-
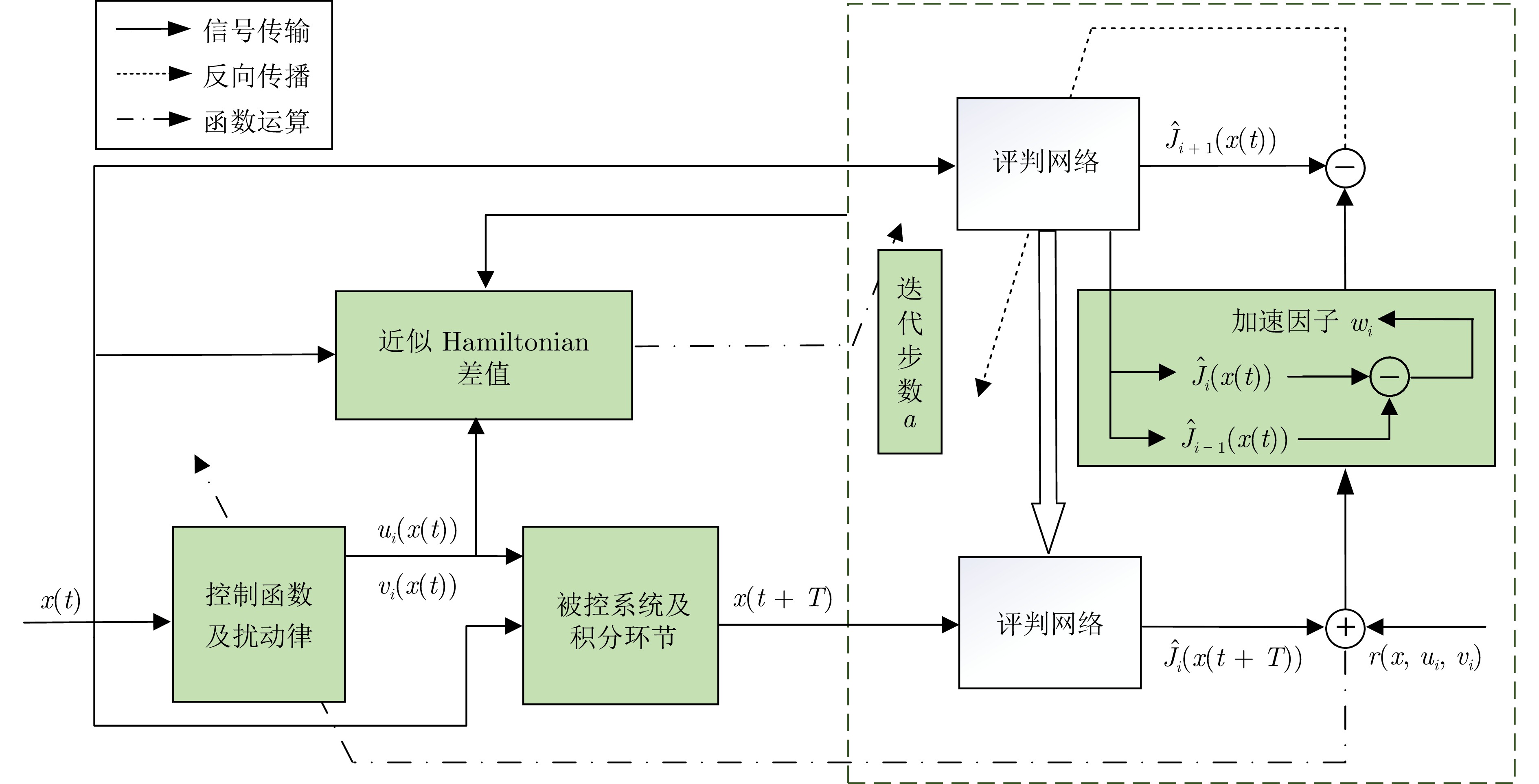
摘要: 针对存在扰动的连续时间非线性系统, 设计一种结合混合迭代机制和自适应评判框架的鲁棒控制方法. 通过优化传统值迭代方法, 实现加速学习并放宽了预设条件的目标. 引入可调参数确保控制策略在迭代过程中的可容许性, 从而放松了加速因子的设置条件. 结合广义策略迭代的思想, 构建新型混合迭代机制, 从而获得更优的收敛性能. 最后, 利用两个仿真实例验证了所提方法的性能. 针对线性系统的仿真结果表明, 本文方法具有较高的收敛精度. 在导弹自动驾驶仪系统仿真中, 相对于值迭代方法, 本文方法不依赖初始可容许控制策略, 同时能使收敛速度提高约49%.Abstract: By integrating a hybrid iteration mechanism with an adaptive critic framework, a robust control method is designed for disturbed continuous-time nonlinear systems. The goal of accelerating learning and relaxing preset conditions are achieved by improving the traditional value iteration method. By incorporating adjustable parameters, the admissibility of the control policy during the iteration process is ensured, thereby relaxing the conditions for setting the accelerated factor. Combined the idea of generalized policy iteration, a novel hybrid iteration mechanism is constructed to acquire better convergence performance. Finally, two simulation examples are used to verify the performance of the proposed method. The simulation results of the linear system show the higher convergence accuracy of the method in this paper. In the simulation of the missile autopilot system, it is demonstrated that the convergence speed is improved by approximately 49% without relying on an initial admissible control policy compared to value iteration method.
-
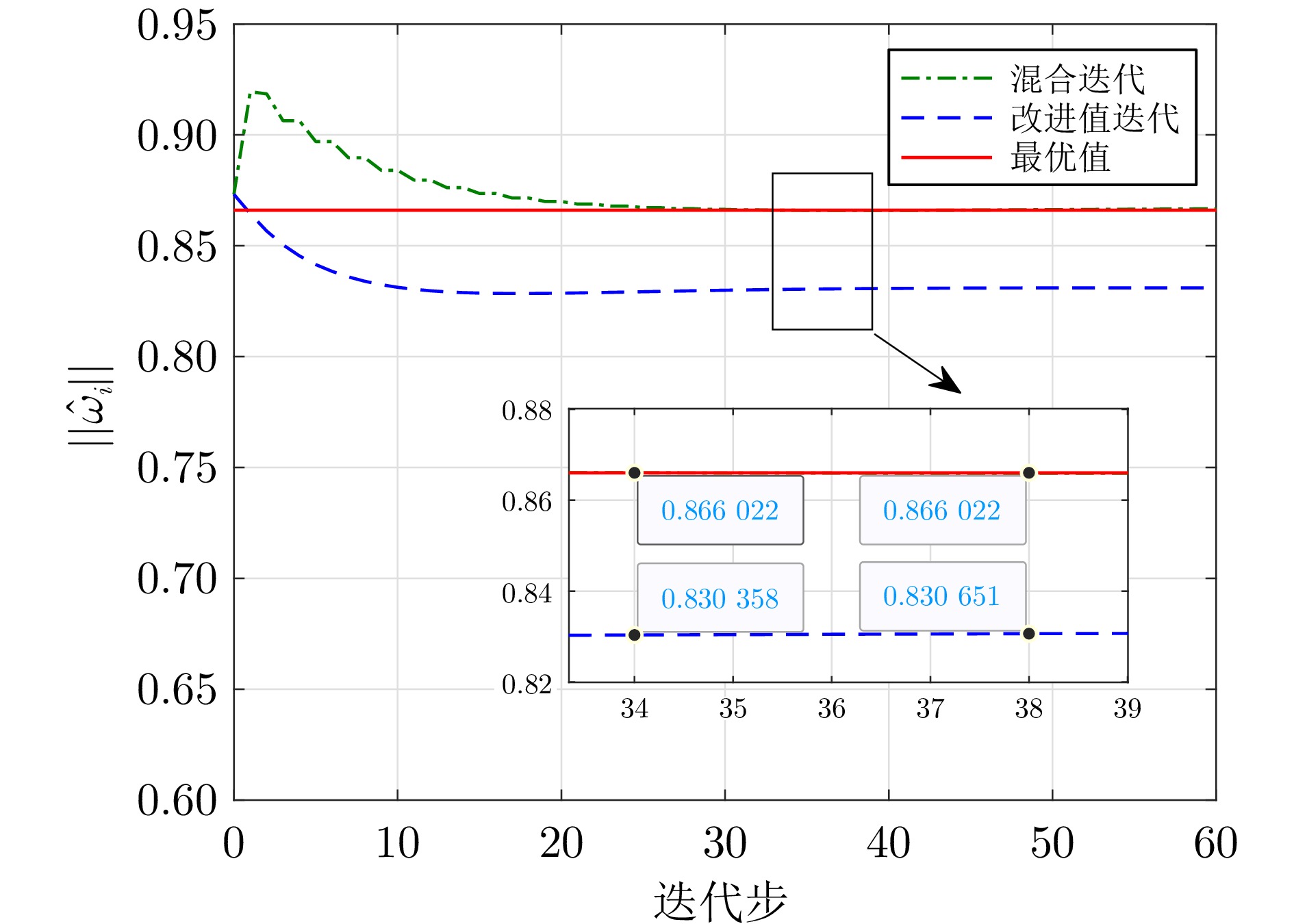
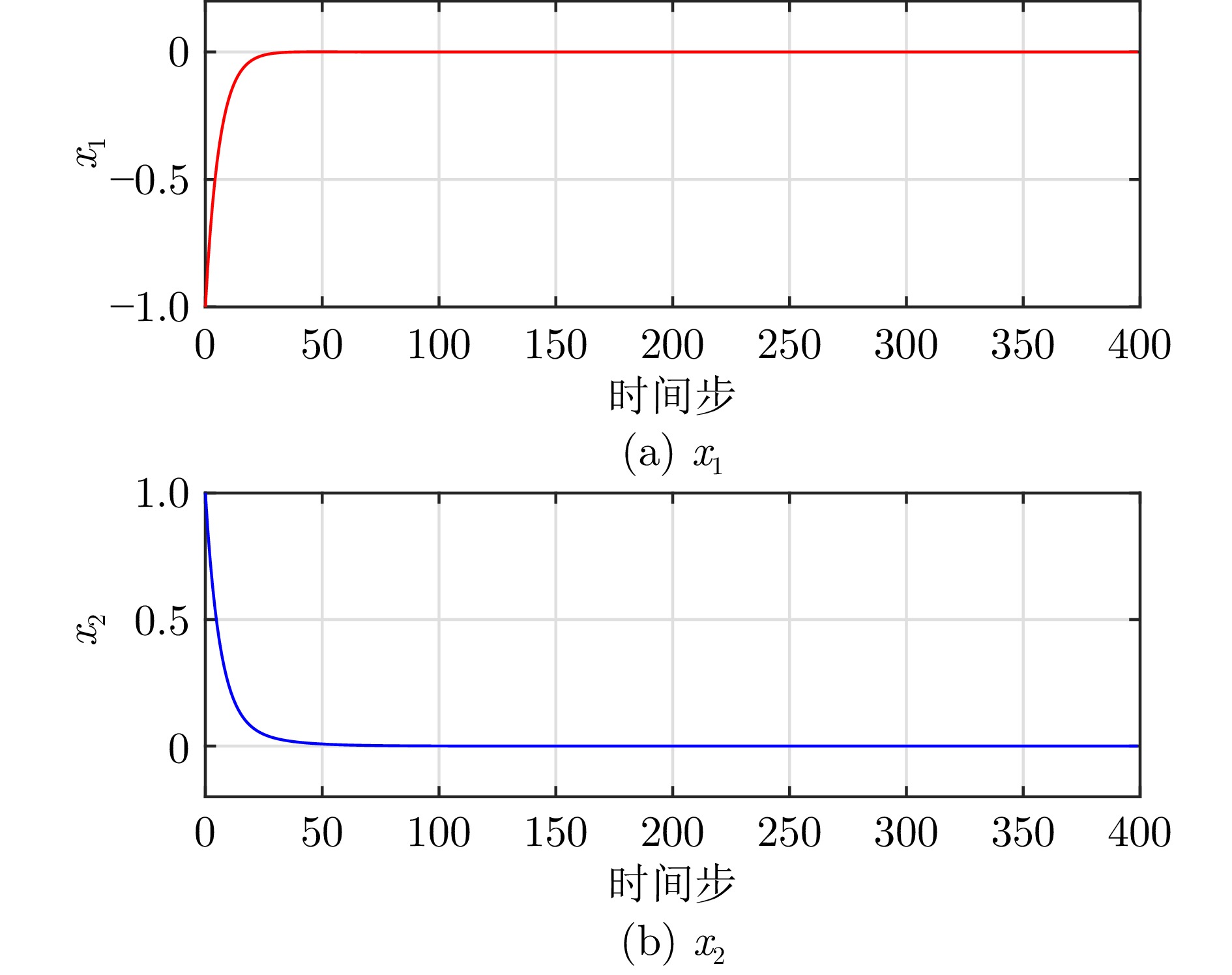
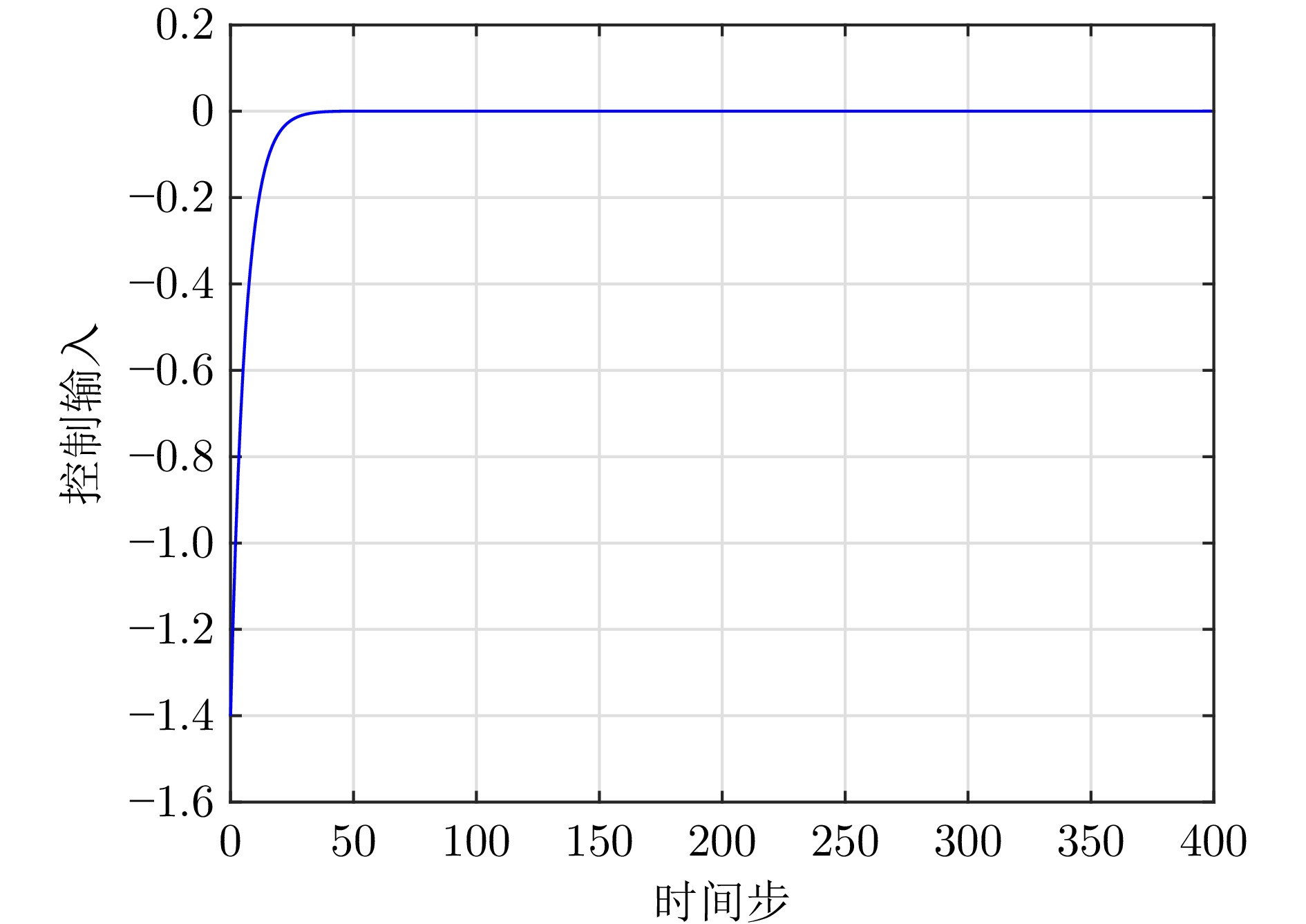
表 1 线性系统算法性能指标对比
Table 1 The comparison of performance indicators for the linear system
算法 CPU运行时间$ ({s}) $ 迭代步数 混合迭代自适应评判 $ 11.170\;1 $ $ 38 $ 改进值迭代 $ 27.419\;7 $ $ 55 $ 表 2 导弹自动驾驶仪系统参数
Table 2 The parameters of the missile autopilot system
符号 参数 数值 $ \mathcal{M} \;(\text{kg}) $ 质量 4410 $ \mathcal{V} \;\rm{\left(m\cdot s^{-1}\right)} $ 速度 947.6 $ \mathcal{P} \;\rm{\left(kg\cdot m^{2}\right)} $ 俯仰力矩 247 $ \mathscr{Q}\;\rm{\left(N\cdot m^{-2}\right)} $ 动压 293 $ S\;(\rm{m^{2}}) $ 参考面积 0.04087 $ D\; (\rm{m}) $ 参考直径 0.229 $ \mathcal{G} \;\rm{\left(m\cdot s^{-2}\right)} $ 重力加速度 9.8 $ \mathscr{H} $ 时间常数 0.1 表 3 导弹自动驾驶仪系统算法性能指标对比
Table 3 The comparison of performance indicators for the missile autopilot system
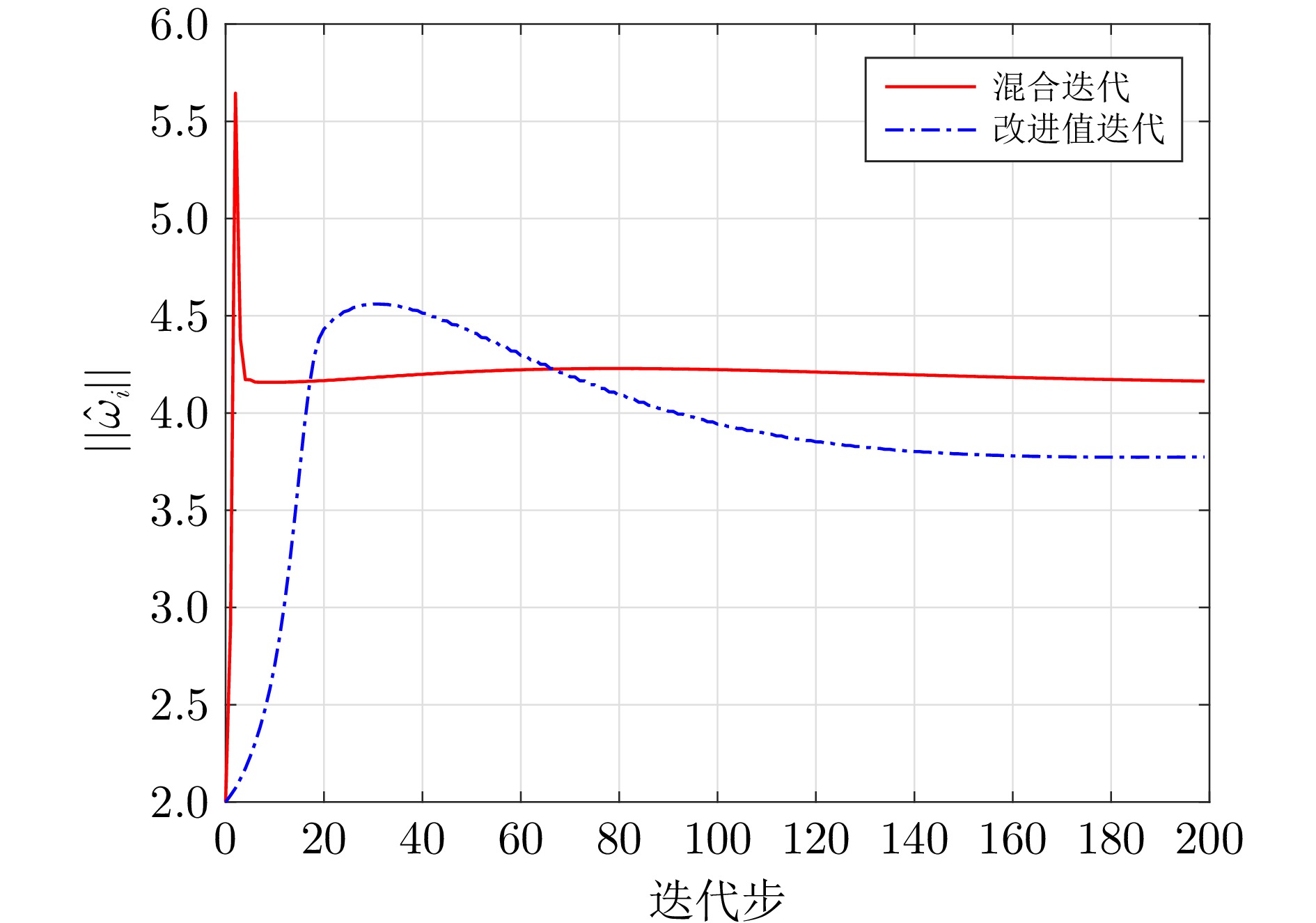
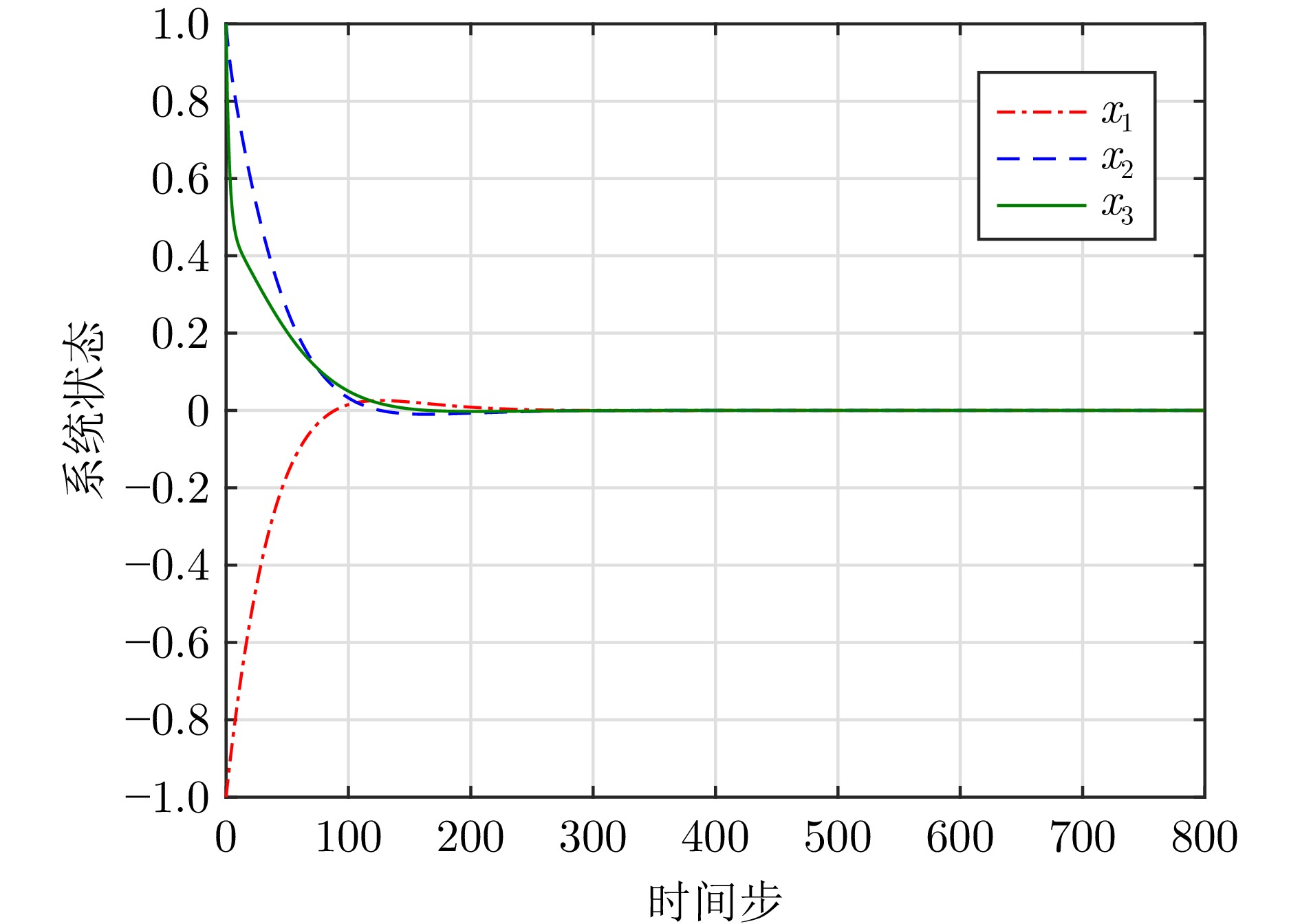
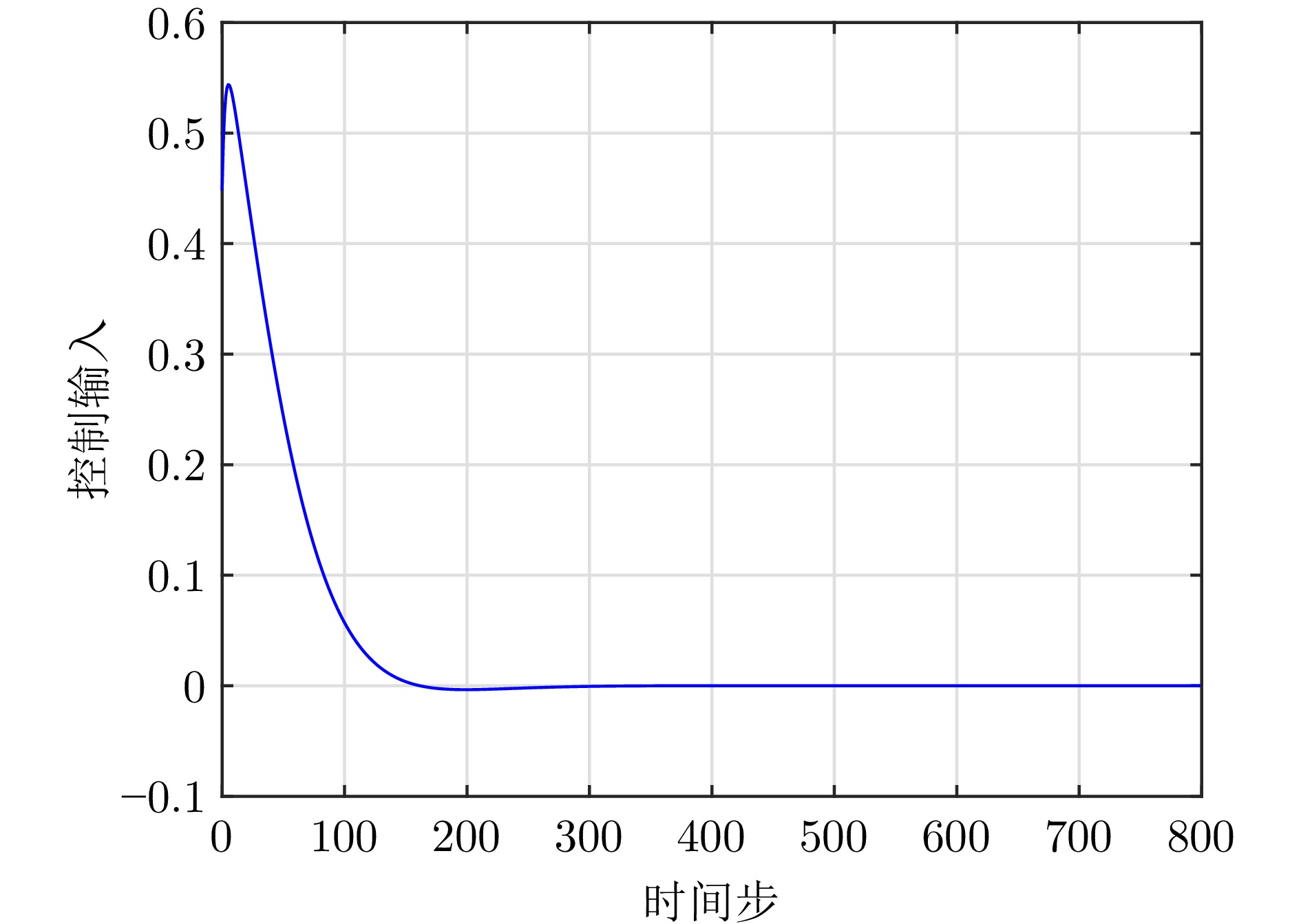
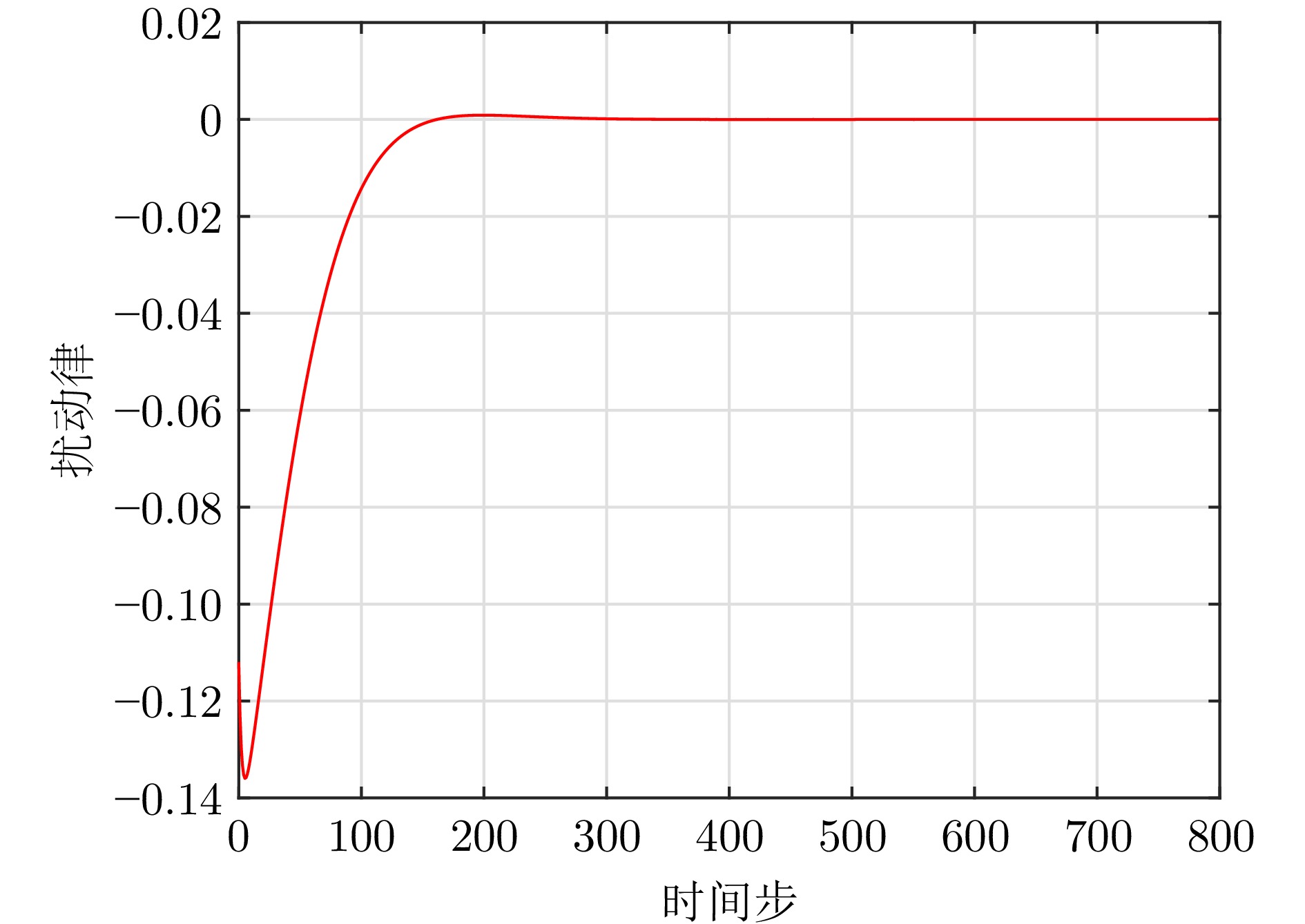
算法 CPU运行时间$ ({s}) $ 迭代步数 混合迭代自适应评判 318.088 1 79 改进值迭代 668.875 9 161 -
[1] Yang R H, Zhang H, Feng G, Yan H C, Wang Z P. Robust cooperative output regulation of multi-agent systems via adaptive event-triggered control. Automatica, 2019, 102: 129−136 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.01.001 [2] Zhang Y, Edwards C, Belmont M, Li G. Robust model predictive control for constrained linear system based on a sliding mode disturbance observer. Automatica, 2023, 154: Article No. 111101 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2023.111101 [3] Pal A, Naskar A K. Mixed H2/H∞ robust formation tracking control of linear multi-agent system using output information. Systems & Control Letters, 2024, 188: Article No. 105802 [4] Wang D, Gao N, Liu D R, Li J N, Lewis F L. Recent progress in reinforcement learning and adaptive dynamic programming for advanced control applications. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2024, 11(1): 18−36 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123843 [5] Werbos P J. Neural networks for control and system identification. In: Proceedings of the 28th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Tampa, FL, USA: IEEE, 1989. 260−265 [6] Yue S, Deng Y H, Wang G B, Ren J, Zhang Y X. Federated offline reinforcement learning with proximal policy evaluation. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2024, 33(6): 1360−1372 doi: 10.23919/cje.2023.00.288 [7] Liu D R, Wang D, Li H L. Decentralized stabilization for a class of continuous-time nonlinear interconnected systems using online learning optimal control approach. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(2): 418−428 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2280013 [8] Zhao F Y, Gao W N, Liu T F, Jiang Z P. Event-triggered robust adaptive dynamic programming with output feedback for large-scale systems. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2023, 10(1): 63−74 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2022.3186623 [9] 王鼎, 范文倩, 刘奥. 未知不匹配互联系统的非对称输入约束分散控制器设计. 工程科学学报, 2024, 46(12): 2269−2278Wang Ding, Fan Wen-Qian, Liu Ao. Decentralized controller design with asymmetric input constraints for unknown unmatched interconnected systems. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2024, 46(12): 2269−2278 [10] Lin M D, Zhao B, Liu D R. Policy gradient adaptive critic designs for model-free optimal tracking control with experience replay. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(6): 3692−3703 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3071968 [11] Li D D, Dong J X. Approximate optimal robust tracking control based on state error and derivative without initial admissible input. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(2): 1059−1069 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3320653 [12] Dahal R, Kar I. Robust tracking control of nonlinear unmatched uncertain systems via event-based adaptive dynamic programming. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2022, 109: 2831−2850 doi: 10.1007/s11071-022-07594-1 [13] Yang X, Xu M M, Wei Q L. Adaptive dynamic programming for nonlinear-constrained H∞ control. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(7): 4393−4403 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3247888 [14] Zhang Y, Zhao B, Liu D R, Zhang S C. Adaptive dynamic programming-based event-triggered robust control for multiplayer nonzero-sum games with unknown dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(8): 5151−5164 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3175650 [15] 王鼎, 王将宇, 乔俊飞. 融合自适应评判的随机系统数据驱动策略优化. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(5): 980−990 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230678Wang Ding, Wang Jiang-Yu, Qiao Jun-Fei. Data-driven policy optimization for stochastic systems involving adaptive critic. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(5): 980−990 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230678 [16] Wang D, Ren J, Huang H M, Qiao J F. Particle swarm optimization for adaptive-critic feedback control with power system applications. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 2025, 34(4): 1265−1274 doi: 10.23919/cje.2024.00.287 [17] Wang D, Hu L Z, Zhao M M, Qiao J F. Adaptive critic for event-triggered unknown nonlinear optimal tracking design with wastewater treatment applications. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(9): 6276−6288 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3135405 [18] 王鼎, 赵慧玲, 李鑫. 基于多目标粒子群优化的污水处理系统自适应评判控制. 工程科学学报, 2024, 46(5): 908−917Wang Ding, Zhao Hui-Ling, Li Xin. Adaptive critic control for wastewater treatment systems based on multiobjective particle swarm optimization. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2024, 46(5): 908−917 [19] Cao W W, Yang Q M, Meng W C, Xie S Z. Data-based robust adaptive dynamic programming for balancing control performance and energy consumption in wastewater treatment process. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(4): 6622−6630 doi: 10.1109/TII.2023.3346468 [20] Wang D, Wang J Y, Zhao M M, Xin P, Qiao J F. Adaptive multi-step evaluation design with stability guarantee for discrete-time optimal learning control. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2023, 10(9): 1797−1809 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123684 [21] Liu D R, Wei Q L. Policy iteration adaptive dynamic programming algorithm for discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(3): 621−634 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2281663 [22] Wei Q L, Zhou T M, Lu J W, Liu Y, Su S, Xiao J. Continuous-time stochastic policy iteration of adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(10): 6375−6387 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3284612 [23] Wang D, Zhao M M, Ha M M, Qiao J F. Stability and admissibility analysis for zero-sum games under general value iteration formulation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(11): 8707−8718 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3152268 [24] Wang D, Mu C X. Adaptive-critic-based robust trajectory tracking of uncertain dynamics and its application to a spring-mass-damper system. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(1): 654−663 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2722424 [25] Duan J L, Li J, Ge Q, Li S E, Bujarbaruah M, Ma F, et al. Relaxed actor-critic with convergence guarantees for continuous-time optimal control of nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2023, 8(5): 3299−3311 doi: 10.1109/TIV.2023.3255264 [26] Bian T, Jiang Z P. Reinforcement learning and adaptive optimal control for continuous-time nonlinear systems: A value iteration approach. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(7): 2781−2790 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3045087 [27] Xiao G Y, Zhang H G. Convergence analysis of value iteration adaptive dynamic programming for continuous-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(3): 1639−1649 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3232599 [28] Ha M M, Wang D, Liu D R. Novel discounted adaptive critic control designs with accelerated learning formulation. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(5): 3003−3016 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3233593 [29] Qasem O, Gutierrez H, Gao W N. Experimental validation of data-driven adaptive optimal control for continuous-time systems via hybrid iteration: An application to rotary inverted pendulum. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(6): 6210−6220 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3292873 [30] Liu A, Wang D, He Y Y, Ye K, Qiao J F. Value-iteration-based robust adaptive critic for disturbed non-affine continuous-time systems. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2025, 35(6): 4407−4415 -




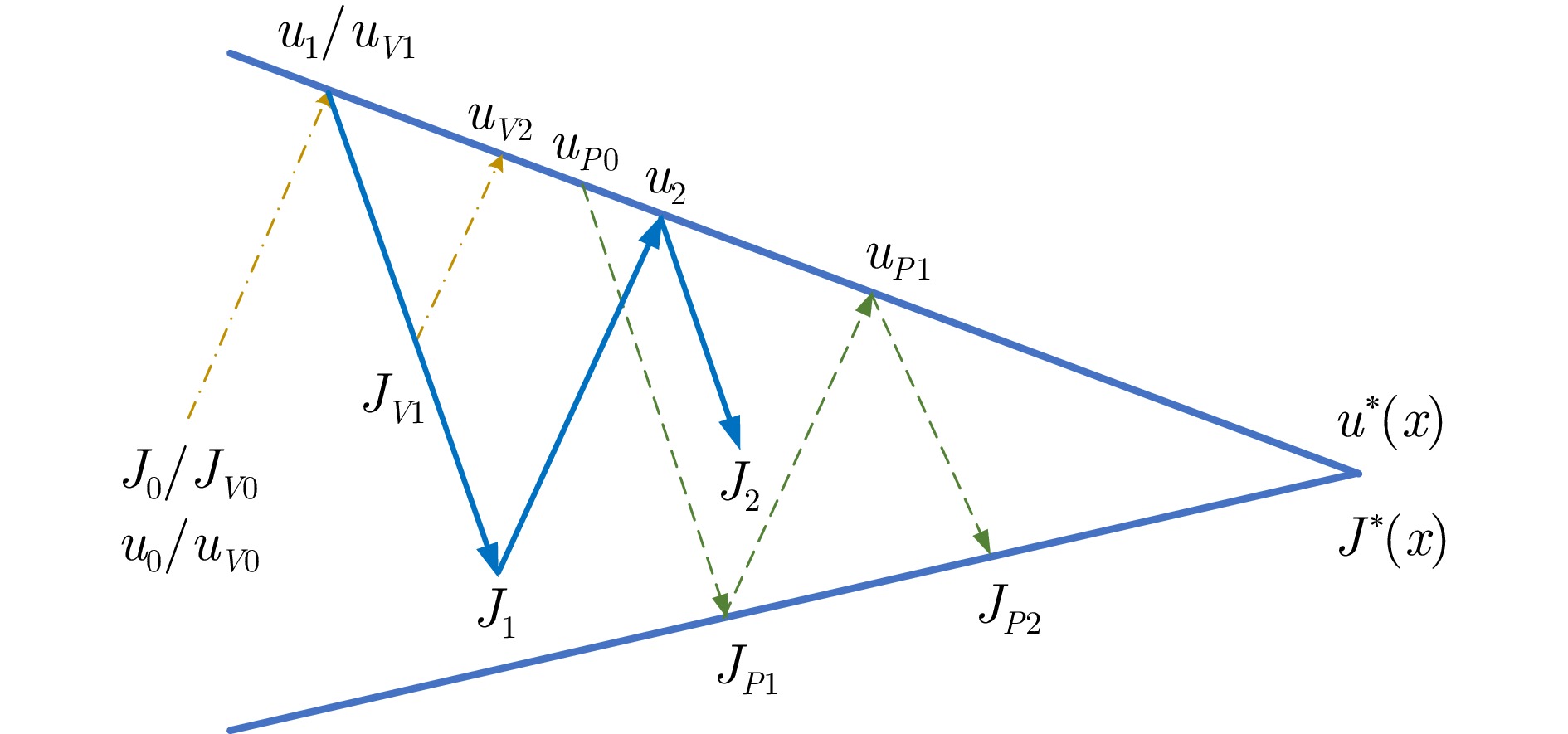
 下载:
下载: