Distributed Online Optimization for Two-network Zero-sum Games Under Communication Constraints
-
摘要: 研究双网络零和博弈中的分布式优化问题, 其中两个网络代表两个对立的玩家. 每个网络由一组具有时变损失函数的智能体组成, 智能体通过通信和协作来优化己方网络在博弈中的收益. 考虑到现实优化场景中通信资源受限和信息反馈受限两种通信受限情形, 设计基于事件触发通信和两点Bandit反馈的分布式在线优化算法, 并采用动态纳什均衡遗憾评估算法的性能. 在某些假设条件下, 建立相对于总博弈次数为次线性的动态纳什均衡遗憾界, 从而验证了算法的有效性. 此外, 将设计的算法拓展为多周期版本并建立次线性的动态纳什均衡遗憾界. 最后, 通过双线性矩阵博弈的仿真算例进一步验证了所设计的两个算法的性能.Abstract: This paper investigates the distributed optimization problem in two-network zero-sum games, where the two networks represent two opposing players. Each network consists of a set of agents with time-varying cost functions, and the agents optimize the payoff of their network in the game through communication and collaboration. Considering the two communication constrained situations in real optimization scenarios, namely, limited communication resources and limited information feedback, a distributed online optimization algorithm based on event-triggered communication and two-point Bandit feedback is designed, and the performance of the algorithm is evaluated using the dynamic Nash equilibrium regret. Under certain assumptions, a sublinear dynamic Nash equilibrium regret bound relative to the total number of game iterations is established, thereby validating the effectiveness of the algorithm. Additionally, the designed algorithm is extended to a multi-epoch version, and a sublinear dynamic Nash equilibrium regret bound is also established. Finally, a simulation example involving a bilinear matrix game is provided to further verify the performance of the two designed algorithms.
-
表 1 主要符号及其含义
Table 1 Main symbols and their meanings
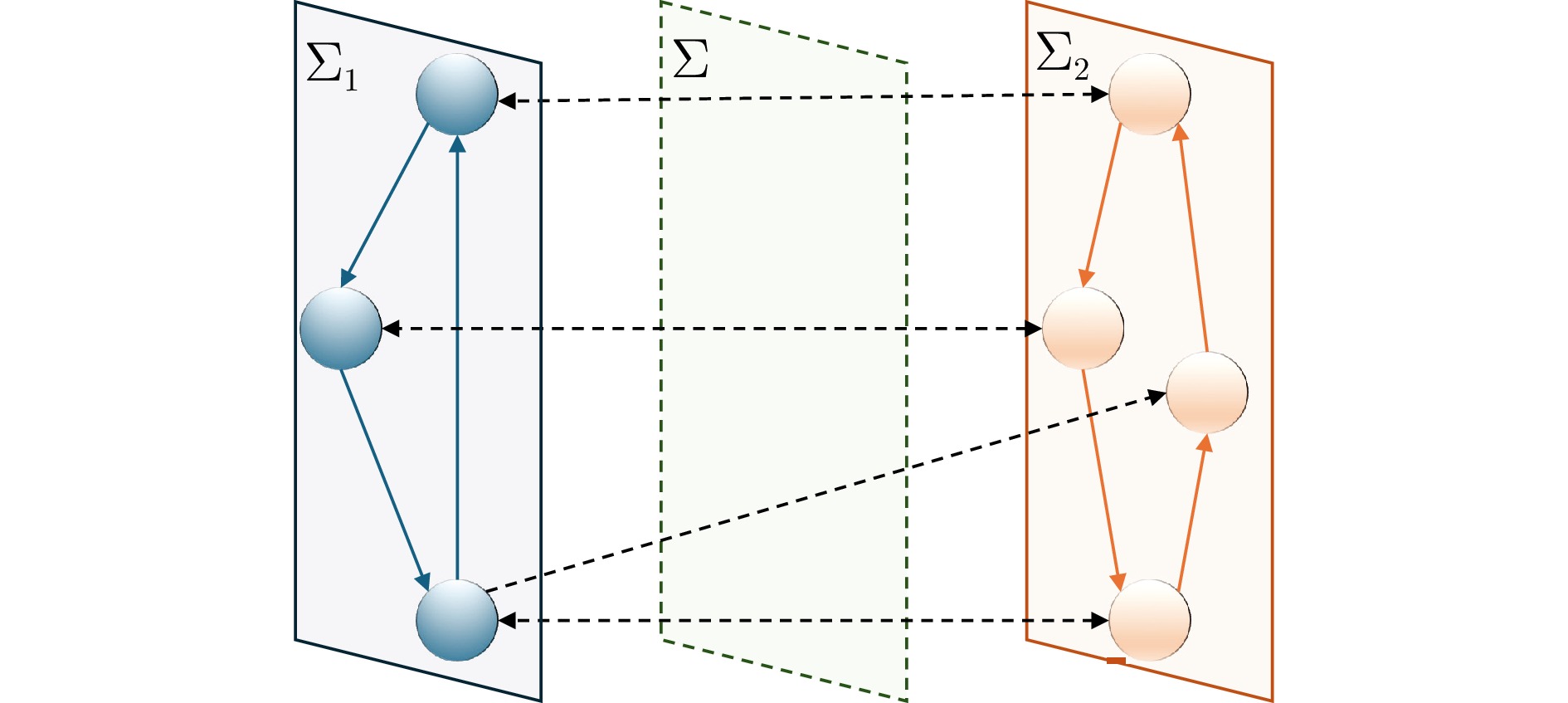
符号 含义 $ \mathbf{R}^{d}$, $ \mathbf{R}^{d_1\times d_2}$ $d$维向量空间, $d_1\times d_2$维矩阵空间 $ \mathcal{V}_l$, $ \mathcal{P}_l^t$, $ \mathcal{A}_l^t$ $\Sigma_l$的智能体集、链路集、权重矩阵 $ \mathcal{P}_{-l}^t$, $ \mathcal{A}_{-l}^t$ $\Sigma_l$获取对手信息的链路集、权重矩阵 $ \mathcal{K}_l\subset \mathbf{R}^{d_l}$ $\Sigma_l$的决策集 $\| u\|$, $ {\boldsymbol{P}}_{ \mathcal{K}}( u)$ $ u$的欧氏范数以及在$ \mathcal{K}$上的欧氏投影 $ {\boldsymbol{B}}_l(r)$ 原点为中心、$r$为半径的$d_l$维欧氏球 $ {\boldsymbol{S}}_l(r)$ 原点为中心、$r$为半径的$d_l$维欧氏球面 $ {\bf{Z}}_n$ 正整数集$\{1,\;2,\;\cdots,\;n\}$ $[ \mathcal{A}]_{ij}$ 矩阵$ \mathcal{A}$的第$i$行第$j$列元素 $o(\cdot)$, $\mathcal{O}(\cdot)$ 低阶无穷大以及等价无穷大 -
[1] Li Y B, Gai K K, Qiu L F, Qiu M K, Zhao H. Intelligent cryptography approach for secure distributed big data storage in cloud computing. Information Sciences, 2017, 387: 103−115 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2016.09.005 [2] Coady Y, Hohlfeld O, Kempf J, McGeer R, Schmid S. Distributed cloud computing: Applications, status quo, and challenges. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2015, 45(2): 38−43 doi: 10.1145/2766330.2766337 [3] Yuan D M, Proutiere A, Shi G D. Multi-agent online optimization. Foundations and Trends® in Optimization, 2024, 7(2−3): 81−263 [4] Yang T, Yi X L, Wu J F, Yuan Y, Wu D, Meng Z Y, et al. A survey of distributed optimization. Annual Reviews in Control, 2019, 47: 278−305 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2019.05.006 [5] Li H Q, Li J, Ran L, Zheng L F, Huang T W. A survey of distributed algorithms for aggregative games. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2025, 12(5): 859−871 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2024.124998 [6] Liu B, Chai L, Yi J W. Convergence analysis of distributed gradient descent algorithms with one and two momentum terms. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(3): 1511−1522 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3218663 [7] Yu Z, Fan J, Shi Z J, Zhou D X. Distributed gradient descent for functional learning. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2024, 70(9): 6547−6571 doi: 10.1109/TIT.2024.3428325 [8] 吴庆涛, 朱军龙, 葛泉波, 张明川. 一种基于条件梯度的加速分布式在线学习算法. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(2): 386−402Wu Qing-Tao, Zhu Jun-Long, Ge Quan-Bo, Zhang Ming-Chuan. An accelerated distributed online learning algorithm based on conditional gradient. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(2): 386−402 [9] Hou J, Zeng X L, Wang G, Sun J, Chen J. Distributed momentum-based Frank-Wolfe algorithm for stochastic optimization. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2023, 10(3): 685−699 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2022.105923 [10] Gong K, Zhang L W. Primal-dual algorithm for distributed optimization with coupled constraints. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 2024, 201(1): 252−279 doi: 10.1007/s10957-024-02393-7 [11] Sawamura R, Hayashi N, Inuiguchi M. A distributed primal-dual push-sum algorithm on open multiagent networks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2025, 70(2): 1192−1199 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2024.3453382 [12] Chen G P, Xu G H, Li W J, Hong Y G. Distributed mirror descent algorithm with Bregman damping for nonsmooth constrained optimization. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(11): 6921−6928 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3244995 [13] 张文韬, 张保勇, 袁德明, 徐胜元. 分布式在线鞍点问题的Bandit反馈优化算法. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(4): 857−874Zhang Wen-Tao, Zhang Bao-Yong, Yuan De-Ming, Xu Sheng-Yuan. Bandit feedback optimization algorithm for distributed online saddle point problem. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(4): 857−874 [14] Zhang Y Q, Lou Y C, Hong Y G, Xie L H. Distributed projection-based algorithms for source localization in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(6): 3131−3142 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2402672 [15] Lee K, Lam M, Pedarsani R, Papailiopoulos D, Ramchandran K. Speeding up distributed machine learning using codes. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2018, 64(3): 1514−1529 doi: 10.1109/TIT.2017.2736066 [16] Yang T, Wu D, Fang H Z, Ren W, Wang H, Hong Y G, et al. Distributed energy resource coordination over time-varying directed communication networks. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2019, 6(3): 1124−1134 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2019.2921284 [17] Cao X Y, Başar T. Decentralized online convex optimization with event-triggered communications. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 69: 284−299 [18] 杨涛, 徐磊, 易新蕾, 张圣军, 陈蕊娟, 李渝哲. 基于事件触发的分布式优化算法. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 133−143Yang Tao, Xu Lei, Yi Xin-Lei, Zhang Sheng-Jun, Chen Rui-Juan, Li Yu-Zhe. Event-triggered distributed optimization algorithms. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 133−143 [19] Xiong M H, Ho D W C, Zhang B Y, Yuan D M, Xu S Y. Distributed online mirror descent with delayed subgradient and event-triggered communications. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2024, 11(2): 1702−1715 doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2023.3329523 [20] Hazan E. Introduction to online convex optimization. Foundations and Trends® in Optimization, 2016, 2(3−4): 157−325 [21] Wang C, Xu S Y, Yuan D M, Zhang B Y, Zhang Z Q. Push-sum distributed online optimization with bandit feedback. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(4): 2263−2273 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2999309 [22] Yuan D M, Zhang B Y, Ho D W C, Zheng W X, Xu S Y. Distributed online bandit optimization under random quantization. Automatica, 2022, 146: Article No. 110590 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2022.110590 [23] 侯瑞捷, 李修贤, 易新蕾, 洪奕光, 谢立华. 具有反馈延迟分布式在线复合优化的动态遗憾性能. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(4): 835−856Hou Rui-Jie, Li Xiu-Xian, Yi Xin-Lei, Hong Yi-Guang, Xie Li-Hua. Dynamic regret for distributed online composite optimization with delayed feedbacks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(4): 835−856 [24] Duggan J. Equilibrium existence for zero-sum games and spatial models of elections. Games and Economic Behavior, 2007, 60(1): 52−74 doi: 10.1016/j.geb.2006.10.004 [25] Crawford V P. Learning the optimal strategy in a zero-sum game. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society, 1974, 885−891 [26] Gharesifard B, Cortés J. Distributed convergence to Nash equilibria in two-network zero-sum games. Automatica, 2013, 49(6): 1683−1692 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2013.02.062 [27] Lou Y C, Hong Y G, Xie L H, Shi G D, Johansson K H. Nash equilibrium computation in subnetwork zero-sum games with switching communications. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2016, 61(10): 2920−2935 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2504962 [28] Huang S J, Lei J L, Hong Y G, Shanbhag U V, Chen J. No-regret distributed learning in subnetwork zero-sum games. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(10): 6620−6635 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2024.3379253 [29] Xiong H Y, Han J X, Nian X H, Li S L. Nash equilibrium computation of two-network zero-sum games with event-triggered communication. Journal of Control and Decision, 2022, 9(3): 334−346 doi: 10.1080/23307706.2021.1977193 [30] Shi C X, Yang G H. Nash equilibrium computation in two-network zero-sum games: An incremental algorithm. Neurocomputing, 2019, 359(24): 114−121 [31] Spyridopoulos T, Karanikas G, Tryfonas T, Oikonomou G. A game theoretic defence framework against DoS/DDoS cyber attacks. Computers & Security, 2013, 38: 39−50 [32] Nedic A, Olshevsky A, Ozdaglar A, Tsitsiklis J N. Distributed subgradient methods and quantization effects. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 47th Conference on Decision and Control (CDC). Cancun, Mexico: IEEE, 2008. 4177−4184 [33] Zhang W T, Shi Y, Zhang B Y, Yuan D M, Xu S Y. Dynamic regret of distributed online saddle point problem. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(4): 2522−2529 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3312033 [34] Zhang M X, Zhao P, Luo H P, Zhou Z H. No-regret learning in time-varying zero-sum games. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2022. 26772−26808 [35] Yi X L, Li X X, Yang T, Xie L H, Chai T Y, Johansson K H. Distributed bandit online convex optimization with time-varying coupled inequality constraints. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(10): 4620−4635 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.3030883 -




 下载:
下载: