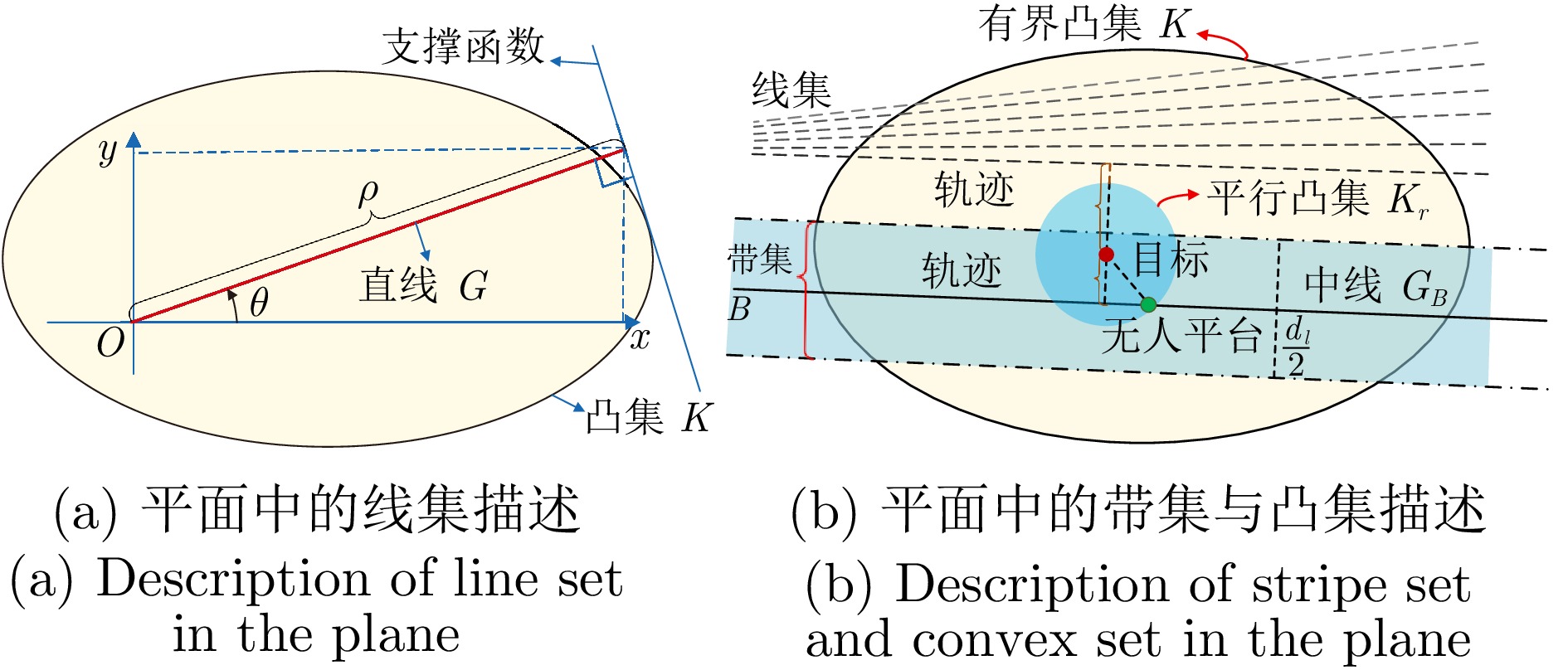
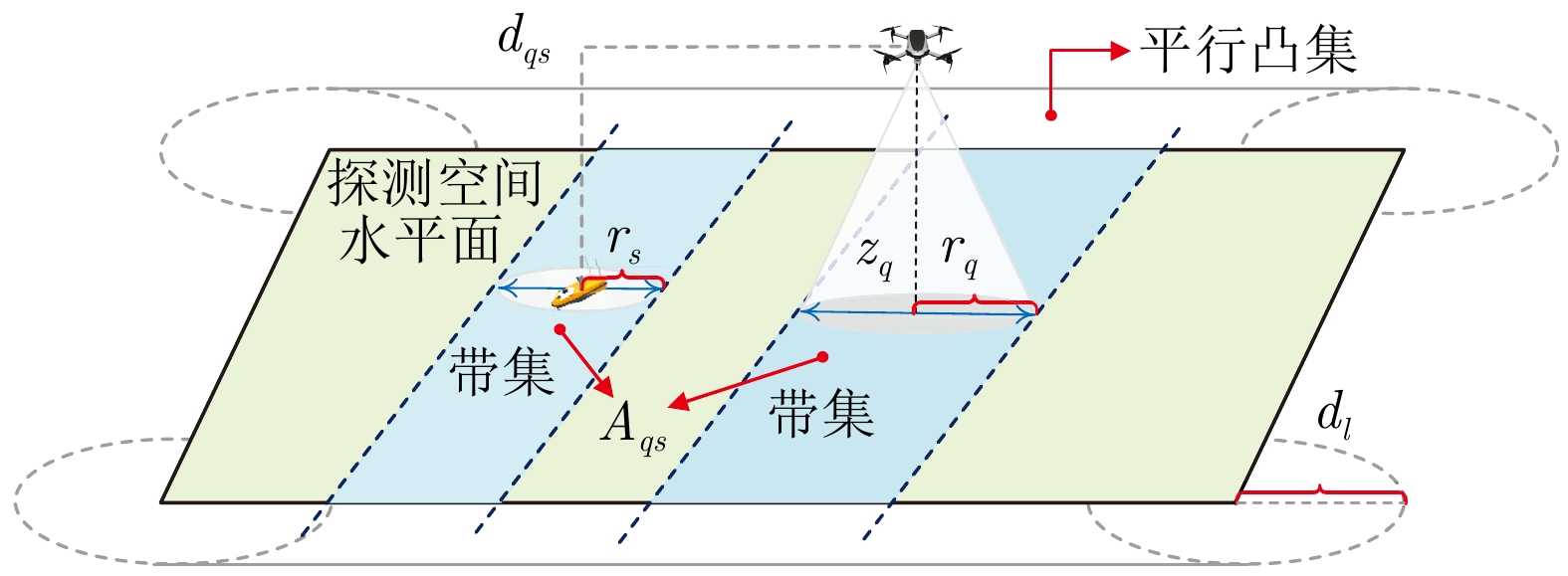
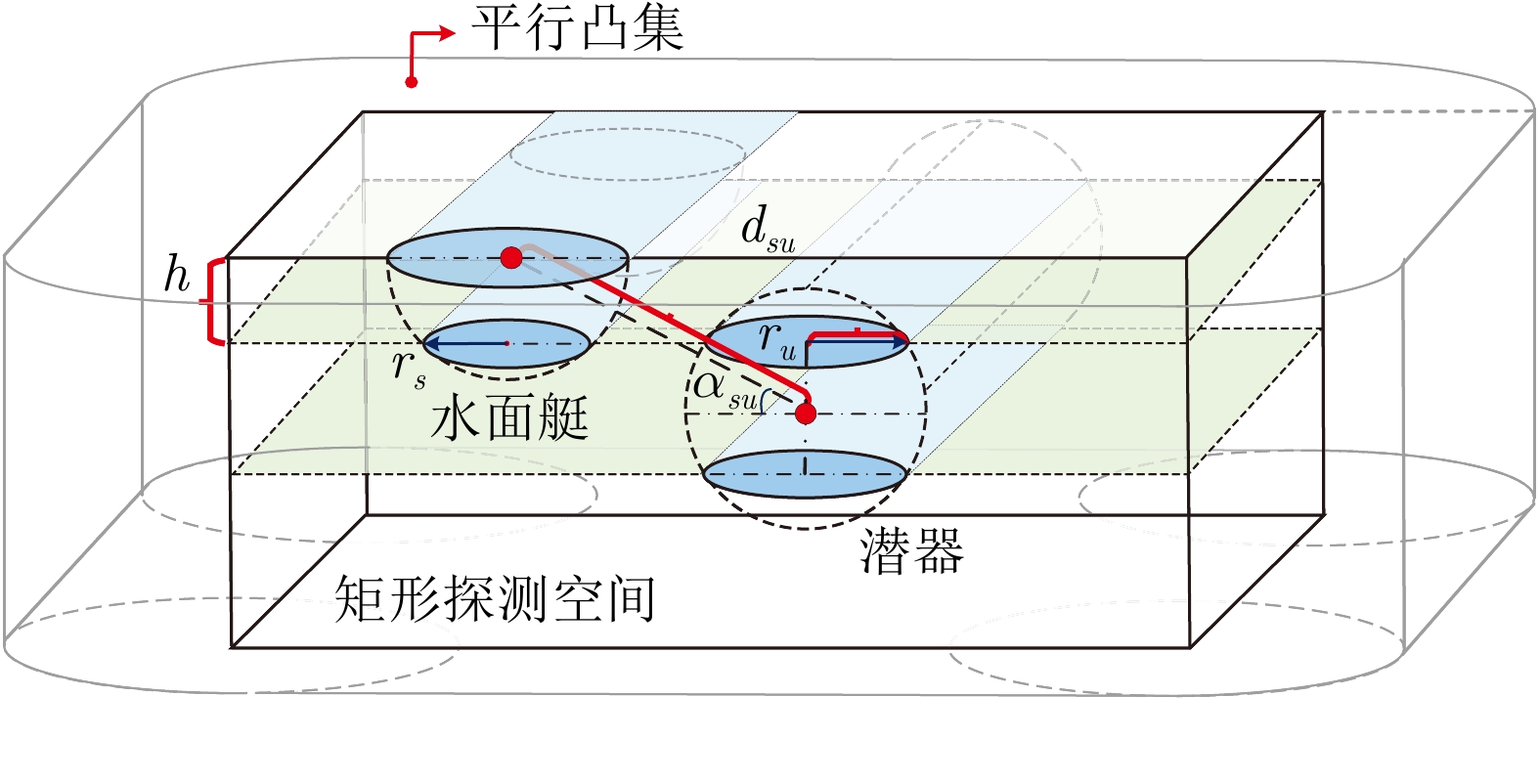
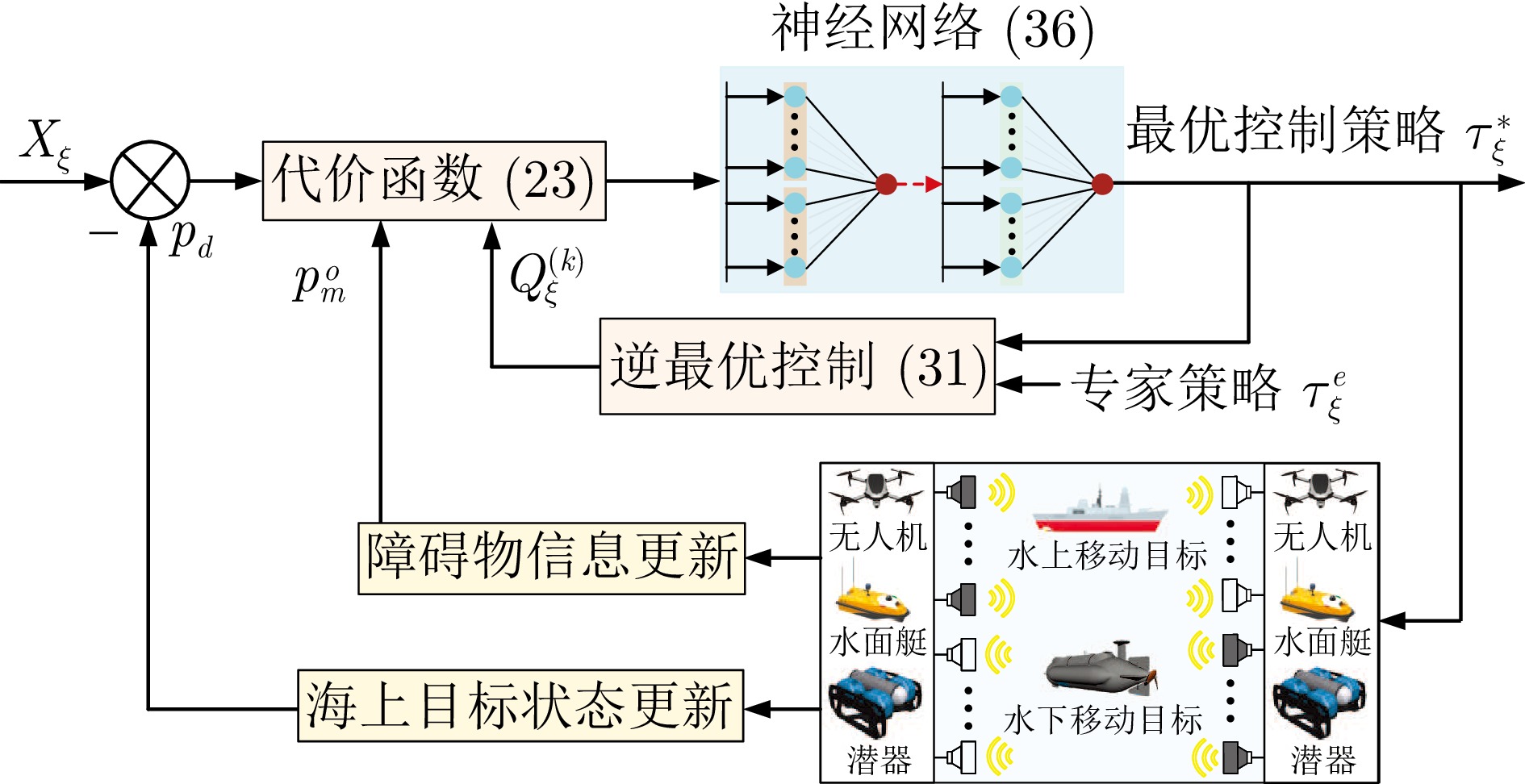
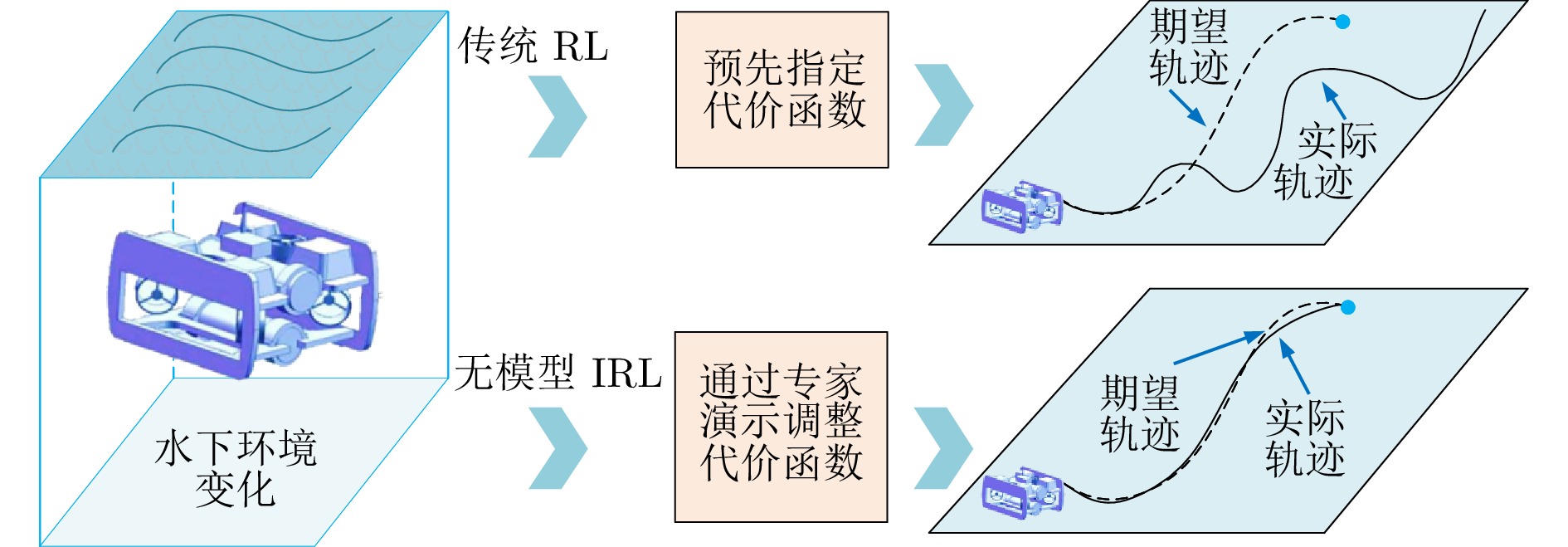
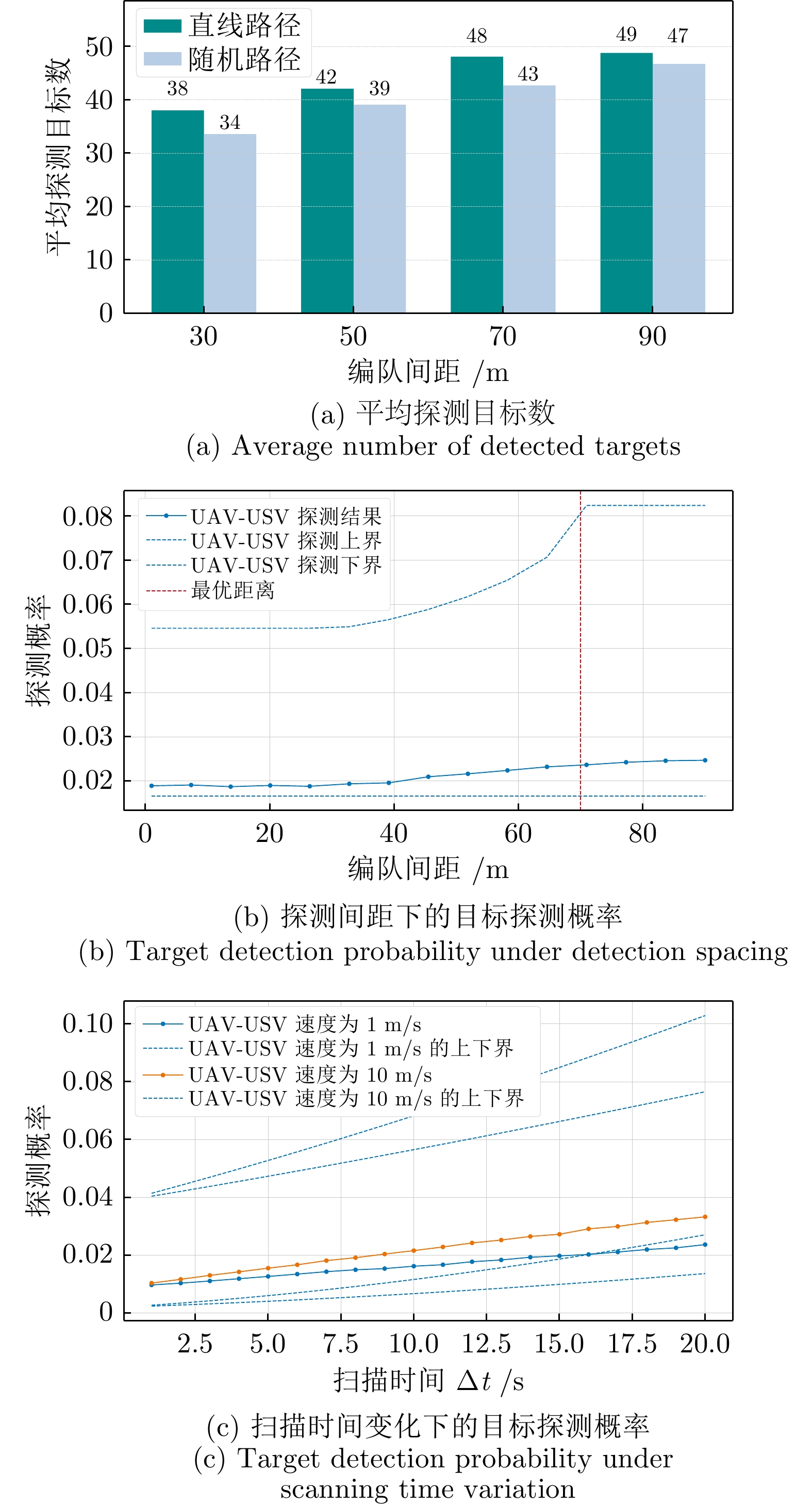
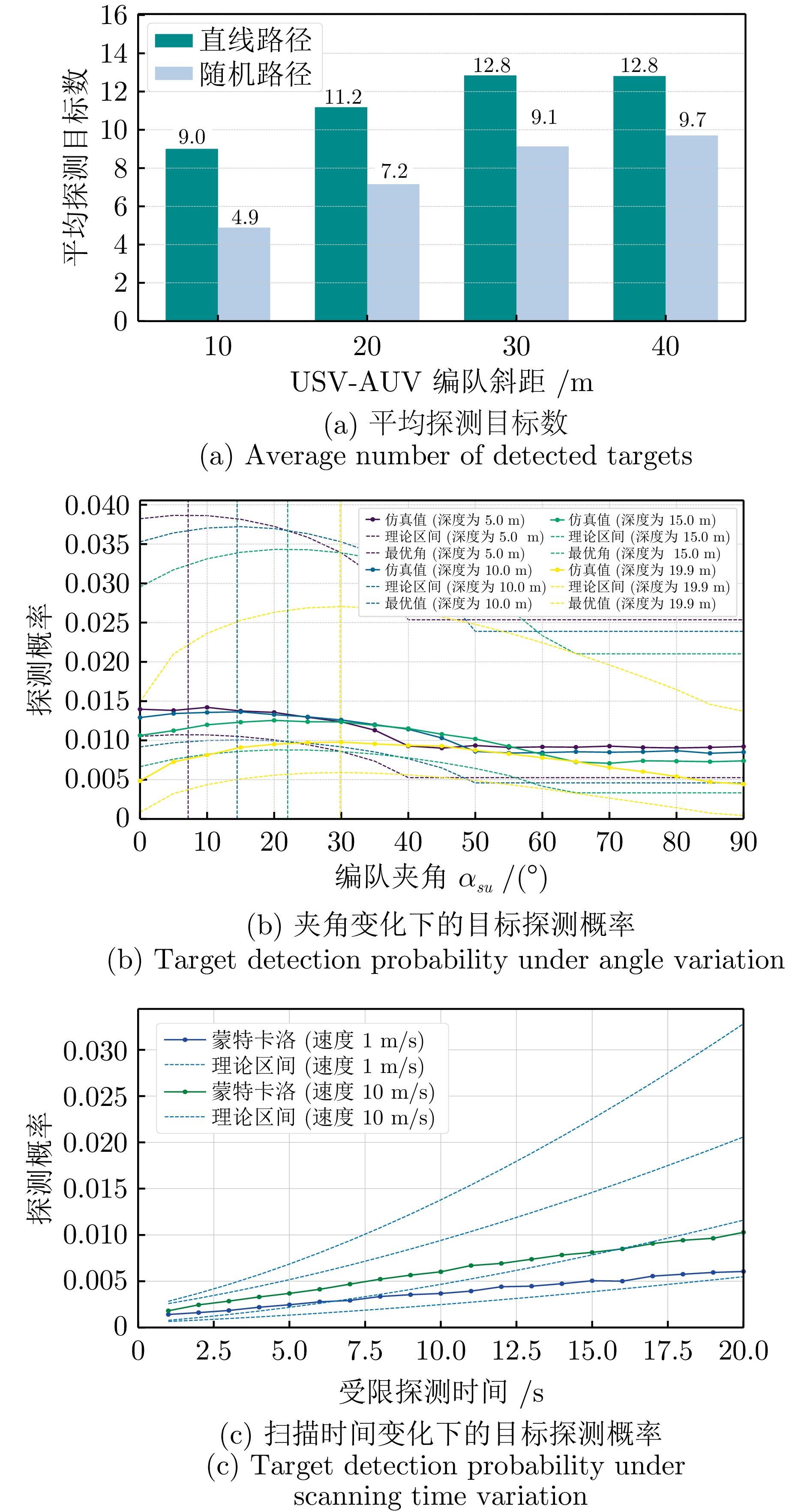
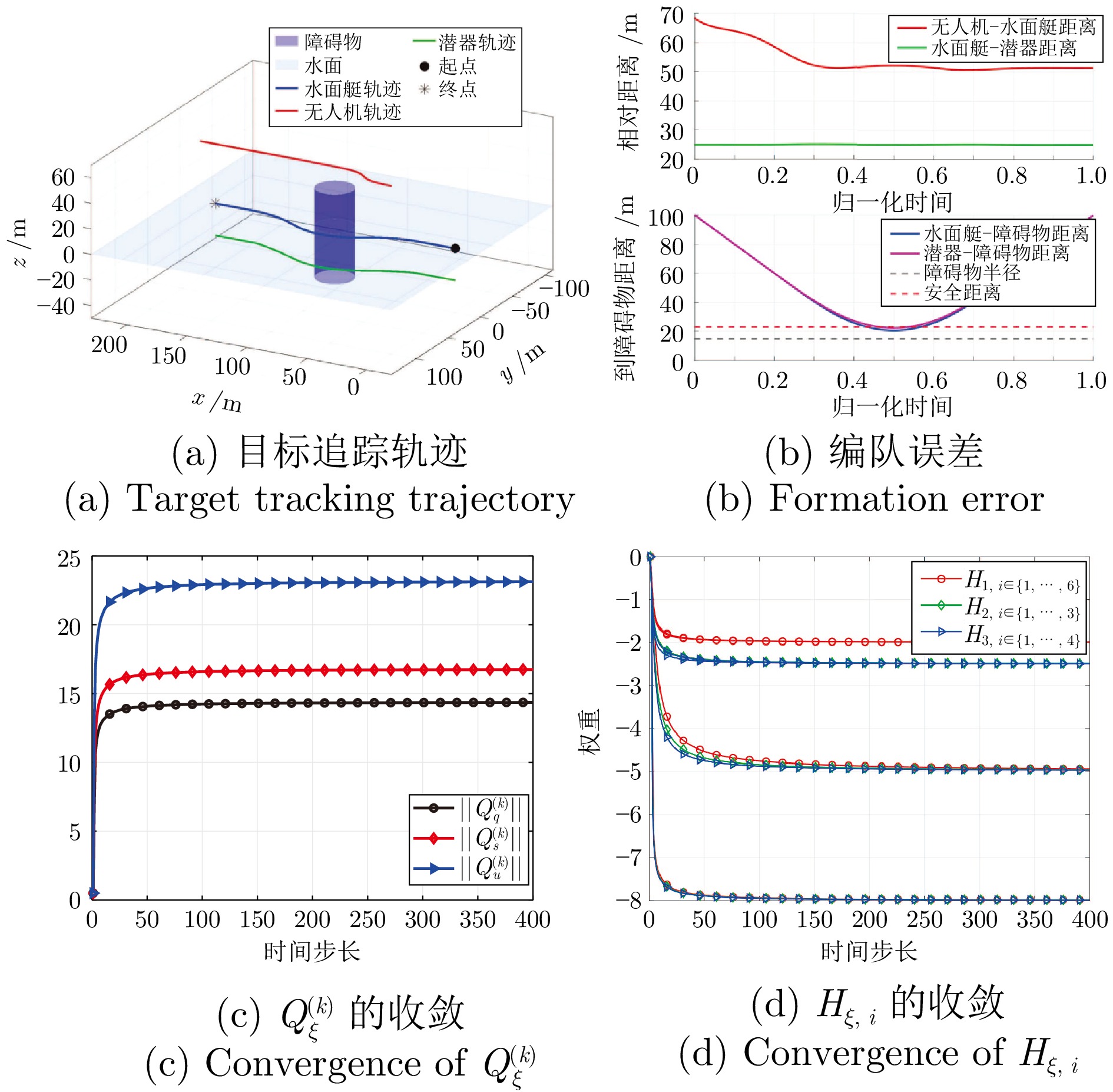
|
[1]
|
闫敬, 关新平. 海上无人系统跨域集群发展现状及其关键技术. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(4): 744−761Yan Jing, Guan Xin-Ping. Development status and key techniques for cross-domain swarm of maritime unmanned systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(4): 744−761
|
|
[2]
|
Cui S W, Wang Y, Wang S, Wang R, Wang W, Tan M. Real-time perception and positioning for creature picking of an underwater vehicle. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(4): 3783−3792 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2973656
|
|
[3]
|
Wang Q, Zhang Y X, He B. Intelligent marine survey: Lightweight multi-scale attention adaptive segmentation framework for underwater target detection of AUV. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025, 22(1): 1913−1927
|
|
[4]
|
Kim J. Surface target tracking using towed array sonars with direct and bottom bounce underwater sound signals. IEEE Transactions on Signal and Information Processing Over Networks, 2022, 8(1): 997−1007
|
|
[5]
|
Chen X L, Huang F H, Pan Y J, Chen Z. Bearing-only-based cooperative target enclosing control for multiple uncrewed surface vehicles with unknown dynamics and sideslip. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2025, 50(2): 1015−1029 doi: 10.1109/JOE.2024.3478311
|
|
[6]
|
Tang P, Zhang Y. LiteFlex-YOLO: A lightweight small target detection network for maritime unmanned aerial vehicles. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 2025, 111(1): 1−22
|
|
[7]
|
Ke C, Chen H F. Cooperative path planning for air-sea heterogeneous unmanned vehicles using search-and-tracking mission. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 262(1): 1−13
|
|
[8]
|
McCammon S, Santos G M D, Frantz M, Welch T P, Best G, Shearman R K, et al. Ocean front detection and tracking using a team of heterogeneous marine vehicles. Journal of Field Robotics, 2021, 38(6): 854−881
|
|
[9]
|
Wu Y, Low K H, Lv C. Cooperative path planning for heterogeneous unmanned vehicles in a search-and-track mission aiming at an underwater target. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(6): 6782−6787 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2991983
|
|
[10]
|
Yan J, Lin J S, Yang X, Chen C L, Guan X P. Cooperation detection and tracking of underwater target via aerial-surface-underwater vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2025, 70(2): 1068−1083 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2024.3447976
|
|
[11]
|
Jiang X W, Jiao R R, Li B, Zhang X H, Yan H C. Finite-time consensus of second-order multiagent systems with input saturation via hybrid sliding-mode control. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025, 22(1): 14623−14632
|
|
[12]
|
Jin D Y, Ahn C K, Xiang Z R. Adaptive distributed fuzzy control for prescribed-time formation of multiple autonomous aerial vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(2): 1589−1599 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3456756
|
|
[13]
|
Sun Z B, Wu B L, Wang D W, Chen J Y. Event-triggered model predictive control of spacecraft formation. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025, 22(1): 7696−7711
|
|
[14]
|
Wei W, Wang J J, Fang Z R, Chen J R, Ren Y, Dong Y H. 3U: Joint design of UAV-USV-UUV networks for cooperative target hunting. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(3): 4085−4090 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3220856
|
|
[15]
|
Zhao W B, Liu H, Valavanis K P, Lewis F L. Fault-tolerant formation control for heterogeneous vehicles via reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 2796−2806 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3139260
|
|
[16]
|
Xue W Q, Kolaric P, Fan J L, Lian B S, Chai T Y, Lewis F L. Inverse reinforcement learning in tracking control based on inverse optimal control. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(10): 10570−10581
|
|
[17]
|
Lian B S, Kartal Y, Lewis F L, Mikulski D G, Hudas G R, Wan Y, et al. Anomaly detection and correction of optimizing auto-nomous systems with inverse reinforcement learning. IEEE Tran-sactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(7): 4555−4566 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3213526
|
|
[18]
|
Tian Z X, Yan J, Yang X, Chen C L, Guan X P. Optimally persistent formation of AUVs with model uncertainty and unknown interaction topology. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2025, 26(9): 13993−14010
|
|
[19]
|
Zhao W B, Liu H, Wan Y, Lin Z L. Data-driven formation control for multiple heterogeneous vehicles in air-ground coordination. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2022, 9(4): 1851−1862 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2022.3181254
|
|
[20]
|
Liu X, Yan H C, Zhou W X, Wang N, Wang Y Y. Event-triggered optimal tracking control for underactuated surface vessels via neural reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(11): 12837−12847 doi: 10.1109/TII.2024.3424573
|
|
[21]
|
Wu H J, Yang Z H, Cao J N, Lai L Q. TRiForm: Formation control for underwater sensor networks with measurement errors. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(7): 7679−7691 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2989363
|
|
[22]
|
Cui R X, Yang C G, Li Y, Sharma S. Adaptive neural network control of AUVs with control input nonlinearities using reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2017, 47(6): 1019−1029
|
|
[23]
|
Liu B, Dousse O, Nain P, Towsley D. Dynamic coverage of mobile sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2012, 24(2): 301−311
|
|
[24]
|
Santaló L A. Integral Geometry and Geometric Probability. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2004.
|
|
[25]
|
Cao W Q, Yan J, Yang X, Luo X Y, Guan X P. Communication-aware formation control of AUVs with model uncertainty and fading channel via integral reinforcement learning. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2023, 10(1): 159−176
|
|
[26]
|
Demo for the target detection and tracking strategy based on the UAV-AUV [Online], available: https://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XNjQ5OTE4OTc4OA==.html?spm=a2hkn.playlist.myhome.d_0&playMode=pugv, November 16, 2025
|




 下载:
下载: