Knowledge-data-model-driven Trajectory Fusion Prediction Method for Low-altitude Moving Target
-
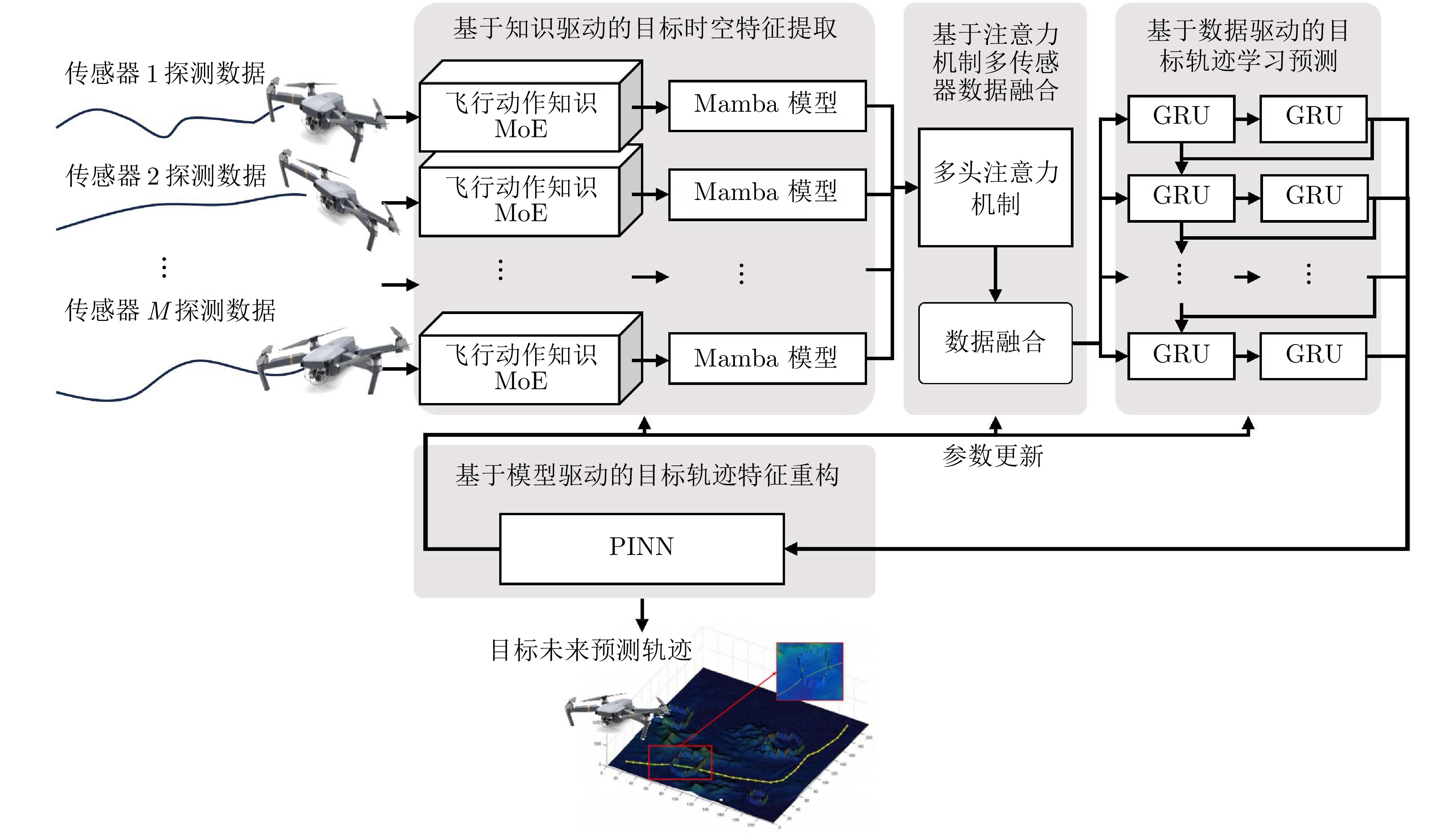
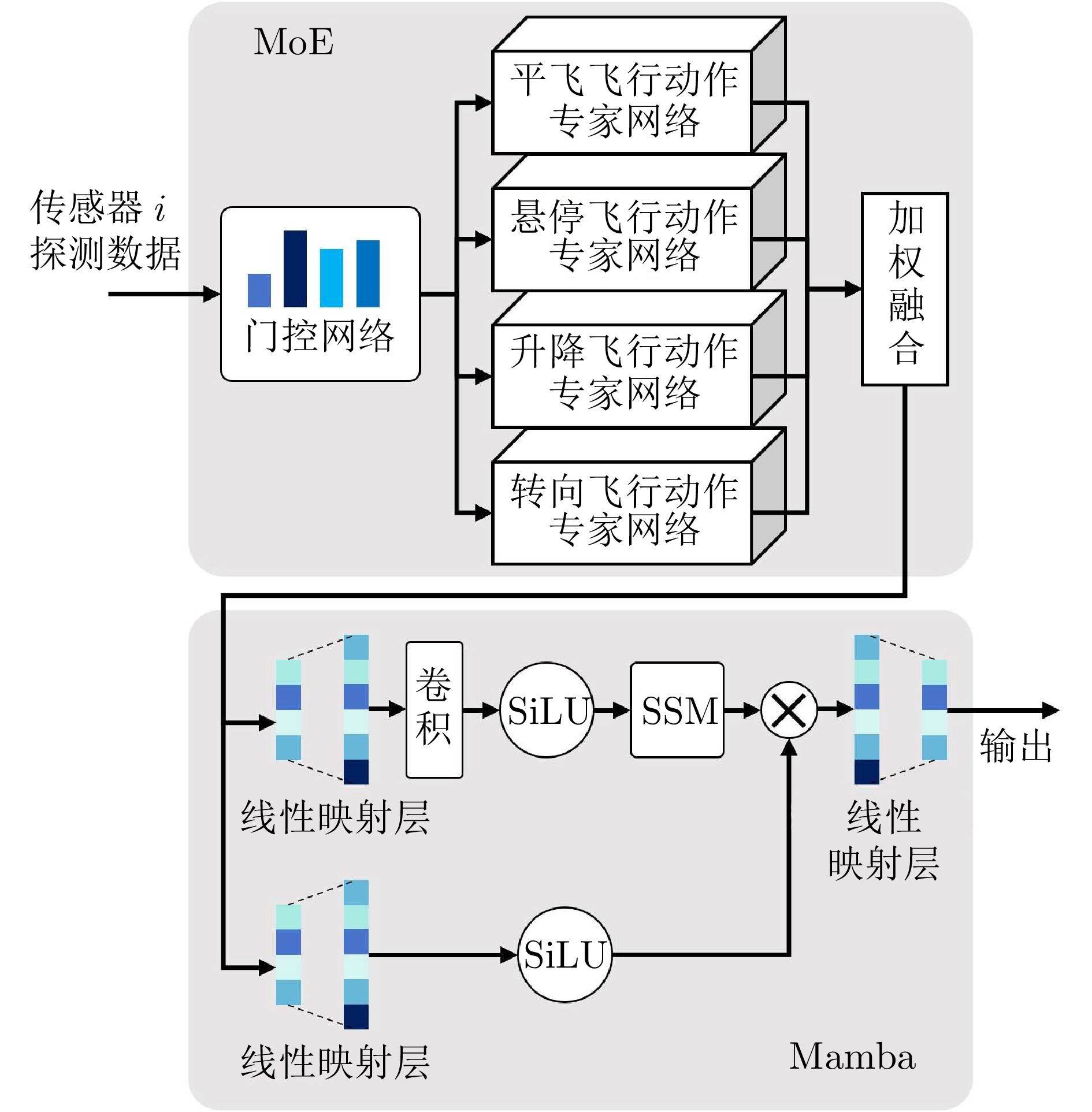
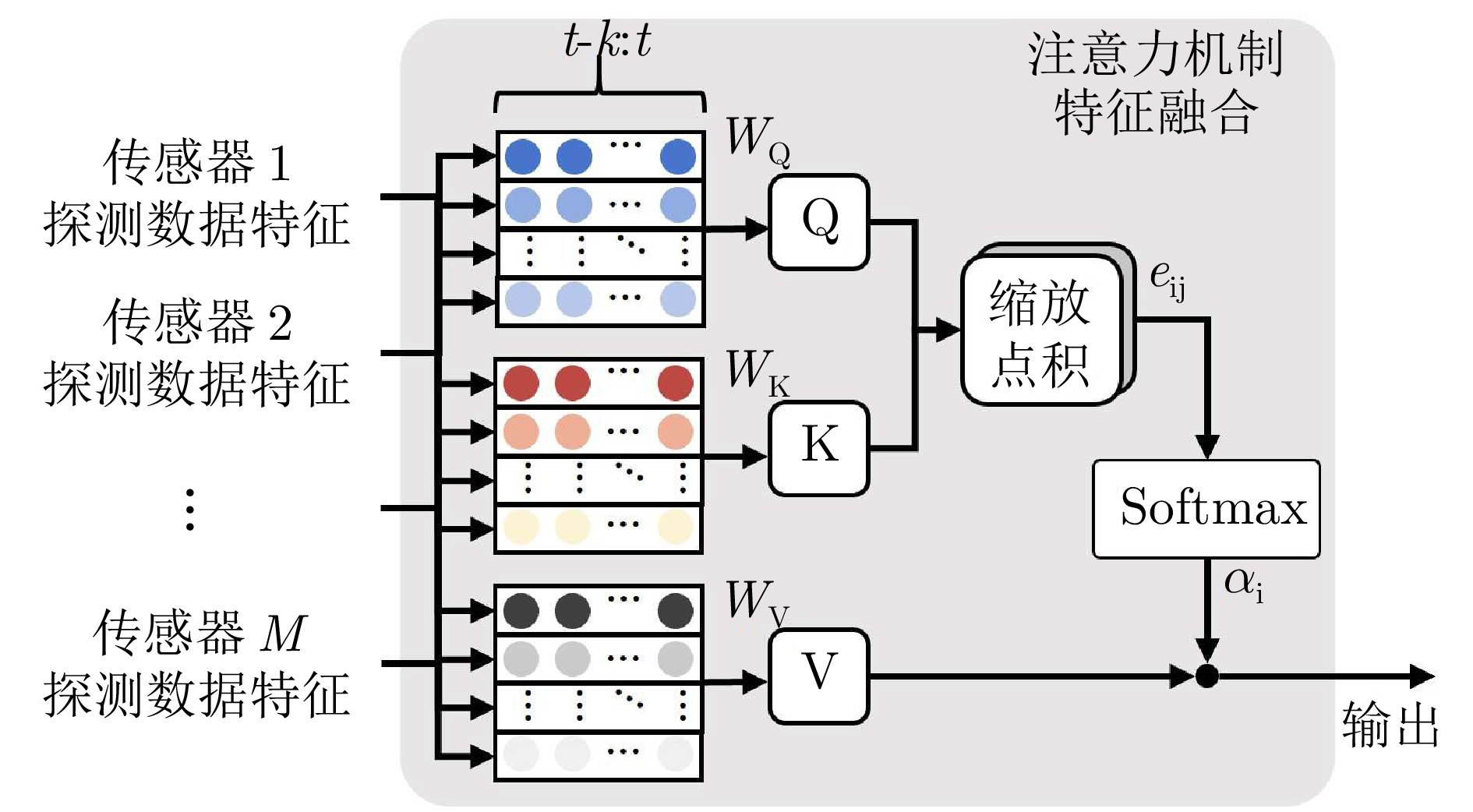
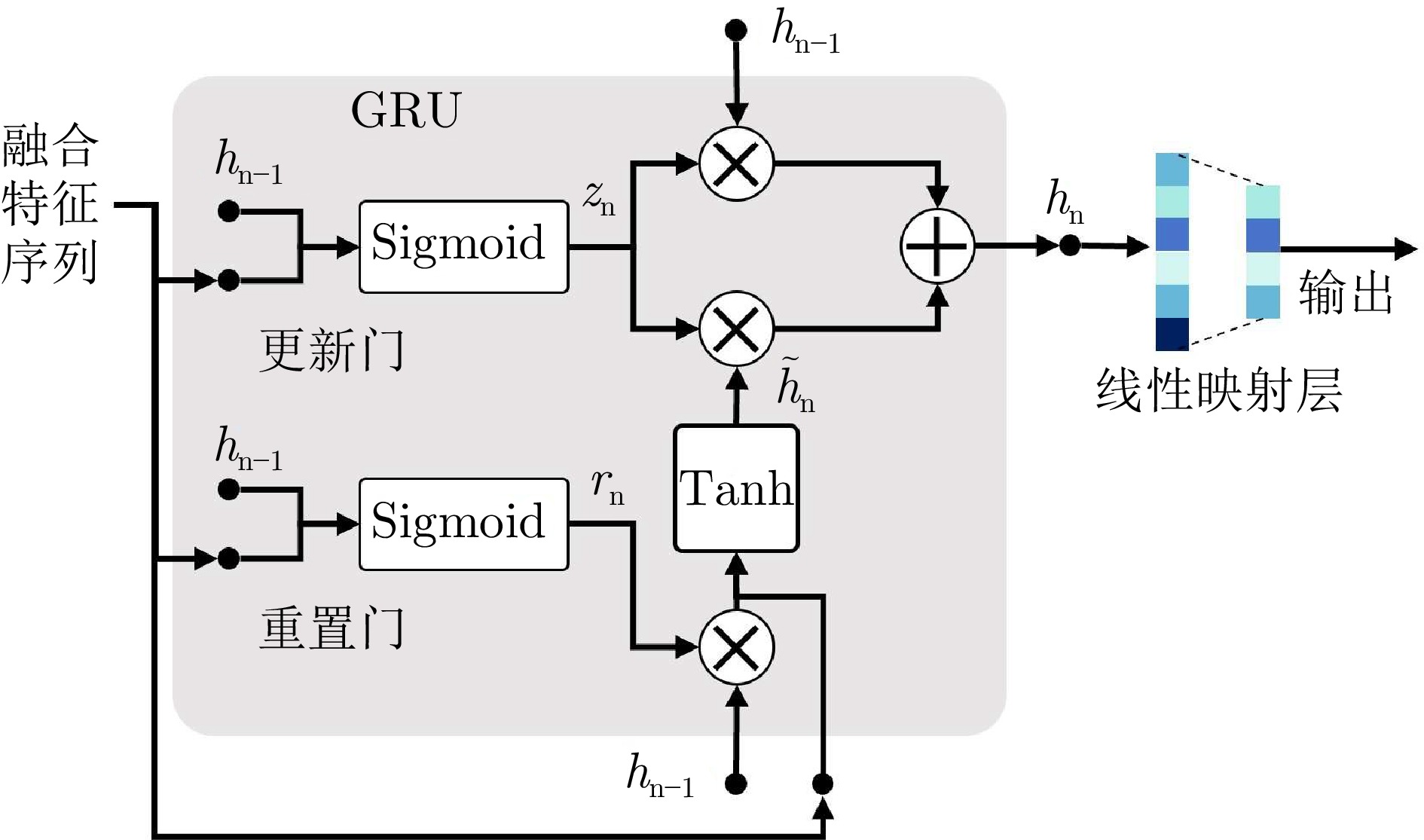
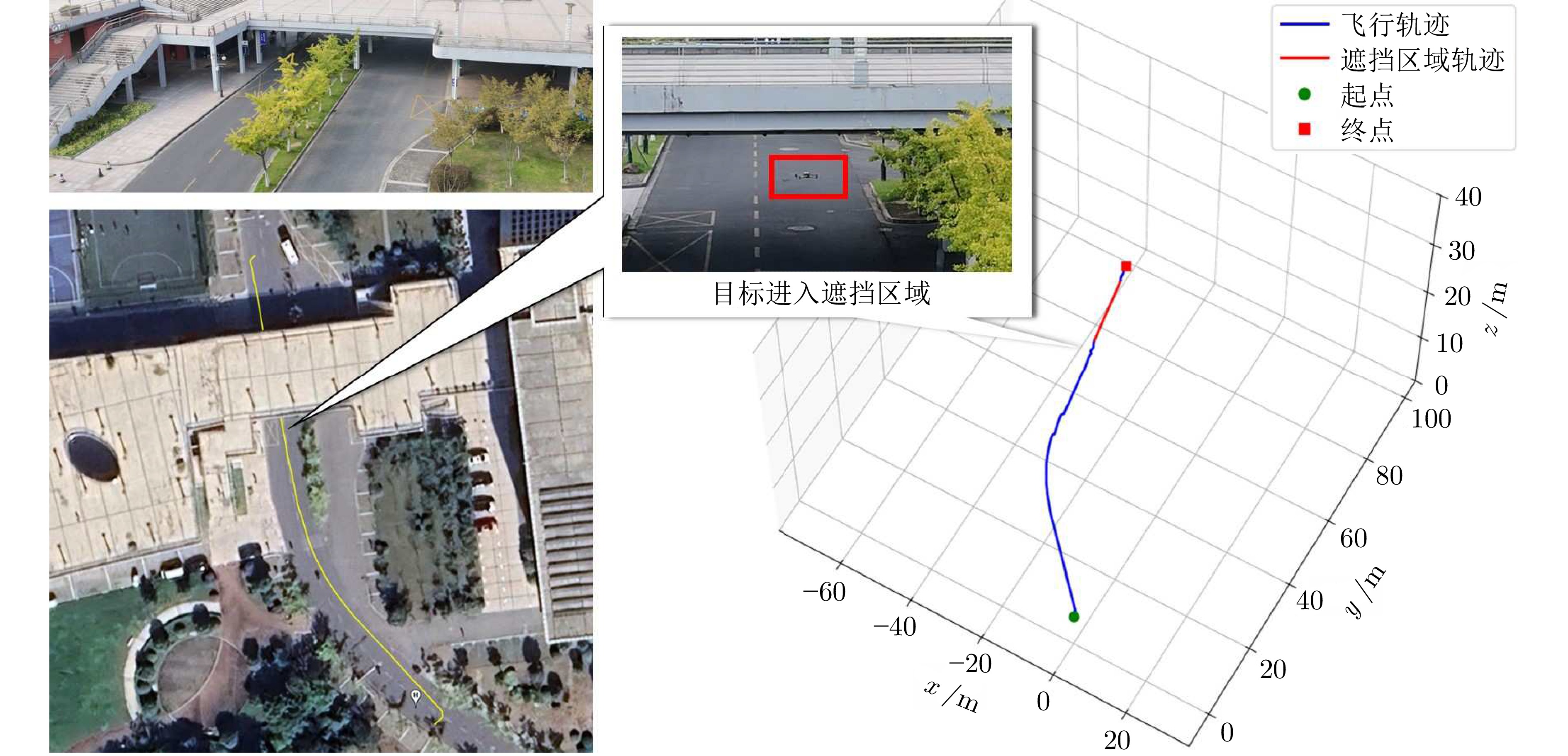
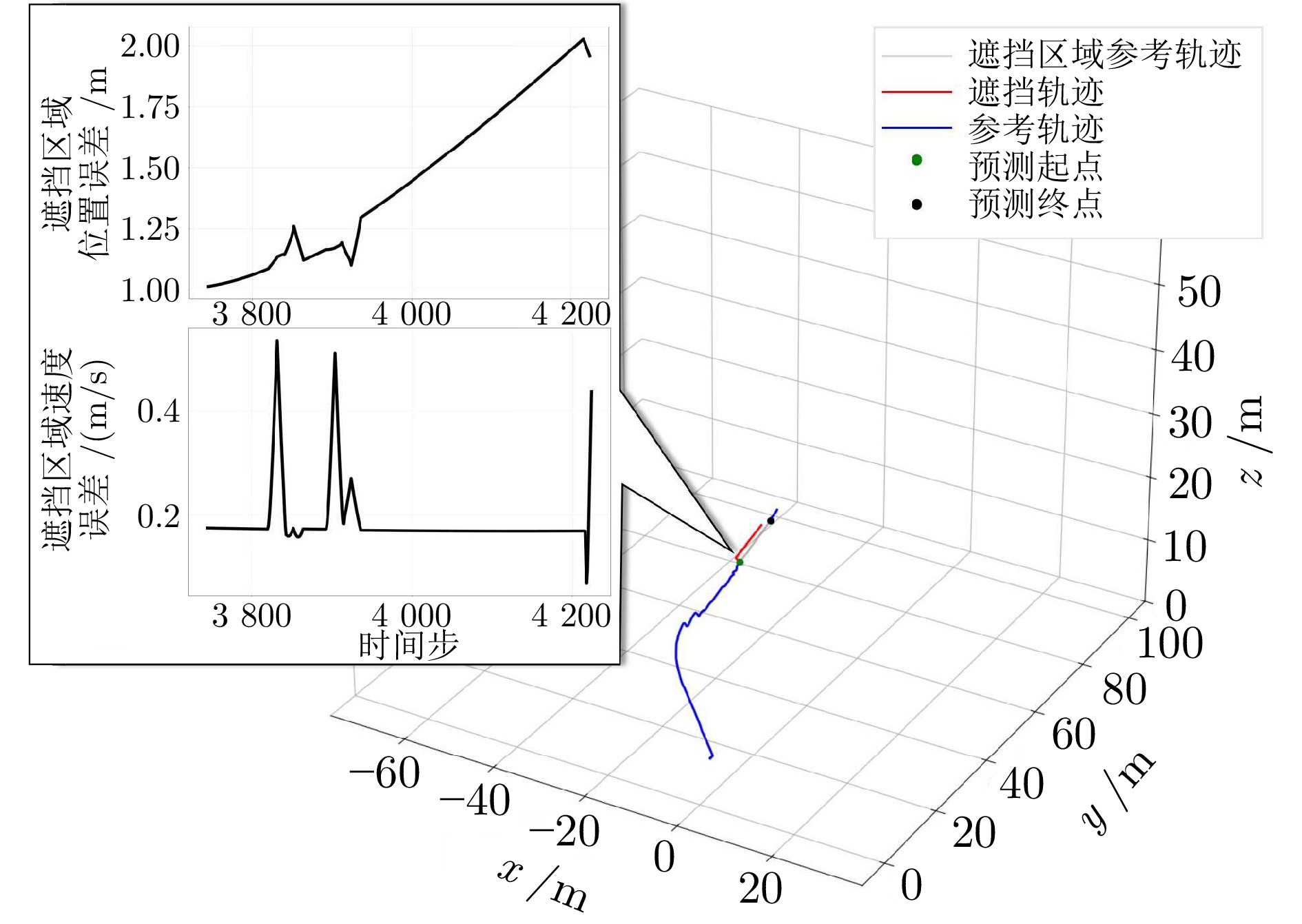
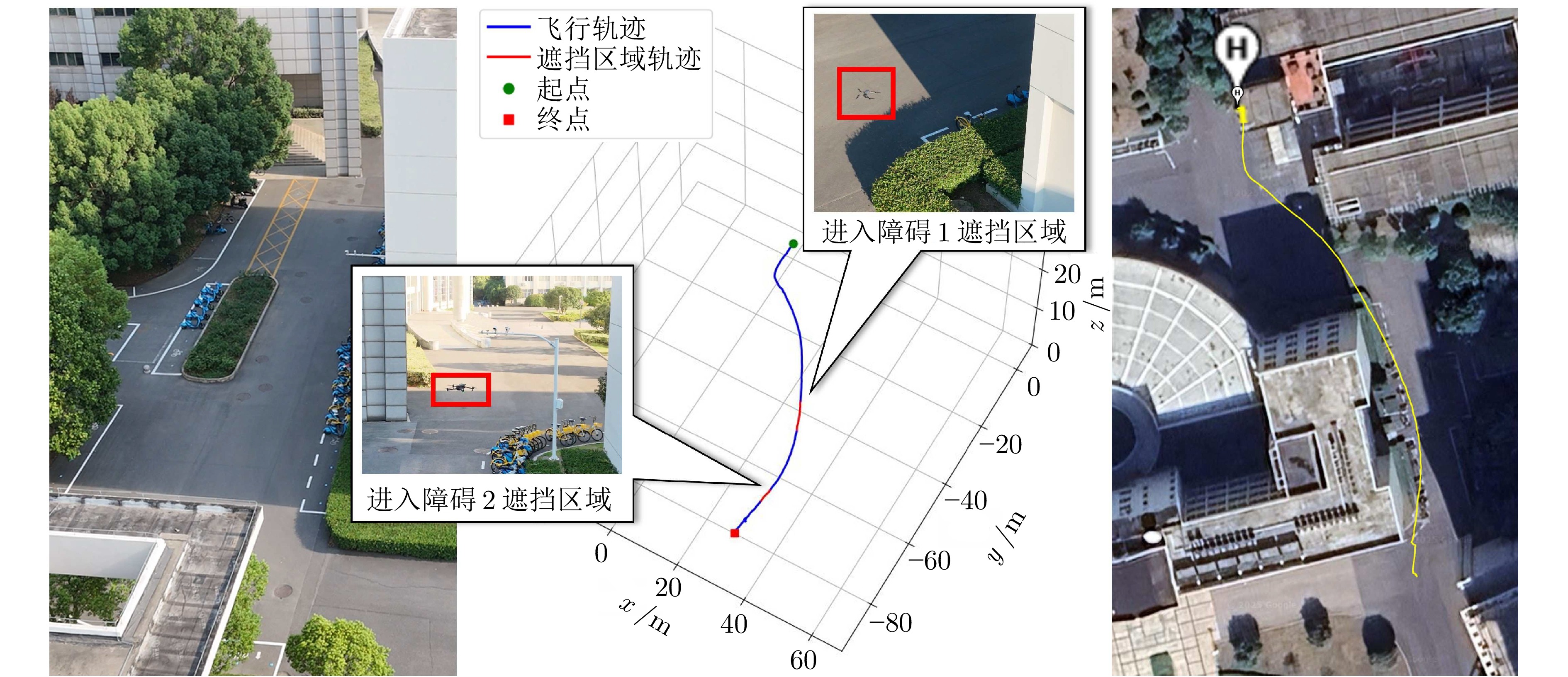
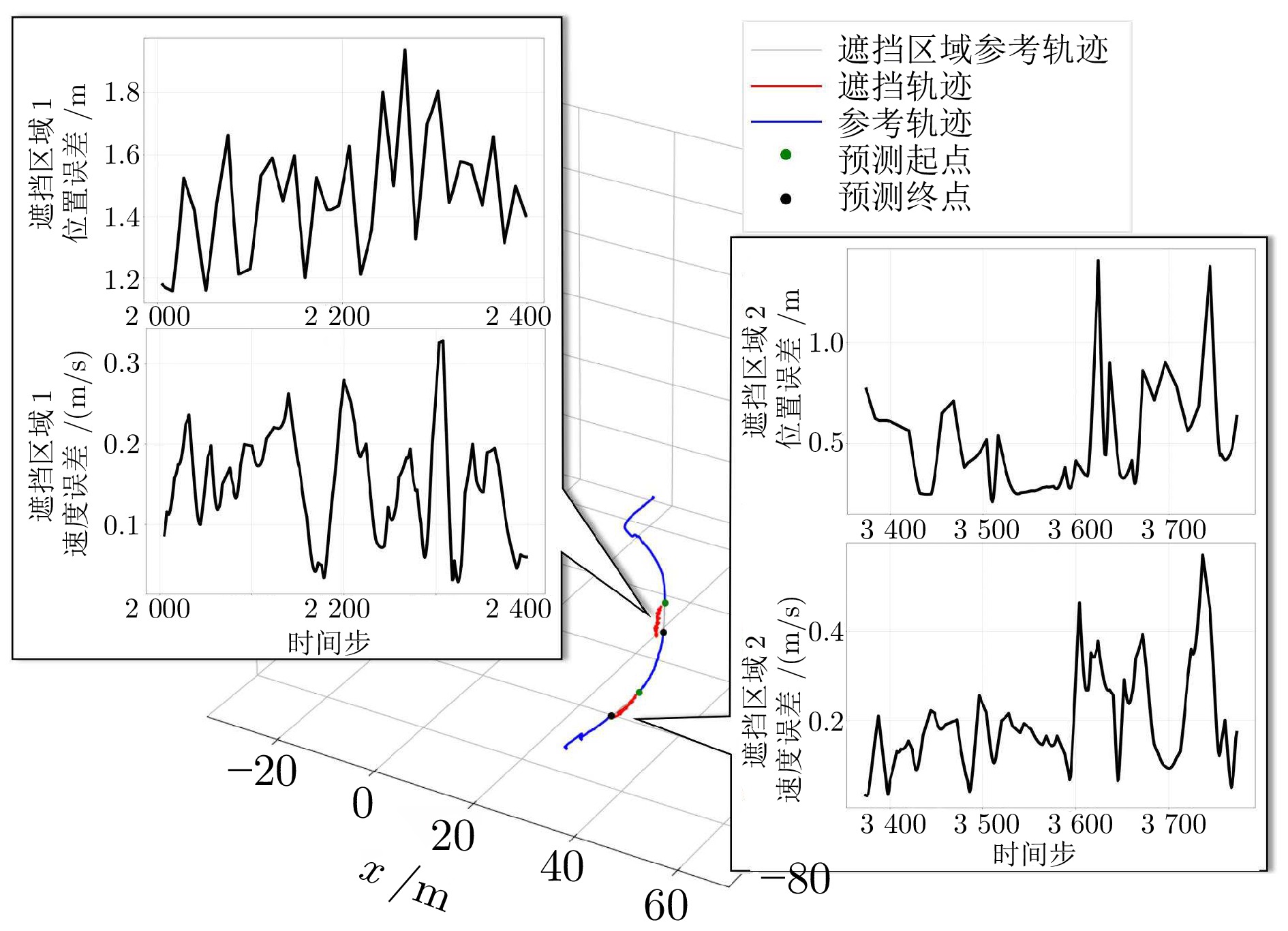
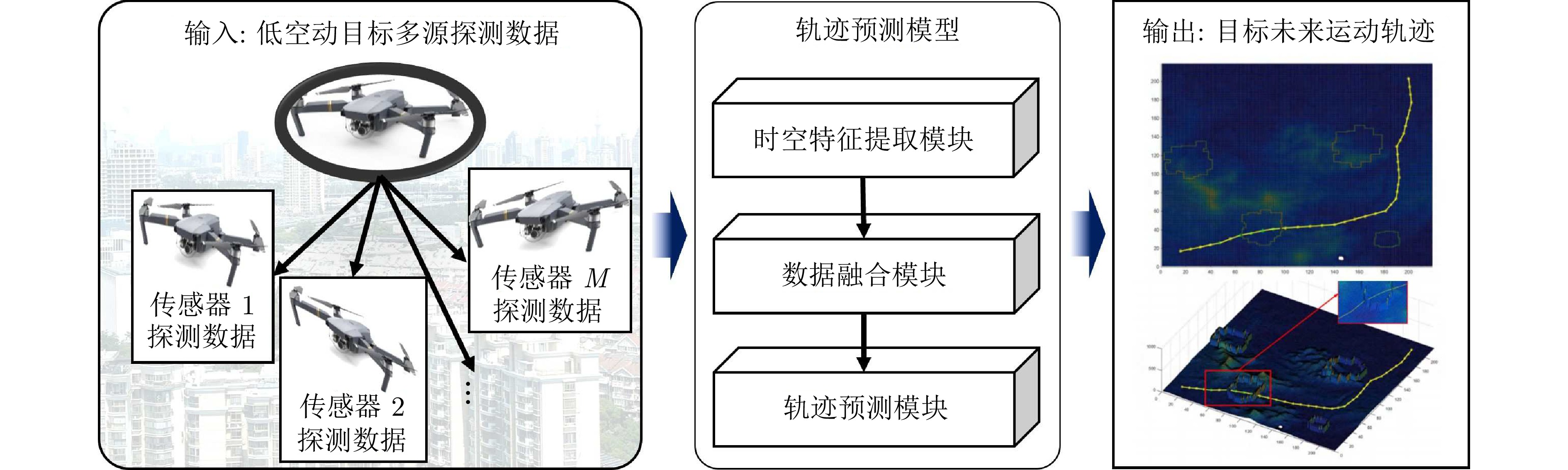
摘要: 针对低空环境下动目标轨迹预测问题, 提出一种知识—数据—模型驱动的动目标轨迹融合预测框架. 基于低空飞行器运动特征构建飞行知识混合专家模型, 通过将多源传感器数据输入至各飞行知识专家模块, 实现目标机动模态的精细化识别, 并使用Mamba模型提取时空关联特征; 设计权值自适应调节机制, 利用注意力机制动态融合多源感知数据, 解决传感器时空异步问题; 采用门控循环单元建模长期时序依赖关系, 根据目标历史飞行数据生成初步预测轨迹; 基于低空目标运动学方程构建物理信息神经网络, 通过动态权衡数据驱动损失与物理约束损失, 矫正数据驱动偏差, 确保预测轨迹满足运动学约束并有效抑制多步预测误差累积. 数值仿真及实验验证结果表明, 所提出的知识—数据—模型驱动的动目标轨迹融合预测方法, 能够有效预测低空目标飞行轨迹.
-
关键词:
- 低空环境 /
- 知识−数据−模型驱动 /
- 动目标 /
- 数据融合 /
- 轨迹预测
Abstract: Aiming at the moving target trajectory prediction problem in low-altitude environments, a knowledge-data-model-driven trajectory fusion prediction framework for moving target is proposed. A flight knowledge Mixture-of-experts model is constructed based on the kinematic characteristics of low-altitude aerial vehicles. Multi-source sensor data are fed into various flight knowledge expert modules to achieve precise identification of target maneuver modes, while spatiotemporal correlation features are extracted by using the Mamba model. A weight adaptive adjustment mechanism is designed to dynamically fuse multi-source perception data by using an attention mechanism, thereby addressing the spatiotemporal asynchrony issue of sensors. Long-term temporal dependencies are modeled using gated recurrent unit to produce preliminary trajectory predictions based on historical flight data of target. A physics-informed neural network is constructed based on the kinematic equations of low-altitude targets. By dynamically balancing data-driven loss and physical constraint loss, the network corrects data-driven biases, ensures predicted trajectories satisfy kinematic constraints, and effectively suppresses error accumulation in multi-step prediction. Numerical simulations and experimental validation results demonstrate that the proposed knowledge-data-model-driven trajectory fusion prediction method can effectively forecast low-altitude moving target flight trajectories. -
表 1 训练参数
Table 1 Training parameters
参数名称 取值 模型输入维度 6 门控网络隐藏单元 12 Mamba隐藏单元 12 Mamba因果卷积核 2 GRU隐藏单元 12 模型输出维度 6 学习率 0.001 表 2 目标位置和目标速度的预测结果对比
Table 2 Comparison of prediction results for target position and velocity
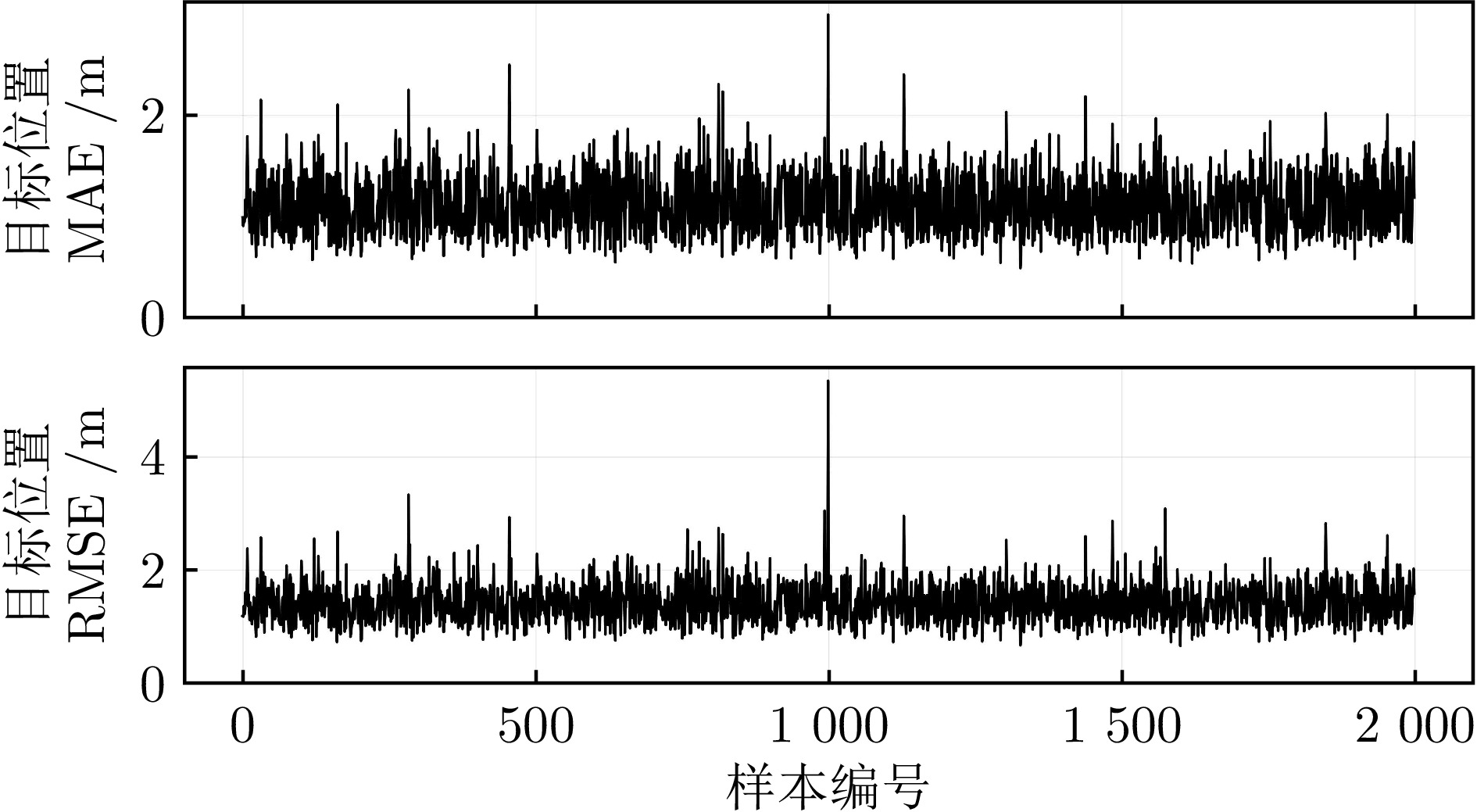
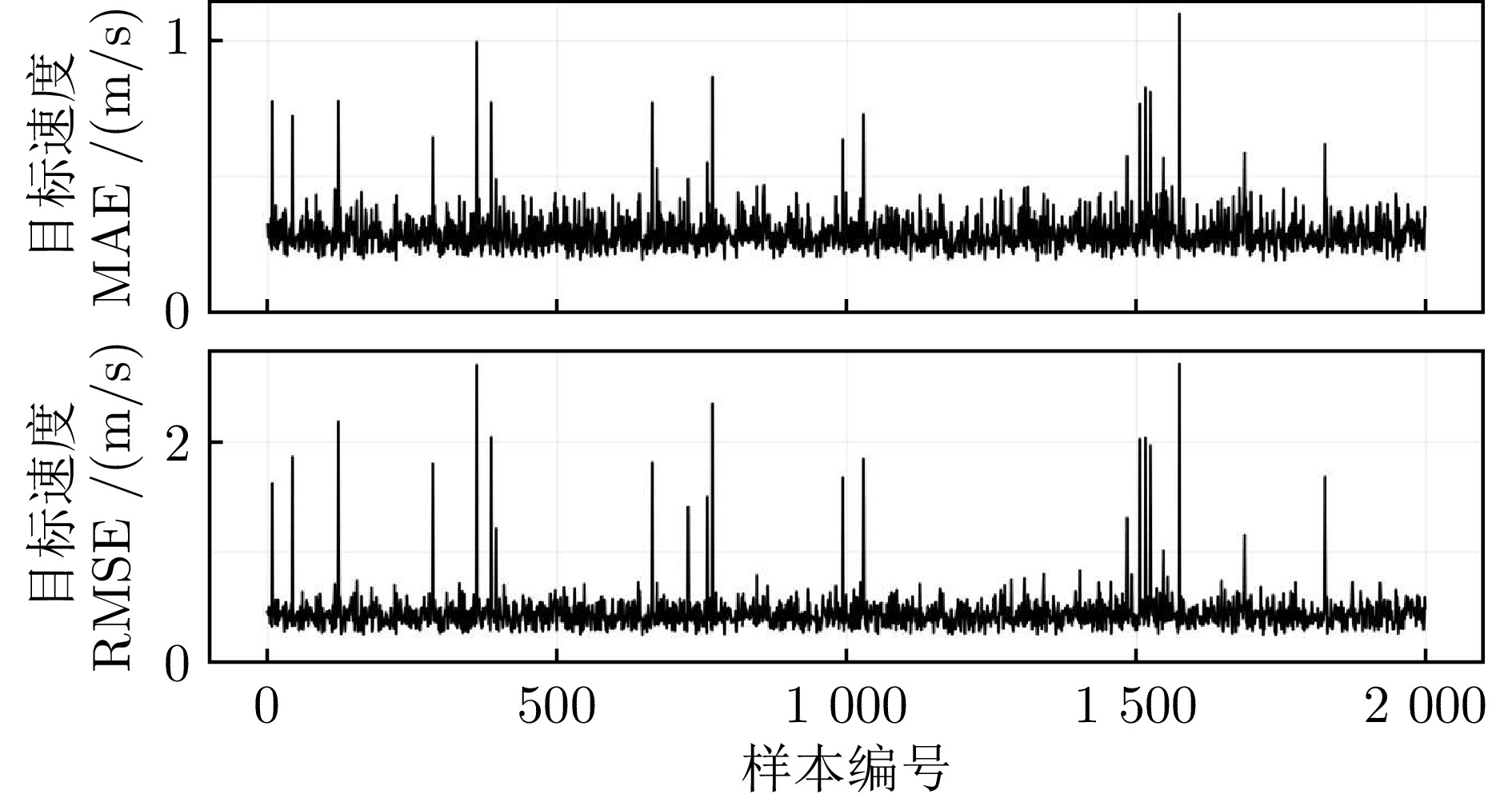
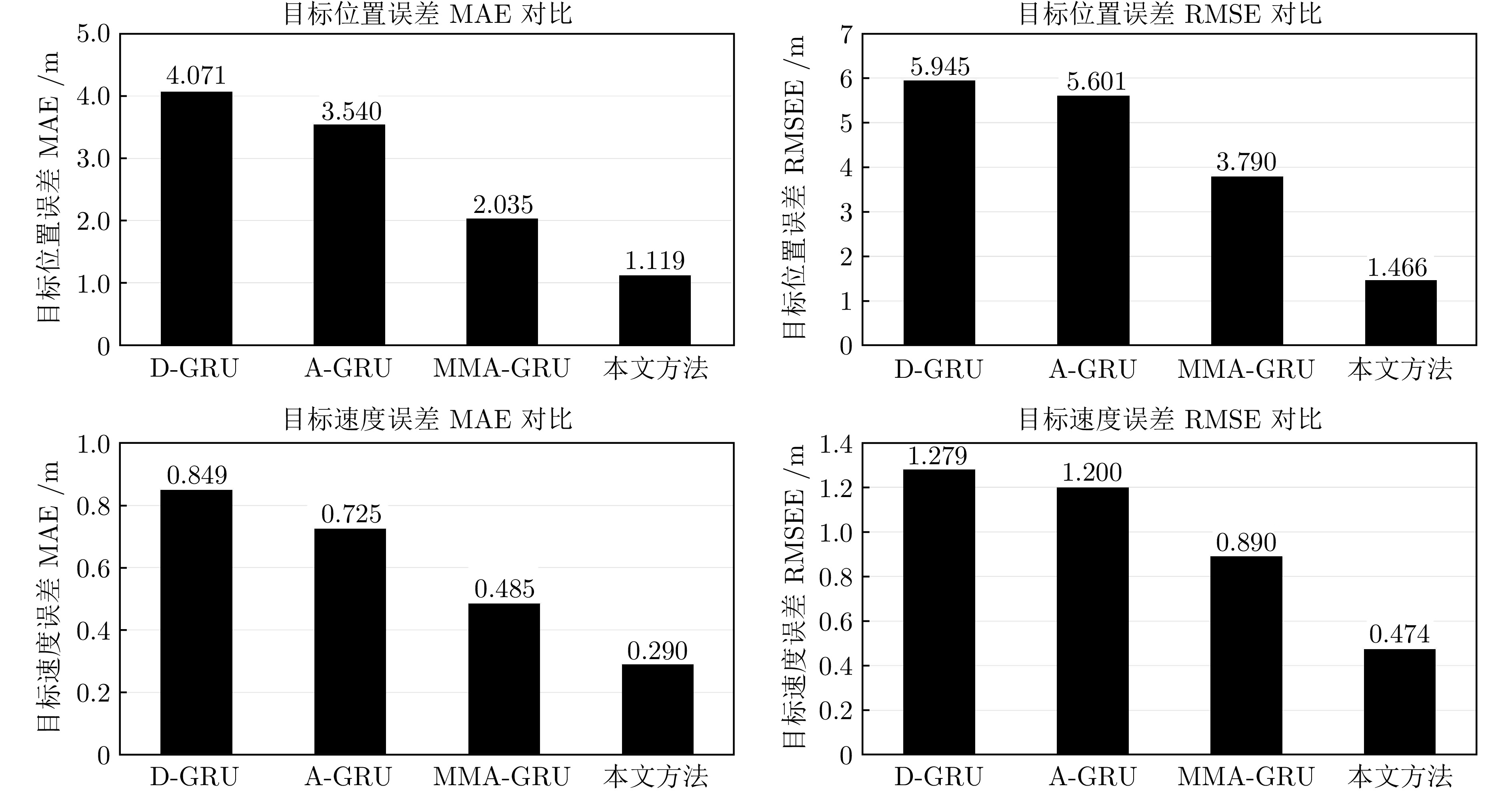
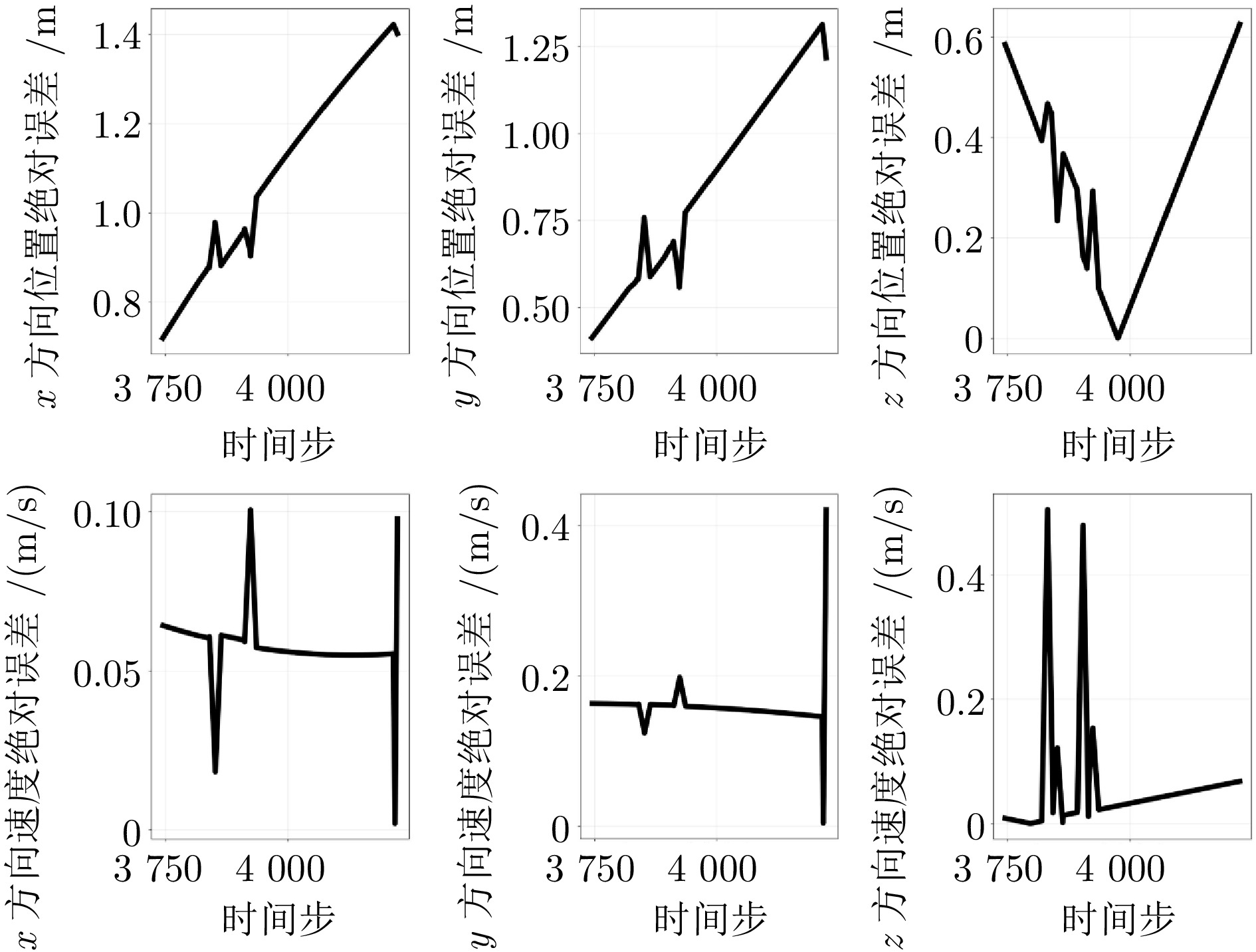
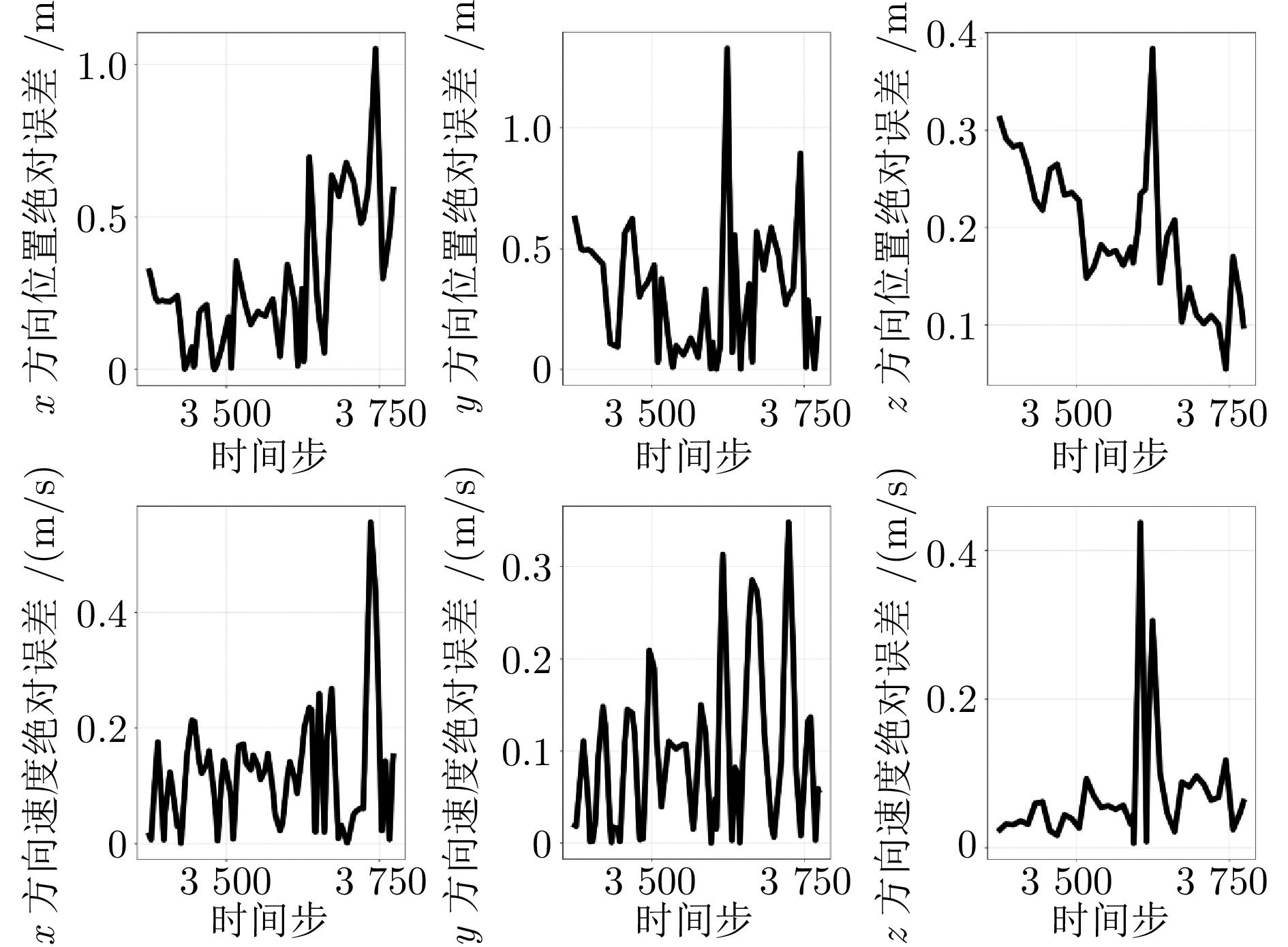
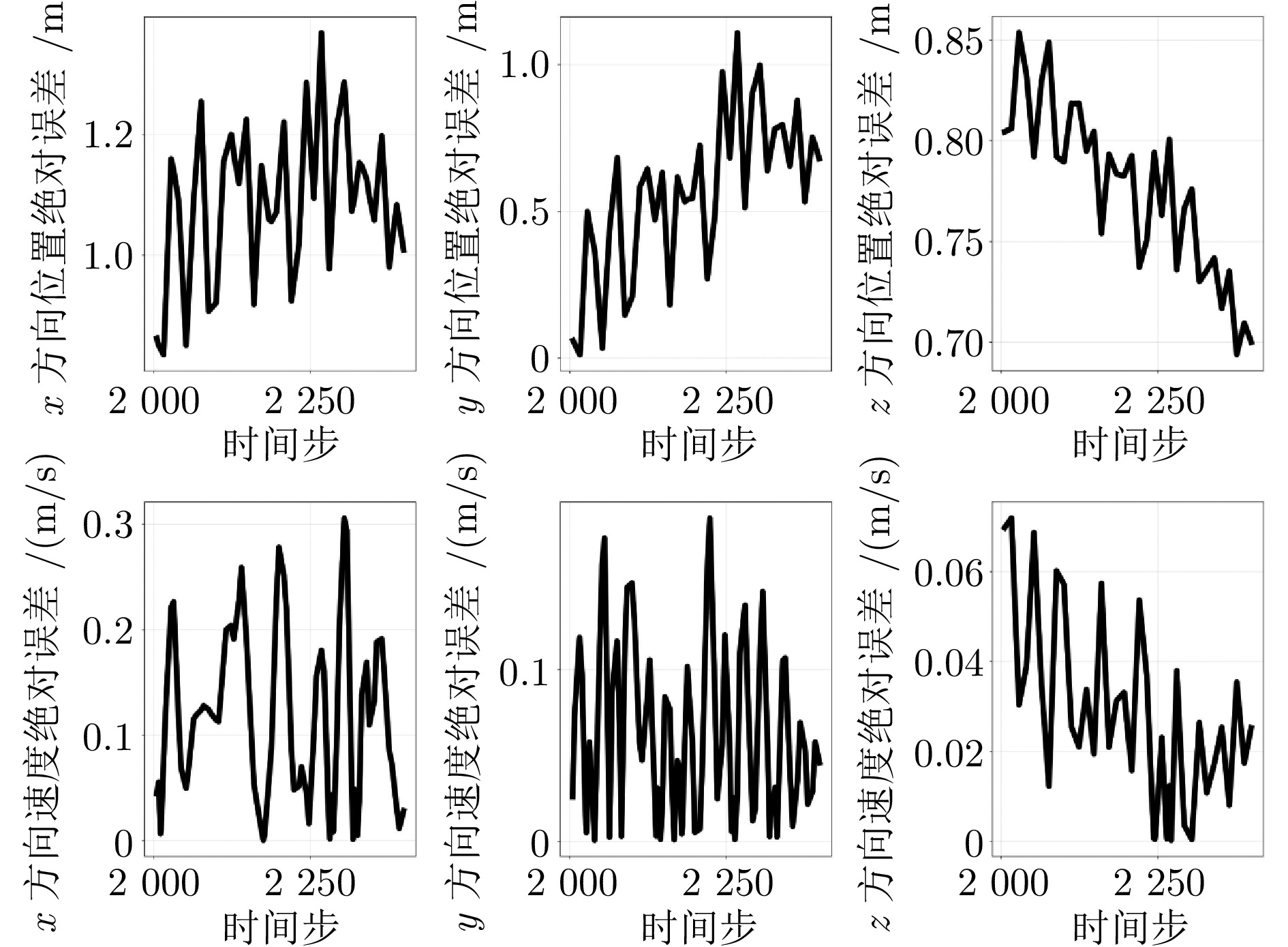
方法 目标位置误差(m) 目标速度误差(m/s) MAE RMSE MAE RMSE D-GRU 4.071 5.945 0.849 1.279 A-GRU 3.540 5.601 0.725 1.200 MMA-GRU 2.035 3.790 0.485 0.890 本文方法 1.119 1.466 0.290 0.474 -
[1] 陈林, 缪志强, 王祥科, 陈谋, 段海滨, 王耀南. 自主飞行器技术及其在低空经济中的应用综述. 机器人, 2021, 47(3): 470−495 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.250073Chen Lin, Miao Zhi-Qiang, Wang Xiang-Ke, Chen Mou, Duan Hai-Bin, Wang Yao-Nan. Overview on autonomous aircraft technology and its application to low-altitude economy. Robot, 2021, 47(3): 470−495 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.250073 [2] 崔亚奇, 熊伟, 何友. 不确定航迹自适应预测模型. 航空学报, 2019, 40(5): Article No. 322557Cui Ya-Qi, Xiong Wei, He You. Adaptive forecast model for uncertain track. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2019, 40(5): Article No. 322557 [3] 韩云祥, 汤新民, 韩松臣. 基于混杂系统理论的无冲突4D航迹预测. 西南交通大学学报, 2012, 47(6): 1069−1074Han Yun-Xiang, Tang Xin-Min, Han Song-Chen. Conflict-free 4D trajectory prediction based on hybrid system theory. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2012, 47(6): 1069−1074 [4] 翟岱亮, 雷虎民, 李炯, 刘滔. 基于自适应IMM的高超声速飞行器轨迹预测. 航空学报, 2016, 37(11): 3466−3475Zhai Dai-Liang, Lei Hu-Min, Li Jiong, Liu Tao. Trajectory prediction of hypersonic vehicle based on adaptive IMM. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2016, 37(11): 3466−3475 [5] 徐正凤, 曾维理, 羊钊. 航空器轨迹预测技术研究综述. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(12): 65−74Xu Zheng-Feng, Zeng Wei-Li, Yang Zhao. Survey of civil aircraft trajectory prediction. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2021, 57(12): 65−74 [6] Takeichi N. Adaptive prediction of flight time uncertainty for ground-based 4D trajectory management. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 95: 335−345 doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2018.07.028 [7] 陈宇燊, 白成超, 颜鹏, 郑红星, 郭继峰. 基于意图推理的城市环境下低空飞行目标轨迹预测方法. 机器人, 2025, 47(3): 459−469 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.250078Chen Yu-Shen, Bai Cheng-Chao, Yan Peng, Zheng Hong-Xing, Guo Ji-Feng. A trajectory prediction method for low-altitude flight targets in urban environments based on intent inference. Robot, 2025, 47(3): 459−469 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.250078 [8] Zhang J D, Shi Z Y, Zhang A L, Yang Q M, Shi G Q, Wu Y. UAV trajectory prediction based on flight state recognition. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic System, 2024, 60(3): 2629−2641 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3303854 [9] Wu Y, Yu H Y, Du J P, Liu B, Yu W T. An aircraft trajectory prediction method based on trajectory clustering and a spatiotemporal feature network. Electronics, 2022, 11(21): Article No. 3453 doi: 10.3390/electronics11213453 [10] Luo A F, Luo Y X, Liu H, Du W C, Wu X P, Chen H, et al. An improved Transformer-based model for long-term 4D trajectory prediction in civil aviation. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2024, 18(9): 1588−1598 doi: 10.1049/itr2.12530 [11] Wang Z H, Kong F H, Feng S, Wang M, Yang X C, Zhao H, et al. Is Mamba effective for time series forecasting?. Neurocomputing, 2025, 619: Article No. 129178 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2024.129178 [12] Zhou S Y, Yang L J, Liu X L, Wang L P. Learning short-term spatial-temporal dependency for UAV 2-D trajectory forecasting. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(22): 38256−38269 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3466516 [13] Yang S R, Liu L P, Chen B W, Cheng S Y, Shi Z W, Zou Z X. GooDFlight: goal-oriented diffusion model for flight trajectory prediction. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(3): 7447−7465 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2025.3536436 [14] 陈兴琳, 任艳丽, 姜博文, 王平. 基于TCN模型的航空器四维航迹预测. 现代电子技术, 2025, 48(17): 1−6Chen Xing-Lin, Ren Yan-Li, Jiang Bo-Wen, Wang Ping. Aircraft four dimensional trajectory prediction based on TCN model. Modern Electronic Technique, 2025, 48(17): 1−6 [15] Fan Y Q, Tan Y J, Wu L W, Ye H, Lyu Z W. Global and local interattribute relationships-based graph convolutional network for flight trajectory prediction. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(3): 2642−2657 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3357668 [16] Tan M H, Shen H, Xi K, Chai B. Trajectory prediction of flying vehicles based on deep learning methods. Applied Intelligence, 2023, 53(11): 13621−13642 doi: 10.1007/s10489-022-04098-8 [17] Zhang Z, Guo D Y, Zhou S Z, Zhang J W, Lin Y. Flight trajectory prediction enabled by time-frequency wavelet transform. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): Article No. 5258 doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40903-9 [18] Yuksel S E, Wilson J N, Gader P D. Twenty years of mixture of experts. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2012, 23(8): 1177−1193 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2200299 [19] Cai W L, Jiang J Y, Wang F, Tang J, Kim S, Huang J Y. A survey on mixture of experts in large language models. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2025, 37(7): 3896−3915 [20] Gu A, Dao T. Mamba: Linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2312.00752, 2024 [21] Zhou T L, Chen M, Zou J. Reinforcement learning based data fusion method for multi-sensors. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2020, 7(6): 1489−1497 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2020.1003180 [22] Lu S Y, Liu M Z, Yin L R, Yin Z T, Liu X, Zheng W F. The multi-modal fusion in visual question answering: A review of attention mechanisms. PeerJ Computer Science, 2023, 9: Article No. e1400 doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1400 [23] 张宗腾, 张琳, 汪文峰, 滕飞, 张搏. 一种基于双向GRU的UAV飞行轨迹预测方法. 电光与控制, 2022, 29(3): 11−15Zhang Zong-Teng, Zhang Lin, Wang Wen-Feng, Teng Fei, Zhang Bo. A method for UAV flight trajectory prediction based on bidirectional GRU. Electronics Optics and Control, 2022, 29(3): 11−15 [24] 张忠豪, 董方敏, 胡枫, 吴义熔, 孙水发. 基于残差的门控循环单元. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(12): 3067−3074Zhang Zhong-Hao, Dong Fang-Min, Hu Feng, Wu Yi-Rong, Sun Shui-Fa. Residual based gated recurrent unit. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(12): 3067−3074 [25] Harsha M, Singh G, Kumar V, Buduru A B, Biswas S K. Tracking an untracked space debris after an inelastic collision using physics informed neural network. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): Article No. 3350 doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51897-9 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 316
- HTML全文浏览量: 418
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: