-
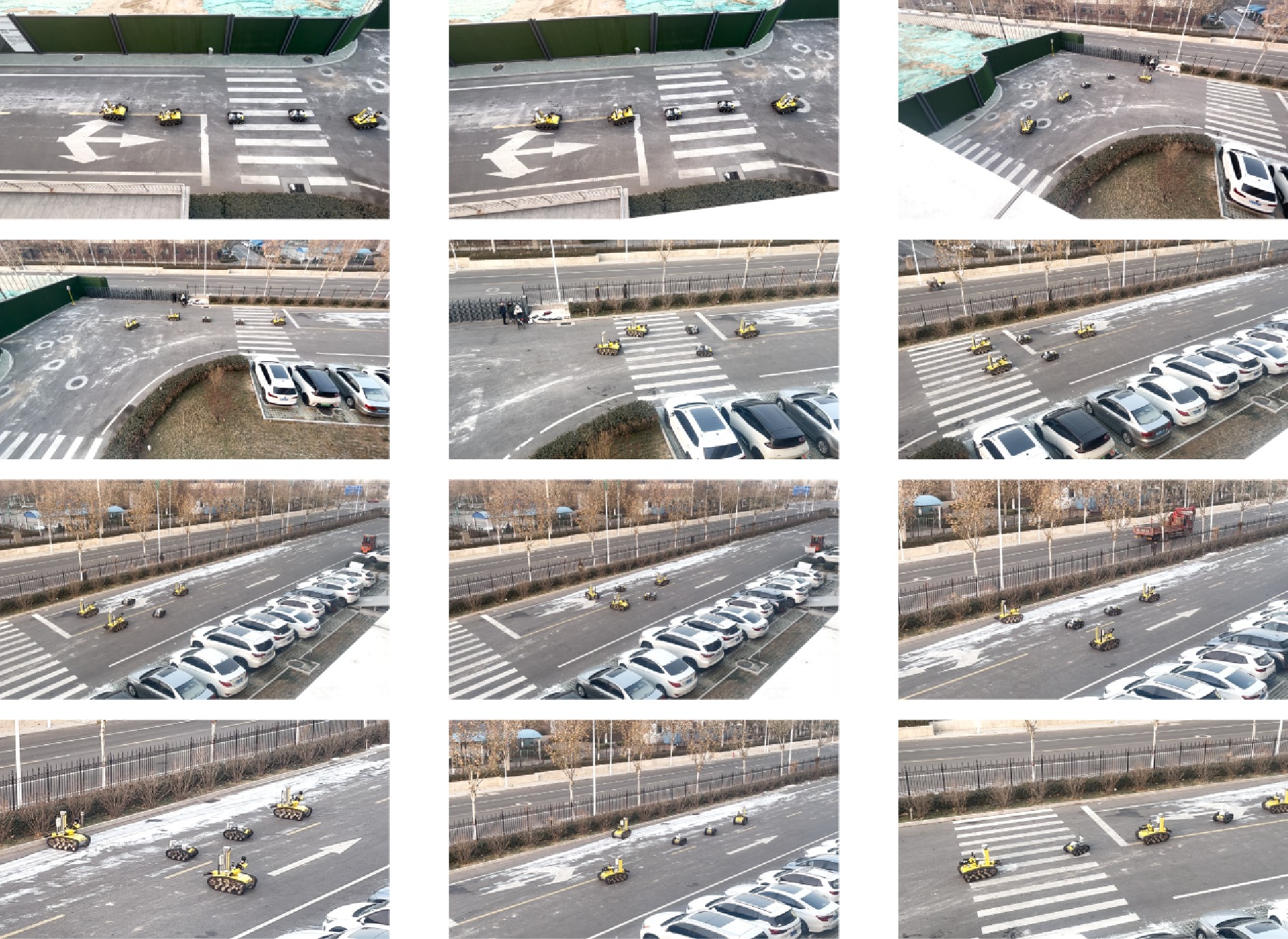
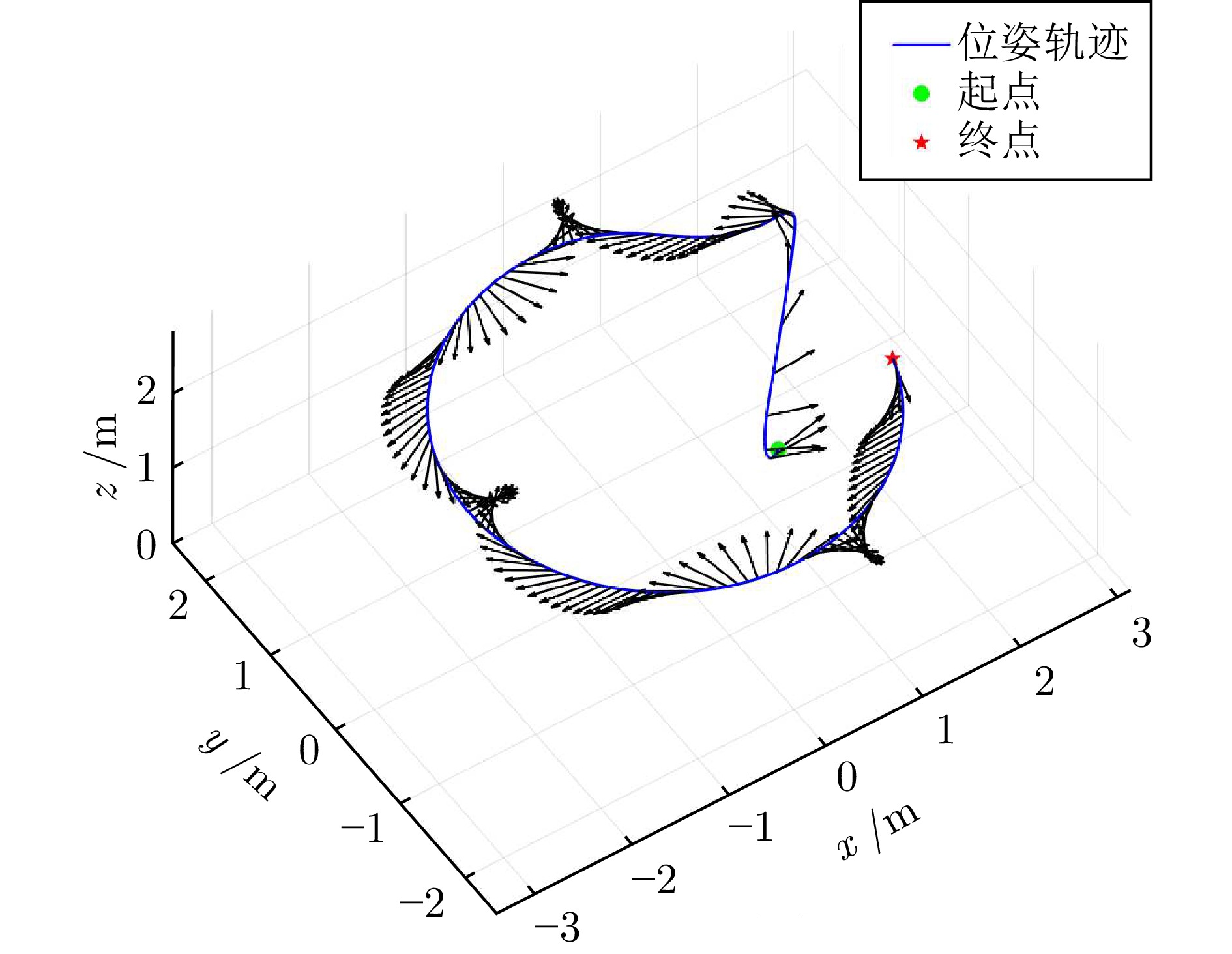
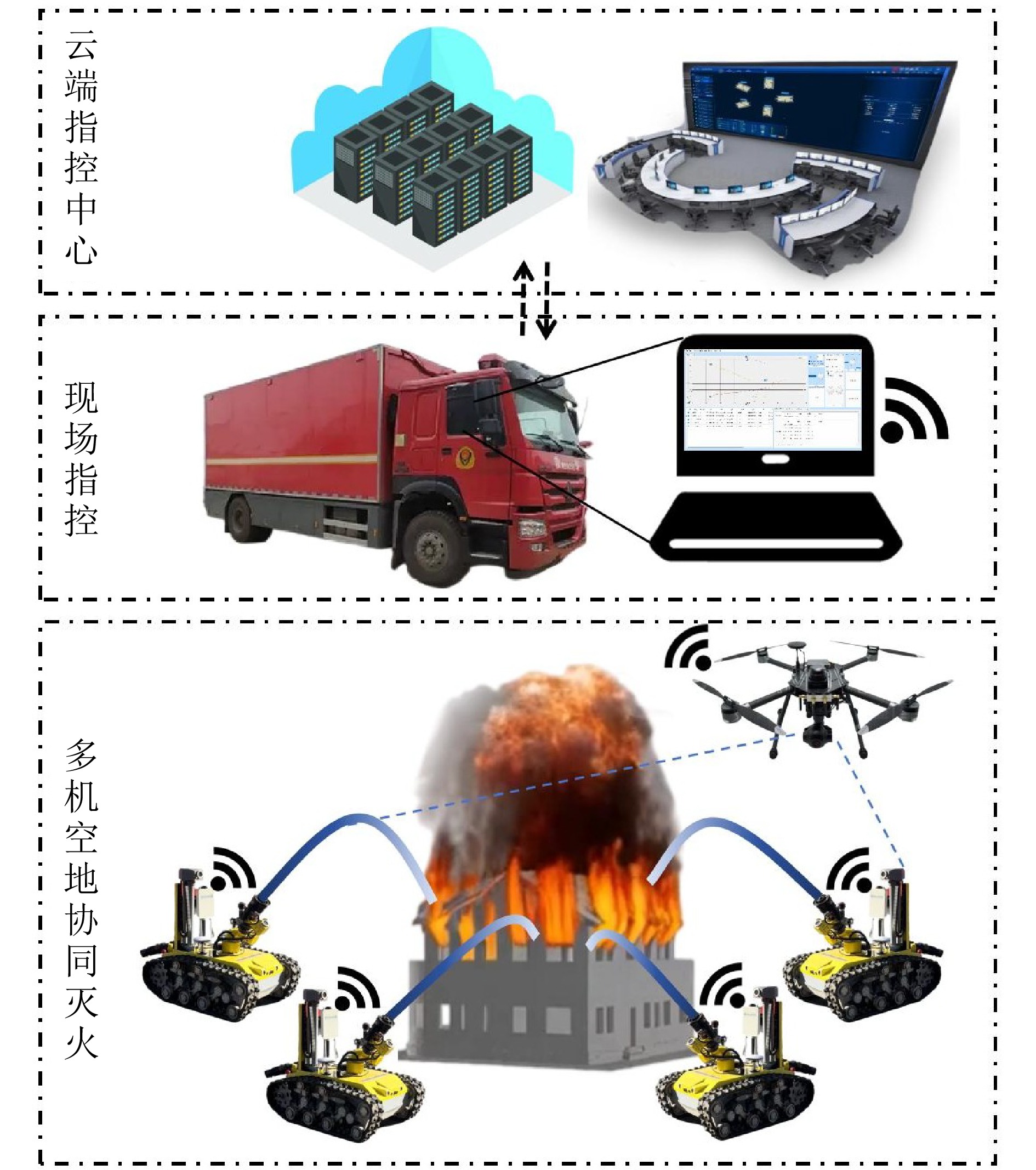
摘要: 复杂火灾场景下传统消防手段存在全局感知能力不足、协同能力弱等问题, 因此提出一种基于无人机空中引导的多消防机器人协同作业系统. 通过构建空−地异构协同架构, 融合无人机全局态势感知与地面消防机器人精准作业能力, 实现火灾动态环境下的高效协同灭火. 通过融合先验地图、高空侦察信息和多视角观测信息, 构建适用于灭火指控的多图层火场地图, 在保障关键信息获取的同时兼顾建图效率. 同时结合水柱轨迹模型、多视角观测信息及结构层数据, 实现水柱轨迹和落点的准确检测. 然后设计队列式与多形态主从编队模式, 配合快速队形重构算法生成编队参考信号. 进而, 基于提出的柔性预定性能函数设计无人机位姿矢量控制器, 以及基于改进视距导引法设计多消防机器人编队控制器. 最后, 开展空−地多机协同控制算法的仿真验证, 并将系统集成到开诚RXB-MC80BD消防机器人上进行应用测试.
-
关键词:
- 多图层火场建图 /
- 柔性预定性能控制 /
- 无人机位姿矢量控制 /
- 消防机器人多模态编队
Abstract: Under complex fire scenarios, traditional firefighting methods suffer from limited global perception and weak collaboration capabilities. Therefore, a collaborative operation system with multiple firefighting robots guided by unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) is proposed. By establishing an air-ground heterogeneous collaborative architecture, the system integrates the global situational awareness of UAVs with the precise operation capabilities of ground firefighting robots, enabling efficient collaborative fire suppression in dynamic fire environments. By fusing prior maps, aerial reconnaissance information, and multi-view observations, a multi-layer fire scene map suitable for firefighting command and control is constructed, ensuring the acquisition of critical information while maintaining mapping efficiency. Combining the water jet trajectory model, multi-view observations, and structural layer data, the trajectory and landing point of the water jet are accurately detected. Furthermore, queue-based and multiform leader-follower formation configurations are designed, and formation reference signals are generated through a fast formation reconfiguration algorithm. Subsequently, a UAV pose-vector controller is developed by using the proposed flexible prescribed performance function, and a formation controller for multiple firefighting robots is designed based on an improved line-of-sight guidance method. Finally, the proposed air-ground multi-agent collaborative control algorithm is validated through simulations and implemented on the KaiCheng RXB-MC80BD firefighting robot platform for practical testing. -
表 1 无人机系统变量与矩阵定义
Table 1 Definition of system variables and matrices of UAVs
符号 表达式 说明 $m$ − 无人机质量 $I$ − 无人机转动惯量矩阵 ${{\boldsymbol{g}}}$ $[0,\; 0,\;-g]^{{\rm{T}}}$ 重力加速度向量 $J_{RP}$ − 旋翼电机组件的转动惯量 $ K_v$ ${\rm{diag}}\{k_x,\; k_y,\; k_z\}$ 线速度阻尼系数矩阵 $ K_\omega$ ${\rm{diag}}\{k_{\phi},\; k_{\theta},\; k_{\psi}\}$ 角速度阻尼系数矩阵 ${\boldsymbol{\Omega}}$ $[0,\; 0,\; \Omega]^{{\rm{T}}}$ 旋翼总转速向量 ${{\boldsymbol{f}}}_b$ $[0,\; 0,\; T]^{{\rm{T}}}$ 机体坐标系下总推力向量 ${\boldsymbol{\tau}}$ $[\tau_\phi,\; \tau_\theta,\; \tau_\psi]^{{\rm{T}}}$ 机体控制力矩向量 表 2 四旋翼仿真系统参数设置
Table 2 System parameter settings of quadrotor simulation
系统参数 符号 数值 无人机质量 $m$ 1.2 kg 转动惯量矩阵 $I$ ${\rm{diag}}\{0.01,\; 0.01,\; 0.02\}\; {\rm{kg}} \cdot {\rm{m}}^2$ 重力加速度 $g$ 9.81 m/s2 电机组件转动惯量 $J_{RP}$ 0.0001 kg·m2线速度阻尼系数 $ K_v$ ${\rm{diag}}\{0.1,\; 0.1,\; 0.2\}\;{\rm{N}} \cdot {\rm{s}}/{\mathrm{m}}$ 角速度阻尼系数 $ K_\omega$ ${\rm{diag}}\{0.05,\; 0.05,\; 0.05\}\;{\rm{N}} \cdot {\rm{m}} \cdot {\mathrm{s}}/{\mathrm{rad}}$ 旋翼臂长 $l$ 0.2 m 推力反扭矩系数 $\kappa$ 0.01 m 旋翼最大推力 $f_{\max}$ 10 N 表 3 四旋翼仿真控制参数设置
Table 3 Control parameter settings of quadrotor simulation
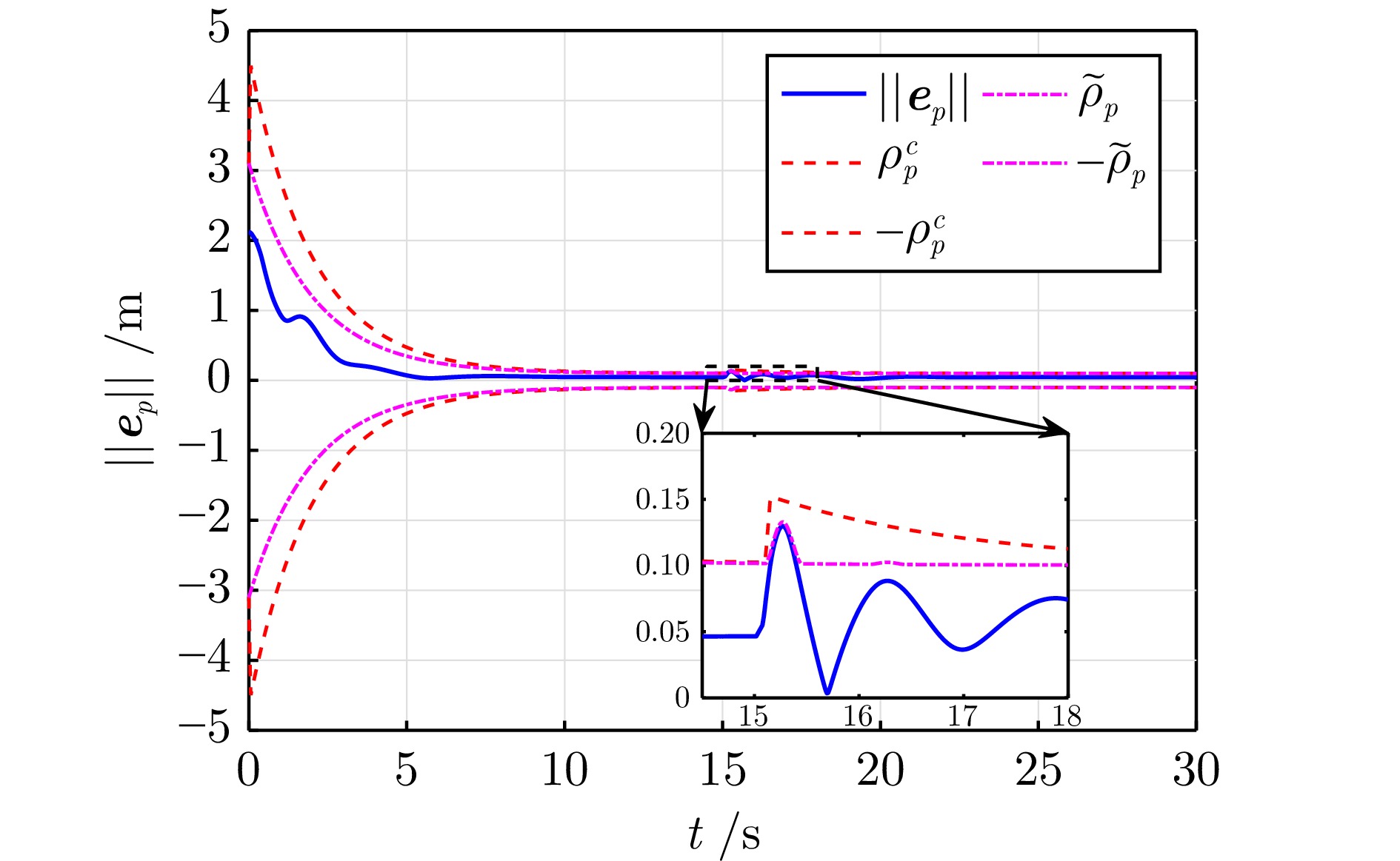
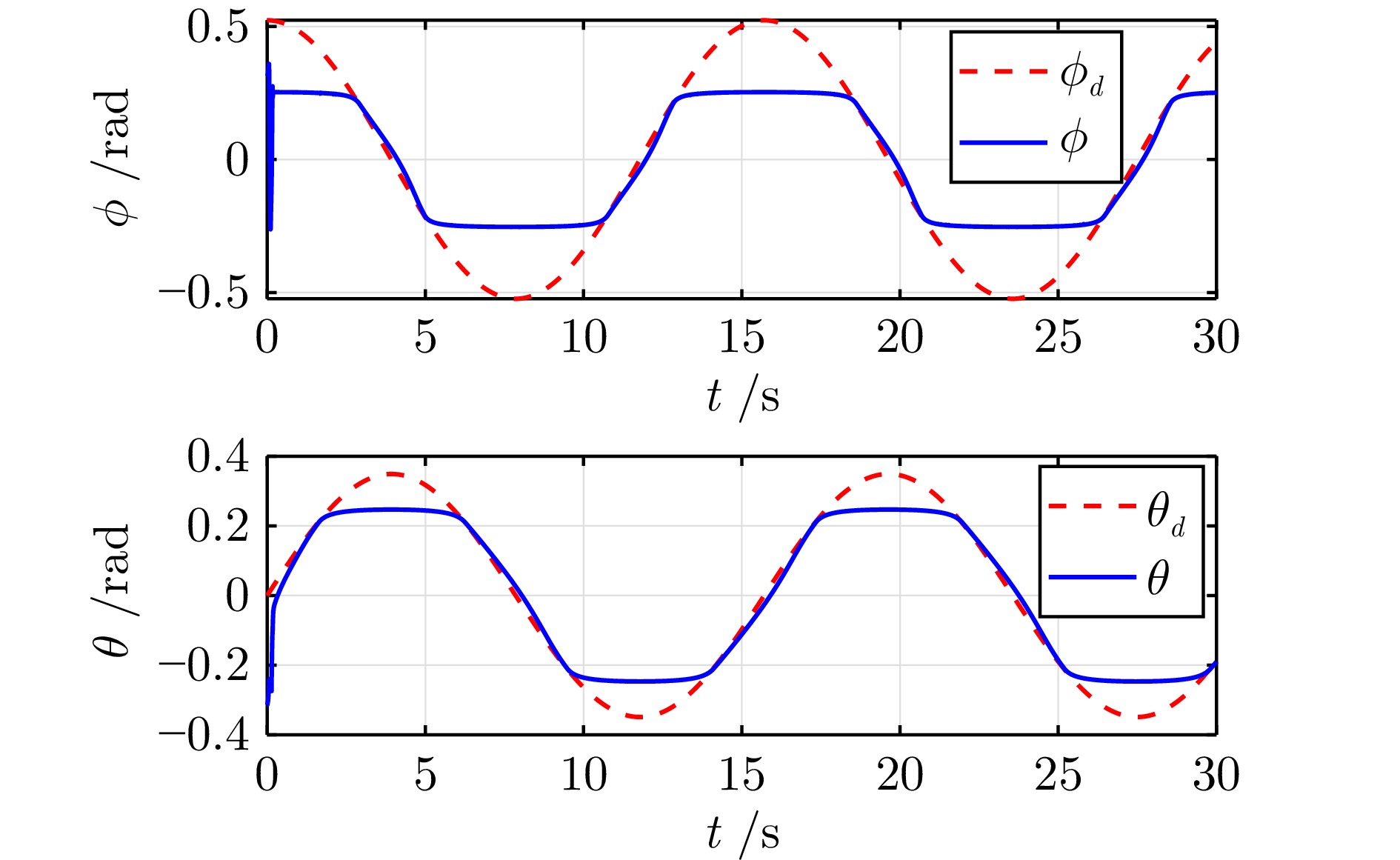
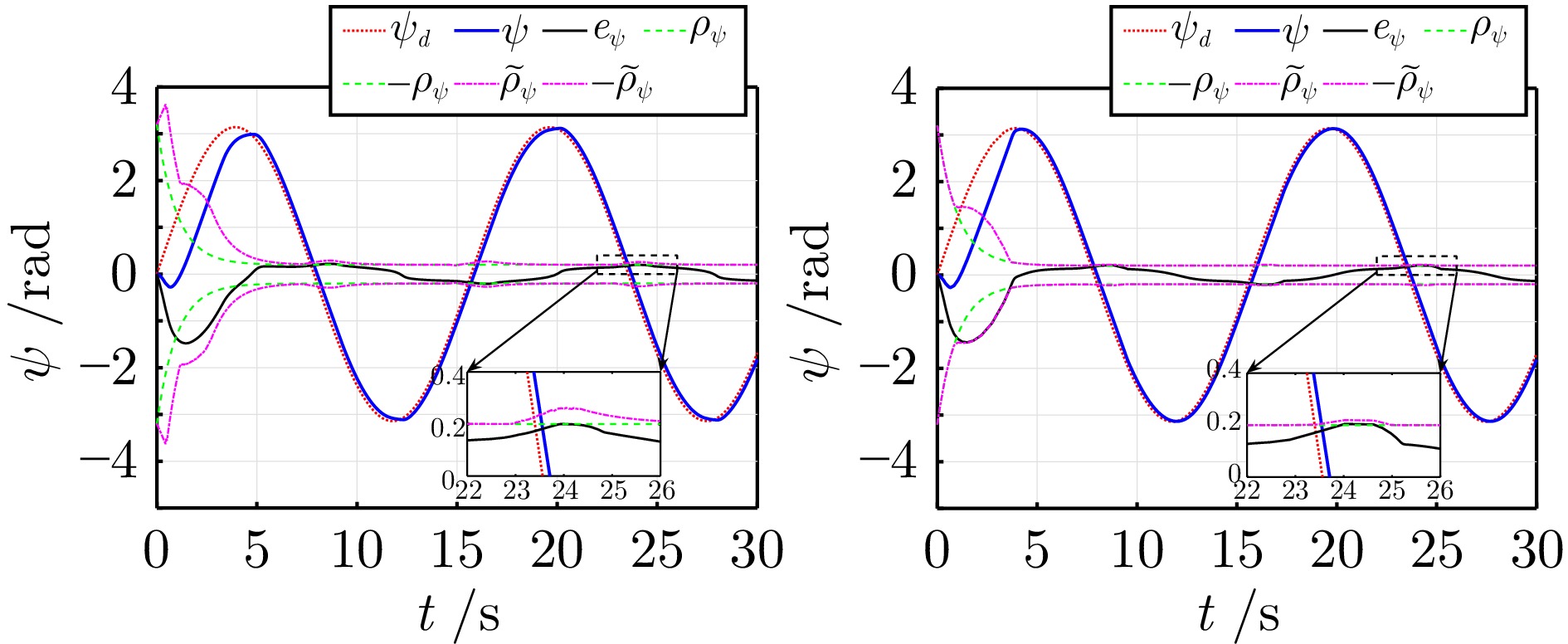
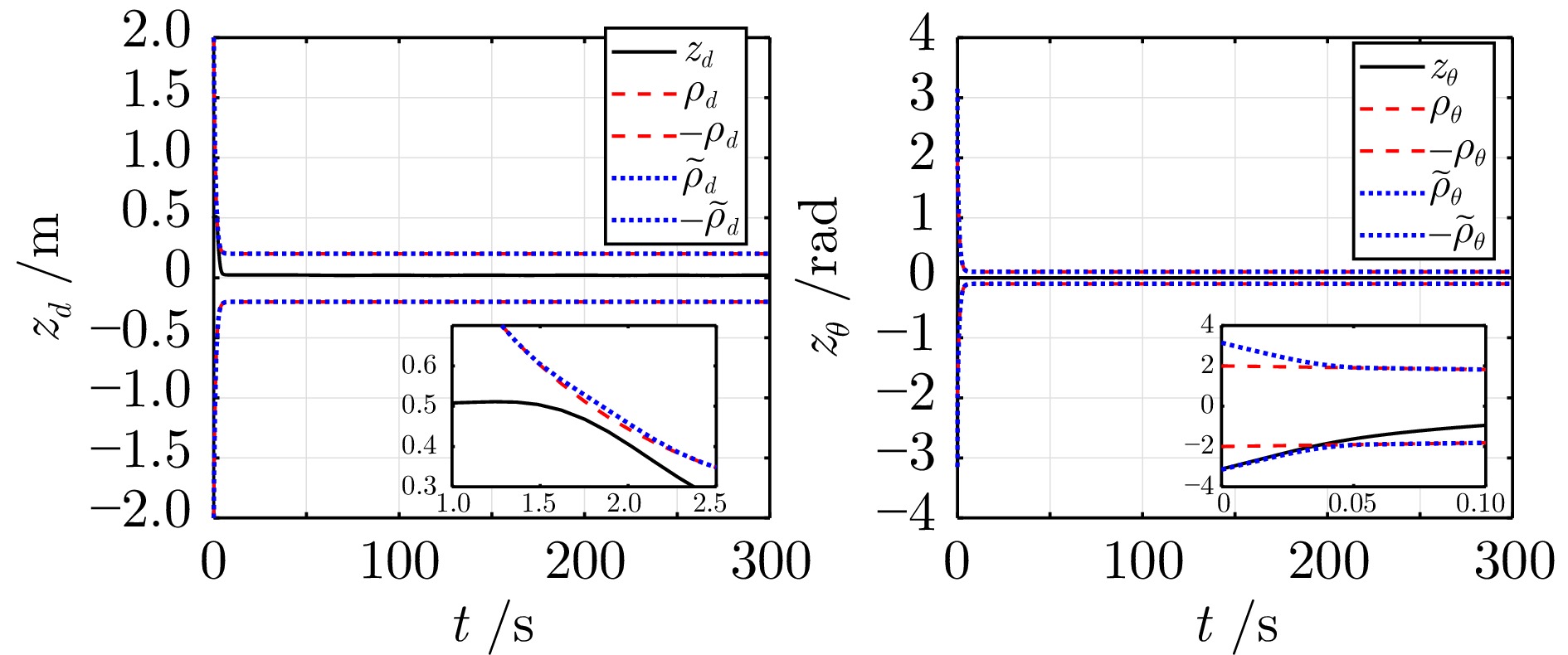
控制参数 符号 数值 最大横滚角 $\phi_{\max}$ 0.26 rad 最大俯仰角 $\theta_{\max}$ 0.26 rad 位置误差预定性能 $\rho_p(t)$ $3 {\mathrm{e}}^{-0.5 t} + 0.1$ m 偏航角误差预定性能 $\rho_\psi(t)$ $3 {\mathrm{e}}^{-t} + 0.2$ rad 柔性边界参数 $\sigma$ 0.8 位置虚拟控制增益 $\Lambda_p$ ${\rm{diag}}\{1.0,\; 1.0,\; 1.2\}$ 速度误差增益 $\Lambda_v$ ${\rm{diag}}\{1.5,\; 1.5,\; 1.5\}$ 姿态误差增益 $\Lambda_\eta$ ${\rm{diag}}\{5.0,\; 5.0,\; 1.0\}$ 角速度误差增益 $\Lambda_\omega$ ${\rm{diag}}\{3.0,\; 3.0,\; 1.5\}$ -
[1] Jones M W, Veraverbeke S, Andela N, Doerr S H, Kolden C, Mataveli G, et al. Global rise in forest fire emissions linked to climate change in the extratropics. Science, 2024, 386(6719): Article No. eadl5889 doi: 10.1126/science.adl5889 [2] Wang W W, Wang X L, Flannigan M D, Guindon L, Swystun T, Castellanos-Acuna D, et al. Canadian forests are more conducive to high-severity fires in recent decades. Science, 2025, 387(6729): 91−97 doi: 10.1126/science.ado1006 [3] 鲍明松, 孙洪阳, 孙增良, 孙洪秀, 刘文涛. 无人机与消防机器人协同侦察灭火作业系统设计. 电子测试, 2020(7): 130−132 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8519.2020.07.050Bao Ming-Song, Sun Hong-Yang, Sun Zeng-Liang, Sun Hong-Xiu, Liu Wen-Tao. Design of cooperative reconnaissance and fire fighting system of UAV and fire fighting robot. Electronic Test, 2020(7): 130−132 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8519.2020.07.050 [4] 刘涵海. 消防机器人自主作业关键技术研究 [硕士学位论文], 中国矿业大学, 中国, 2024.Liu Han-Hai. Key Technology Research on Autonomous Operation of Firefighting Robot [Master thesis], China University of Mining and Technology, China, 2024. [5] Wang M, Chen X H, Huang X Y. Robotic firefighting: A review and future perspective. Intelligent Building Fire Safety and Smart Firefighting. Cham: Springer, 2024. 475−499 [6] Schmuck P, Chli M. CCM-SLAM: Robust and efficient centralized collaborative monocular simultaneous localization and mapping for robotic teams. Journal of Field Robotics, 2019, 36(4): 763−781 doi: 10.1002/rob.21854 [7] Tian Y L, Chang Y, Arias F H, Nieto-Granda C, How J P, Carlone L. Kimera-multi: Robust, distributed, dense metric-semantic slam for multi-robot systems. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2022, 38(4): 2022−2038 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2021.3137751 [8] Zuo C L, Feng Z, Xiao X H. CCMD-SLAM: Communication-efficient centralized multirobot dense SLAM with real-time point cloud maintenance. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: Article No. 7504812 doi: 10.1109/tim.2024.3398100 [9] Jie Y R, Zhu Y L, Cheng H. Heterogeneous deep metric learning for ground and aerial point cloud-based place recognition. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2023, 8(8): 5092−5099 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2023.3292623 [10] 耿庆田, 于繁华, 赵宏伟, 王闯. 基于颜色特征的火焰检测新算法. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1787−1792 doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb201406038Geng Qing-Tian, Yu Fan-Hua, Zhao Hong-Wei, Wang Chuang. New algorithm of flame detection based on color features. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(6): 1787−1792 doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb201406038 [11] Wang Y F, Hua C C, Ding W L, Wu R N. Real-time detection of flame and smoke using an improved YOLOv4 network. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2022, 16(4): 1109−1116 doi: 10.1007/s11760-021-02060-8 [12] Wu R N, Hua C C, Ding W L, Wang Y F, Wang Y B. Flame and smoke detection algorithm for UAV based on improved YOLOv4-tiny. In: Proceedings of the 18th Pacific Rim International Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Hanoi, Vietnam: Springer, 2021. 226−238 [13] 刘元浩. 基于可见光和红外多模态图像的火焰检测与定位方法研究 [硕士学位论文], 浙江大学, 中国, 2024.Liu Yuan-Hao. Research on Fire Detection and Localization Method Based on Visible and Infrared Multimodal Images [Master thesis], Zhejiang University, China, 2024. [14] 陈泰宇. 消防机器人火焰烟雾实时检测与定位技术研究 [硕士学位论文], 燕山大学, 中国, 2023.Chen Tai-Yu. Research on Real-time Detection and Localization Technology of Fire and Smoke for Firefighting Robots [Master thesis], Yanshan University, China, 2023. [15] 高荣. 隧道火灾红外双目视觉定位系统研究 [硕士学位论文], 长安大学, 中国, 2014.Gao Rong. Research on Infrared Stereo Vision Based Tunnel Fire Positioning System [Master thesis], Chang'an University, China, 2014. [16] Blazic S. On periodic control laws for mobile robots. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2014, 61(7): 3660−3670 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2013.2287222 [17] Dai S L, He S D, Chen X, Xu J. Adaptive leader-follower formation control of nonholonomic mobile robots with prescribed transient and steady-state performance. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(6): 3662−3671 doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2939263 [18] Gu D B, Hu H S. Receding horizon tracking control of wheeled mobile robots. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2006, 14(4): 743−749 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2006.872512 [19] Chen J N, Luo X, Hua C C, Mu D R, Sun F C. Modeling and robust adaptive practical predefined time and precision tracking control of unmanned fire fighting robot. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(7): 4273−4283 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3378703 [20] 廖智麟, 李侠, 肖琪, 李一凡. 某型消防系留无人机多源扰动下的精细抗干扰稳态控制技术研究. 自动化应用, 2025, 66(9): 1−5 doi: 10.19769/j.zdhy.2025.09.001Liao Zhi-Lin, Li Xia, Xiao Qi, Li Yi-Fan. Research on fine anti-interference steady-state control technology of fire tethered UAV under multi-source disturbance. Automation Application, 2025, 66(9): 1−5 doi: 10.19769/j.zdhy.2025.09.001 [21] 王储, 袁晓明, 杨志刚, 孟昭亮, 孙靖. 消防水炮射流轨迹理论模型研究. 燕山大学学报, 2020, 44(5): 442−449 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-791X.2020.05.003Wang Chu, Yuan Xiao-Ming, Yang Zhi-Gang, Meng Zhao-Liang, Sun Jing. Investigation on theoretical model of jet trajectory of fire water monitor. Journal of Yanshan University, 2020, 44(5): 442−449 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-791X.2020.05.003 [22] 张尧. 消防水炮火源定位方法与机电控制的研究与实现 [硕士学位论文], 福州大学, 中国, 2021.Zhang Yao. Research and Implementation of Fire Water Fire Localization Method and Electromechanical Control [Master thesis], Fuzhou University, China, 2021. [23] John J, Harikumar K, Senthilnath J, Sundaram S. An efficient approach with dynamic multiswarm of UAVs for forest firefighting. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(5): 2860−2871 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3352660 [24] Zhou B Y, Xu H, Shen S J. RACER: Rapid collaborative exploration with a decentralized multi-UAV system. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2023, 39(3): 1816−1835 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2023.3236945 [25] 黎星华. 面向多消防机器人的协同控制方法研究 [博士学位论文], 北京邮电大学, 中国, 2024.Li Xing-Hua. Research on Collaborative Control Methods for Multiple Firefighting Robots [Ph.D. dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China, 2024. [26] 王迎宾. 火灾环境下多消防机器人协同任务规划研究 [硕士学位论文], 燕山大学, 中国, 2023.Wang Ying-Bin. Research on Collaborative Task Planning of Multiple Fire Robots in Fire Environment [Master thesis], Yanshan University, China, 2023. [27] Yang Y H, Mei J, Wu A G, Ma G F. Fully distributed event-triggered consensus of MIMO MASs with parametric uncertainties and external disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(7): 4294−4304 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3379396 [28] Shi X T, Li Y J, Du C L, Shi Y, Yang C H, Gui W H. Fully distributed event-triggered control of nonlinear multiagent systems under directed graphs: A model-free DRL approach. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2025, 70(1): 603−610 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2024.3439655 [29] Yang Y H, Mei J, Shi X T, Ma G F. Fully distributed consensus of multiple Euler-Lagrange systems with time-varying asymmetric full-state constraints. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2025, 70(8): 5483−5490 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2025.3546080 [30] 李润梅, 张立威, 王剑. 基于时变间距和相对角度的无人车跟随控制方法研究. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(11): 2031−2040 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170106Li Run-Mei, Zhang Li-Wei, Wang Jian. A control method of unmanned car following under time-varying relative distance and angle. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(11): 2031−2040 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170106 [31] Berger T. Input-constrained funnel control of nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(8): 5368−5382 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2024.3352362 [32] Trakas P S, Bechlioulis C P. Adaptive performance control for input constrained MIMO nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(12): 7733−7745 [33] Dai S L, Lu K, Jin X. Fixed-time formation control of unicycle-type mobile robots with visibility and performance constraints. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(12): 12615−12625 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.3040686 [34] Jin X. Fault-tolerant iterative learning control for mobile robots non-repetitive trajectory tracking with output constraints. Automatica, 2018, 94: 63−71 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2018.04.011 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 116
- HTML全文浏览量: 119
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: