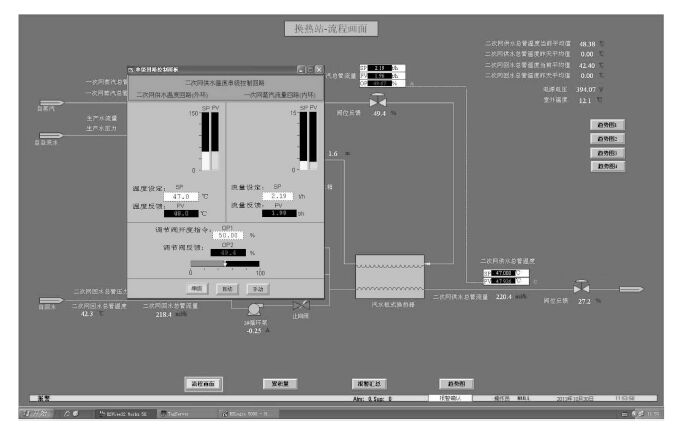
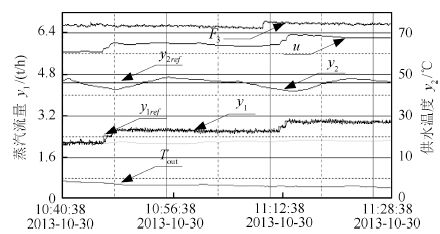
摘要: 汽水板式换热过程是以蒸汽阀门开度为输入,以蒸汽流量为内环输出,以供水温度为外环输出的强非线性串级工业过程,受到室外温度和厂区热用户放水的随机干扰,导致供水温度和蒸汽流量大范围波动.本文针对处于干扰环境下的具有不确定性和强非线性串级工业过程,将前馈补偿、串级PI控制和规则推理区间补偿控制相结合,提出了由外环供水温度前馈PI控制、内环蒸汽流量PI控制的串级控制与规则推理的内外环设定值区间补偿控制组成的区间串级智能控制方法,并成功应用于某选矿厂的汽水板式换热过程,工业应用结果表明所提出的方法在室外温度和热用户放水的随机干扰下,可以将供水温度和蒸汽流量同时控制在工艺要求的范围内.Abstract: The vaper-water plate-type heat exchange process(PHEP) is a strong nonlinear cascade industrial process where the input is the steam valve position and the outputs are the inner loop steam flow-rate and the outer loop supply water temperature. During its operation, some large random disturbances are generated from the outside temperature and the water discharged by users, the supply water temperature and the steam flow-rate undergo large fluctuations. This paper aims at the cascade industrial process with uncertainty and strong nonlinearity under disturbance environment, and combines feedforward compensation, cascade control and the rule based reasoning(RBR) interval compensation control together. A novel intelligent control method is established that includes the outer loop supply water temperature control with feedforward compensation, loop steam flow cascade control and set-point interval of compensation control based on interval RBR. An application to a real vaper-water plate-type heat exchanger is provided. The real application has shown that the proposed method can ensure the supply water temperature and the steam flow within their target ranges when the process is subject to random disturbances of outside temperature and water discharged by users.
-
表 1 变量参数表
Table 1 Variable parameter list
变量 描述 变量 描述 $T$ 室内温度 $V$ 换热板体积 $T_{\rm out}$ 室外温度 $\mu$ 换热面修正系数 $y_2$ 供水温度 $K$ 换热系数 $y_1$ 蒸汽流量 $\eta$ 换热效率 ${y_{2\min} }$ 供水温度下限值 $H_v$ 蒸汽热含 ${y_{2\max} }$ 供水温度上限值 ${\rho _w}$ 水密度 ${y_{1\min} }$ 蒸汽流量下限值 $c_w$ 水比热 ${y_{1\max} }$ 蒸汽流量上限值 $k_0$ 蒸汽流量比例系数 ${y_{2ref}}$ 温度预设定值 $\tau$ 蒸汽流量实际常数 ${y_{2sp}}$ 温度设定值 $J$ 回水相对流量 ${y_{1ref}}$ 流量预设定值 $I$ 热交换特性参数 ${y_{1sp}}$ 流量设定值 ${\varphi _1},{\varphi _2}$ 设计参数 $u$ 阀门开度 $K_2$ 温度过程增益 $P_1$ 蒸汽压力 $T_2$ 温度时间常数 $T_1$ 蒸汽温度 ${\tau_2}$ 温度延迟时间 $T_3$ 回水温度 ${k_{p2}},{k_{i2}}$ 外环PI控制参数 $T_4$ 冷凝水温度 ${k_{f1}},{k_{f2}}$ 前馈控制参数 $F_2$ 供水流量 ${k_{p1}},{k_{i1}}$ 内环PI控制参数 $F_3$ 回水流量 $\varepsilon ,\lambda ,\alpha ,\beta $ 区间补偿控制参数 $F_4$ 冷凝水流量 $\phi $ 阀门阈值 $F_b$ 补水流量 ${T_{m1}}$ 流量采样周期 $F_r$ 放水总流量 ${T_{m2}}$ 温度采样周期 表 2 采用本文控制方法与人工控制方法对比数据
Table 2 Comparison of the data between the proposed method and the artificial control method
$y_2$ ~(℃) $y_1$ ~(t/h) $u$ ~(%) 本文 ±3 ±0.6 20 人工 ±8 ±2.0 40 -
[1] 石兆玉. 供热系统运行调节与控制. 北京:清华大学出版社, 1999.Shi Zhao-Yu. The Adjustment of Heating System and Control. Beijing:Tsinghua University Press, 1999. [2] 葛楠, 李铁鹰, 王宇慧. 变论域模糊PID算法在供热控制中的应用. 科学技术与工程, 2012, 12(34):9203-9206 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201234017.htmGe Nan, Li Tie-Ying, Wang Yu-Hui. The application of variable universe fuzzy PID algorithm in heating control system. Science Technology and Engineering, 2012, 12(34):9203-9206 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201234017.htm [3] Rauh A, Dittrich C, Aschemann H, Nedialkov N S, Pryce J D. A differential-algebraic approach for robust control design and disturbance compensation of finite-dimensional models of heat transfer processes. In:Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics. Vicenza, Italy:IEEE, 2013. 40-45 [4] Kharitonov A, Sawodny O. Flatness-based feedforward and feedback control for heat and mass transfer processes. In:Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Conference on Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics. Bangkok, Thailand:IEEE, 2006. 1-6 [5] Bobál V, Kubaltčík M, Dostál P. Identification and self-tuning predictive control of heat exchanger. In:Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Process Control. Strbske Pleso, Slovakia:IEEE, 2013. 219-224 [6] Holman J P. Heat Transfer. New York:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co., 2001. [7] 李海波, 柴天佑, 赵大勇. 混合选别浓密机底流矿浆浓度和流量区间智能切换mm控制方法. 自动化学报, 2013, 40(9):1967-1975 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18467.shtmlLi Hai-Bo, Chai Tian-You, Zhao Da-Yong. Intelligent switching control of underflow slurry concentration and flowrate intervals in mixed separation thickener. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 40(9):1967-1975 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18467.shtml [8] 涂光备. 供热计量技术. 北京:中国建筑工业出版社, 2003.Tu Guang-Bei. Heat Metering Technology. Beijing:China Architecture&Building Press, 2003. [9] 张煜. 换热站供热系统研究及智能控制方案设计[硕士学位论文], 辽宁科技大学, 中国, 2011.Zhang Yi. The Study of Heat Exchange Station Heating System and the Design of Intelligent Control Program[Master dissertation], University of Science and Technology Liaoning, China, 2011. [10] 梁元元. 供水温度分栋可调的控制策略[硕士学位论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 中国, 2011.Liang Yuan-Yuan. The Control Strategy on Supply Water Temperature Building Regulation System[Master dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, China, 2011. [11] Seborg D E, Edgar T F, Mellichamp D A[著], 王京春, 王凌, 金以慧[译]. 过程的动态特性与控制. 北京:电子工业出版社, 2006.Seborg D E, Edgar T F, Mellichamp D A[Author], Wang Jing-Chun, Wang Ling, Jin Yi-Hui[Translator]. Process Dynamics and Control. Beijing:Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2006. [12] 赵大勇, 柴天佑. 再磨过程泵池液位区间与给矿压力模糊切换控制. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(5):556-564 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17816.shtmlZhao Da-Yong, Chai Tian-you. Fuzzy switching control for sump level interval and hydrocyclone pressure in regrinding process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(5):556-564 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17816.shtml [13] Lequin O, Gevers M, Mossberg M, Bosmans E, Triest L. Iterative feedback tuning of PID parameters:comparison with classical tuning rules. Control Engineering Practice, 2003, 11(9):1023-1033 doi: 10.1016/S0967-0661(02)00303-9 [14] Dai W, Chai T Y, Yang S X. Data-driven optimization control for safety operation of hematite grinding process. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(5):2930-2941 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2014.2362093 [15] Li W, Hori Y. An algorithm for extracting fuzzy rules based on RBF neural network. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2006, 53(4):1269-1276 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2006.878305 [16] Wang Y F, Wang D H, Chai T Y. Extraction and adaptation of fuzzy rules for friction modeling and control compensation. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2011, 19(4):682-693 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2011.2134104 [17] Aström K J, Anton J J, Arz'en K E. Expert control. Automatica, 1986, 22(3):277-286 doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(86)90026-9 [18] 刘建昌, 关守平, 周玮. 计算机控制系统. 北京:科学出版社, 2009.Liu Jian-Chang, Guan Shou-Ping, Zhou Wei. Computer Control System. Beijing:Science Press, 2009. [19] (Katsuhiko Ogata[著], 蔡涛, 张娟[译]. 离散时间控制系统. 第2版. 北京:电子工业出版社, 2014.)Katsuhiko Ogata[Author], Cai Tao, Zhang Juan[Translator]. Discrete-Time Control Systems(Second edition). Beijing:Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2014. [20] 金以慧. 过程控制. 北京:清华大学出版社, 1993.Jin Yi-Hui. Process Control. Beijing:Tsinghua University Press, 1993. -





 下载:
下载: