Integrated Guidance and Control of Flight Vehicles by Fusing Evolutionary Algorithms and Deep Reinforcement Learning
-
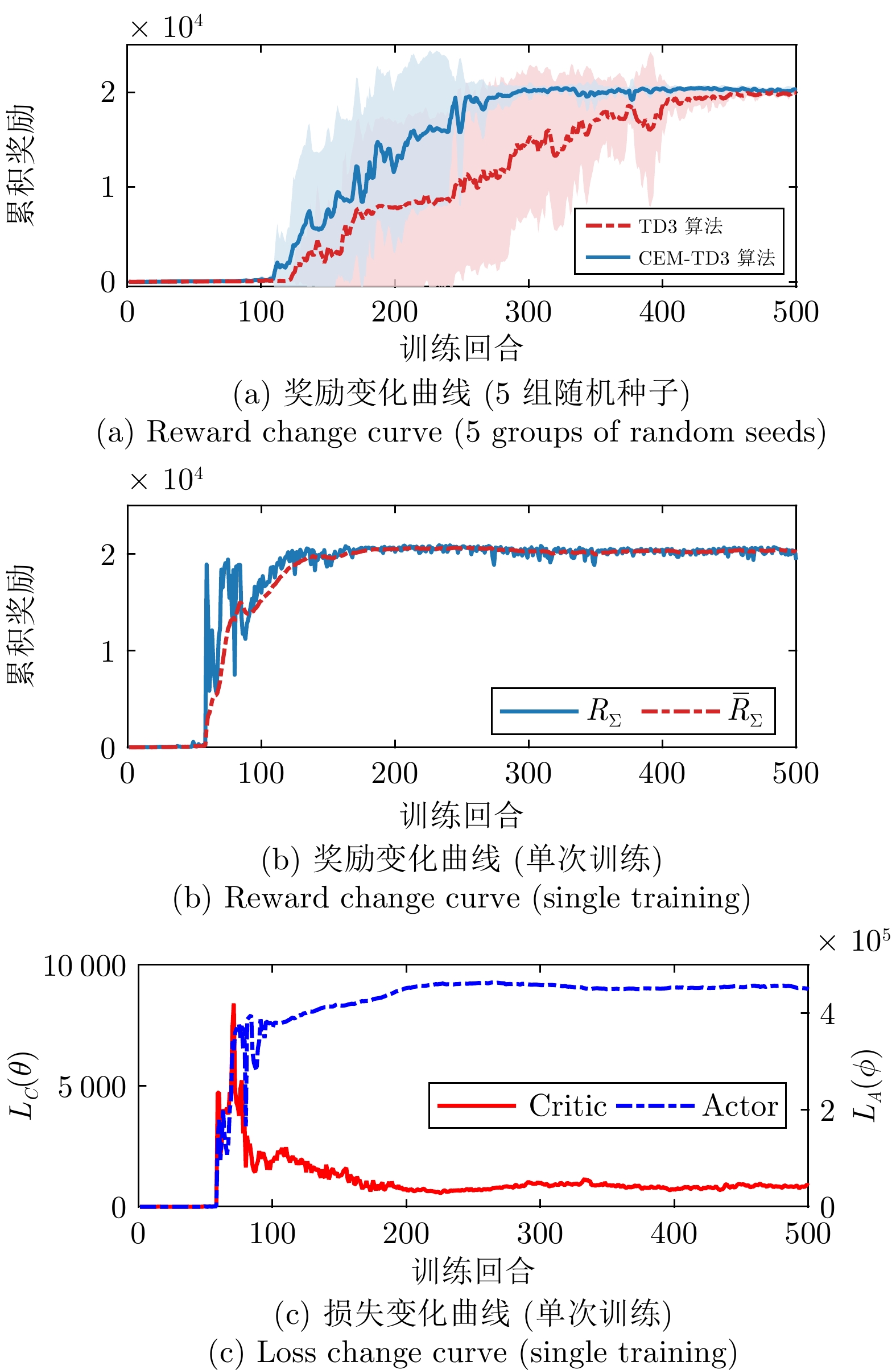
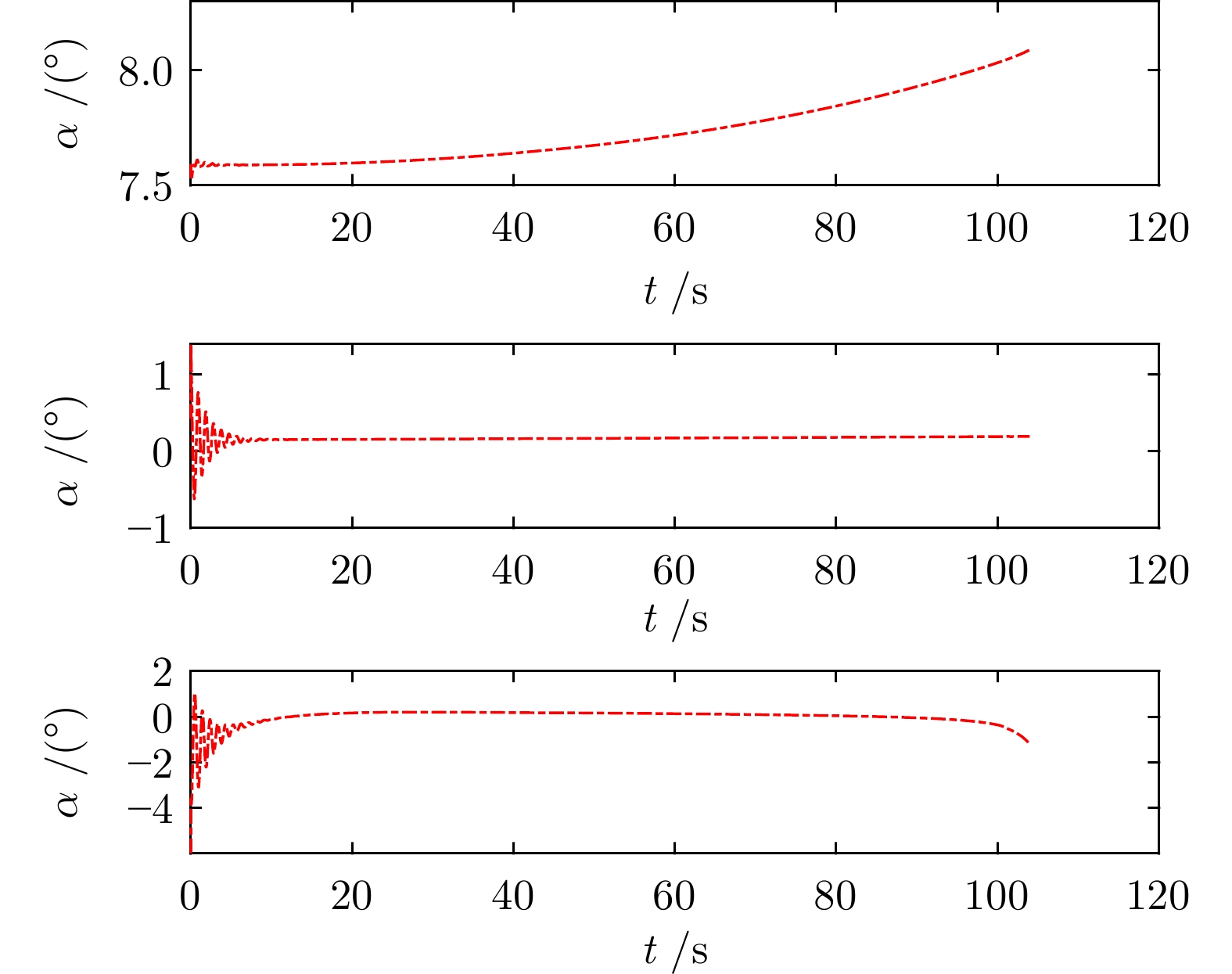
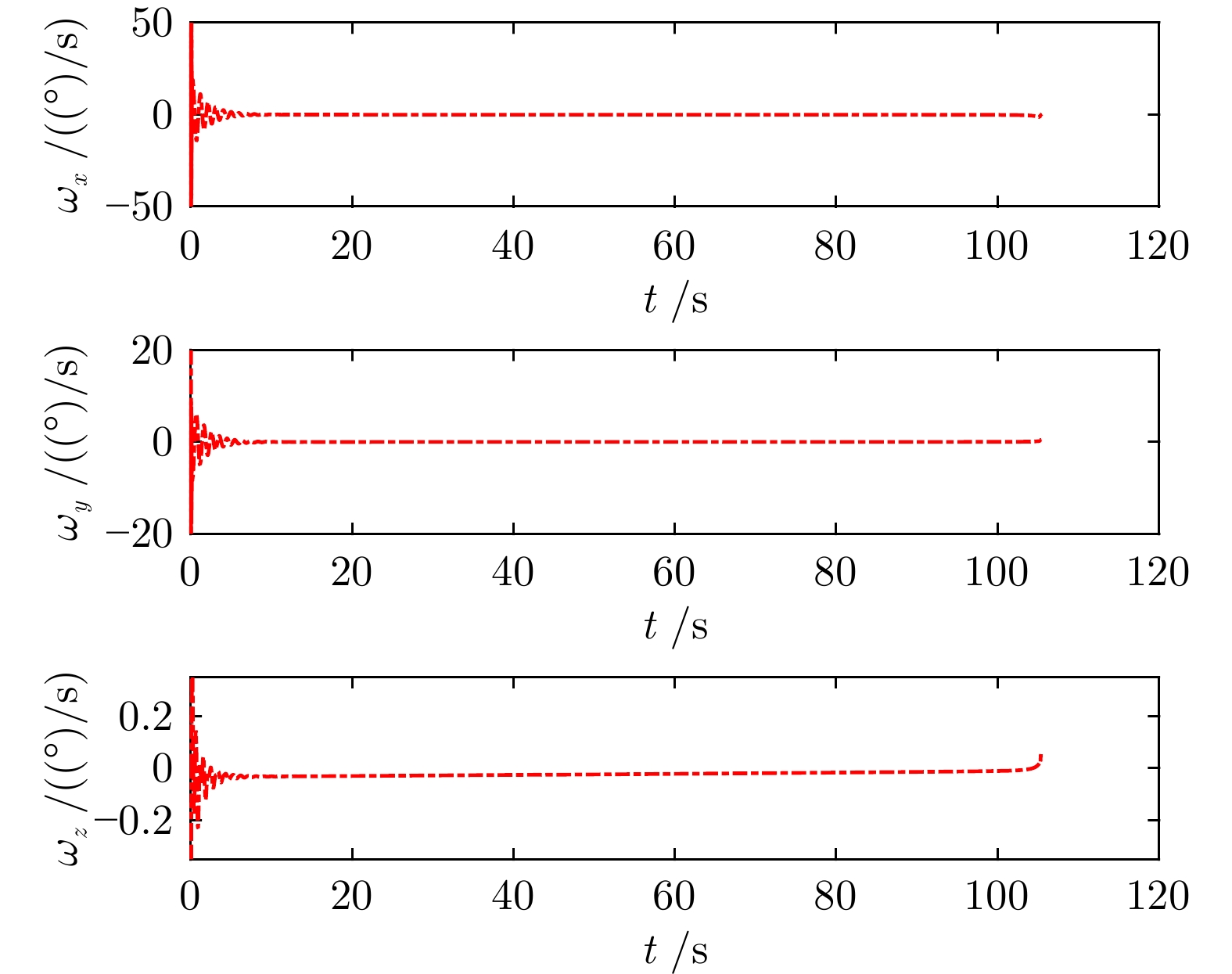
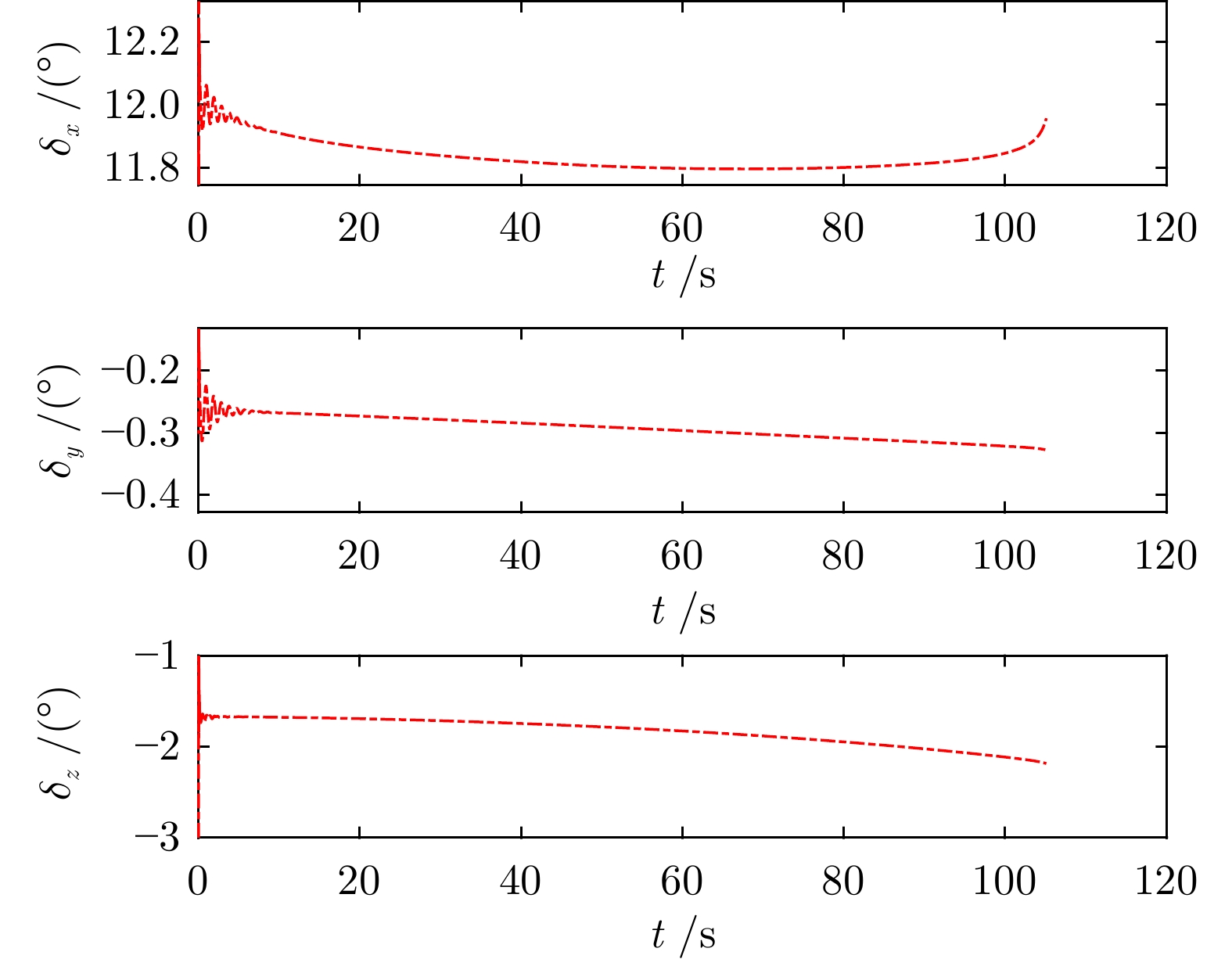
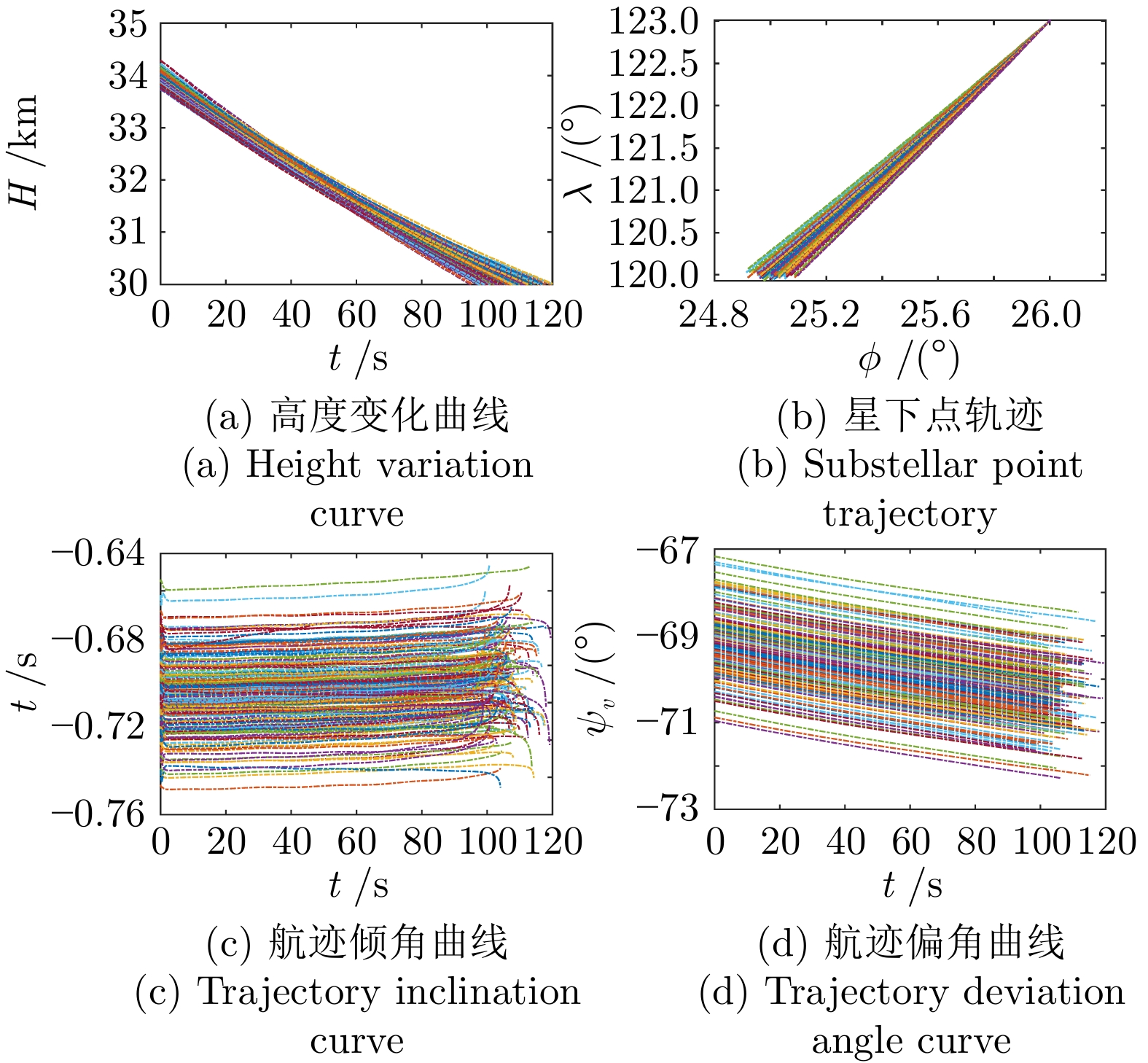
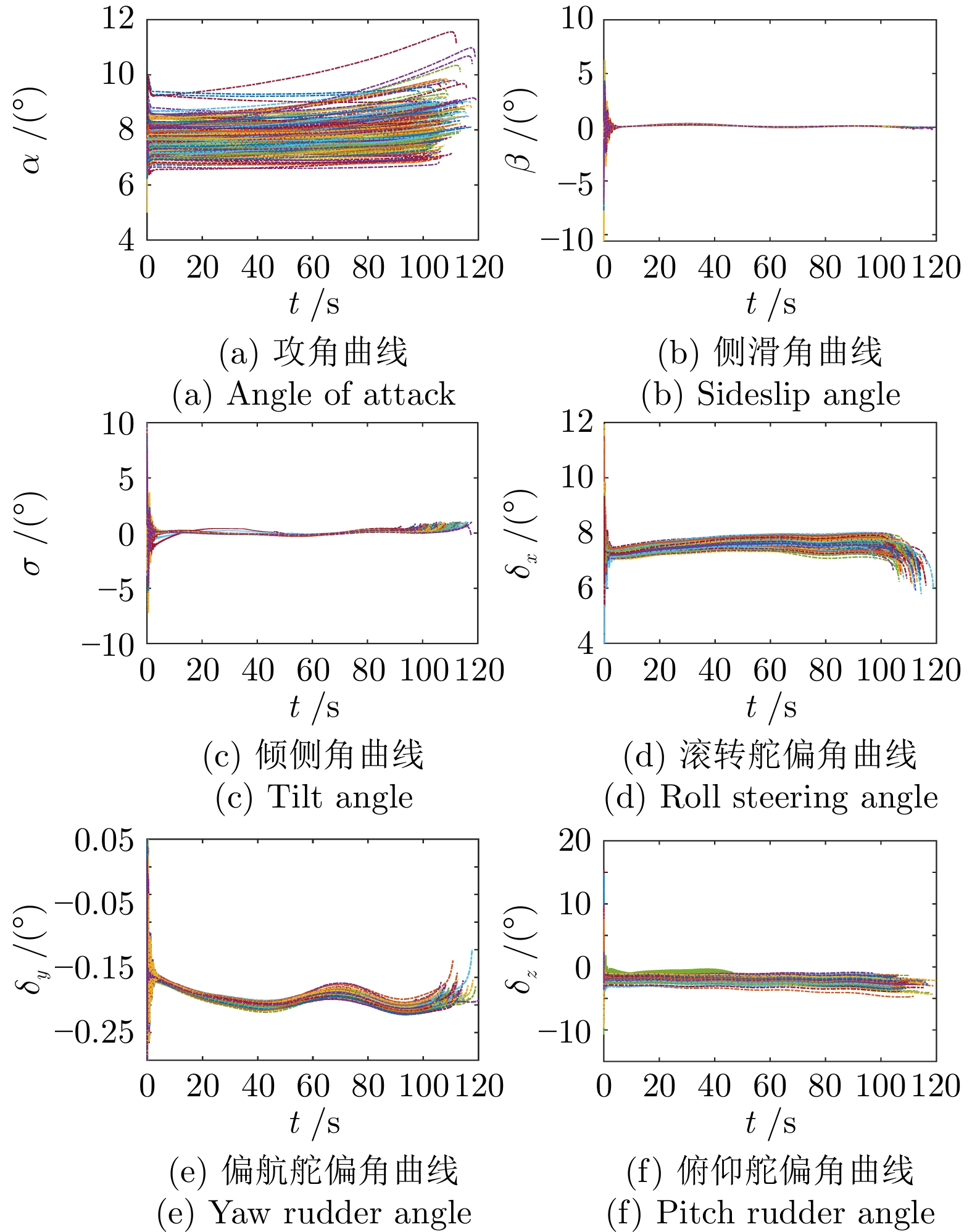
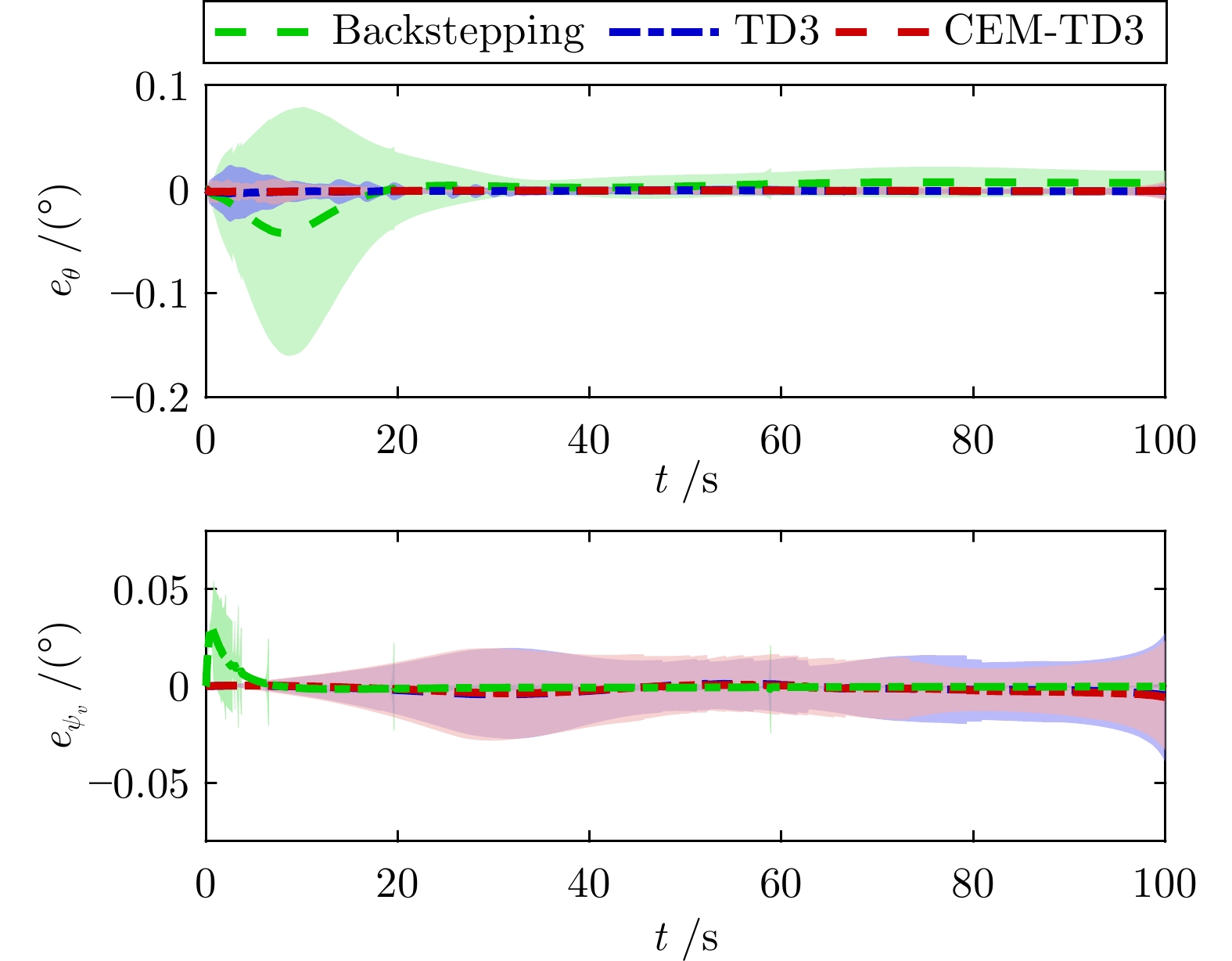
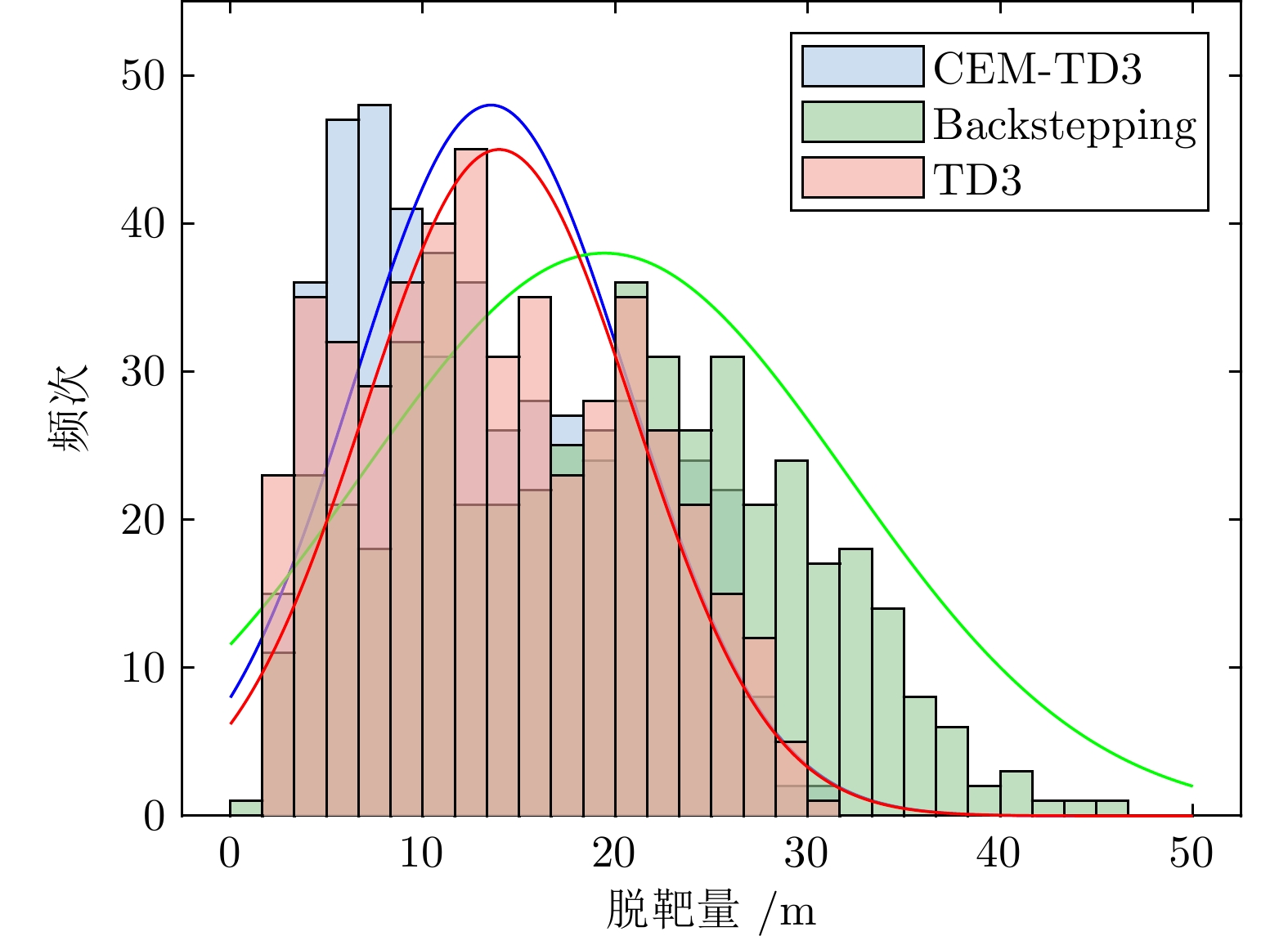
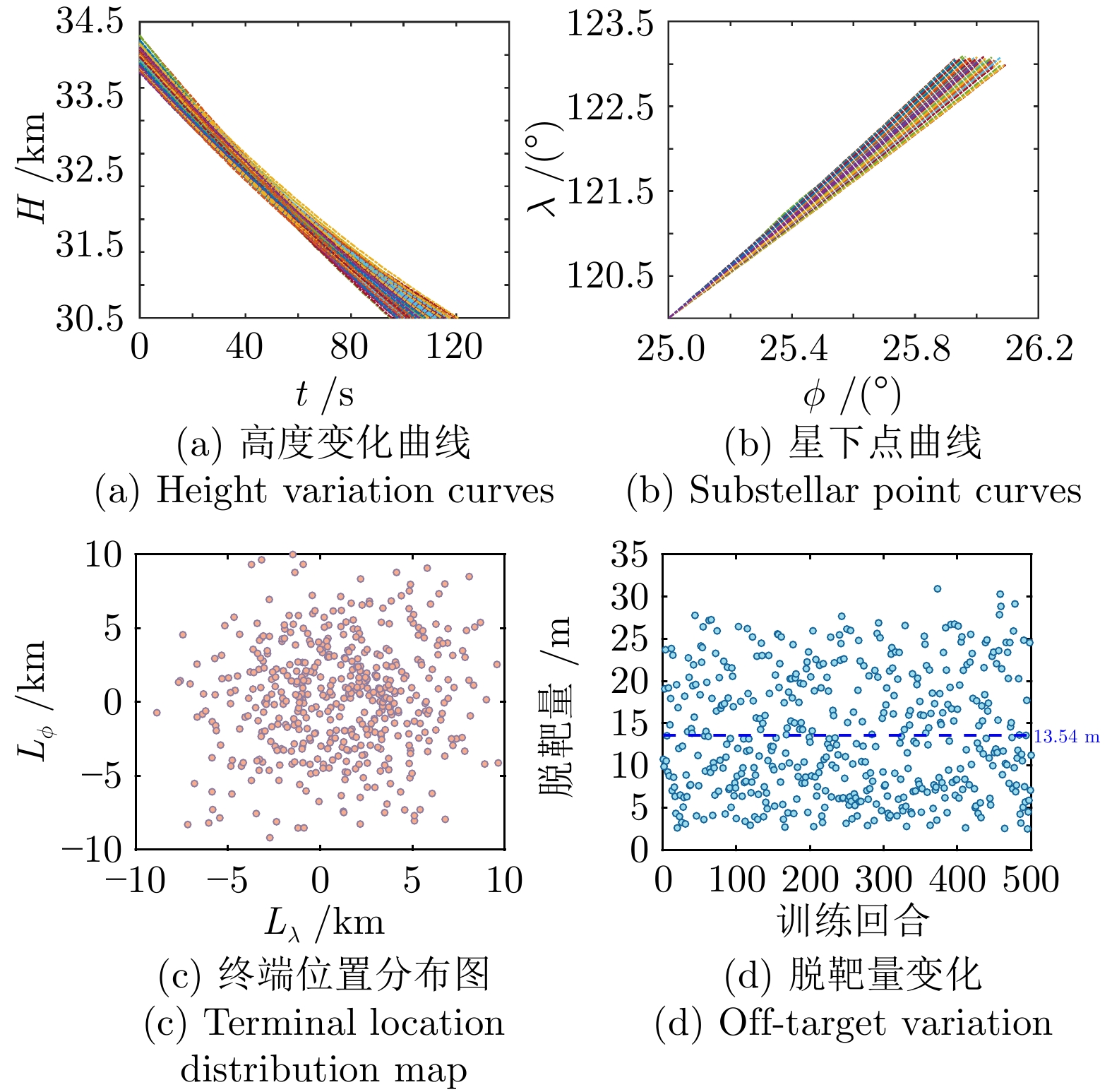
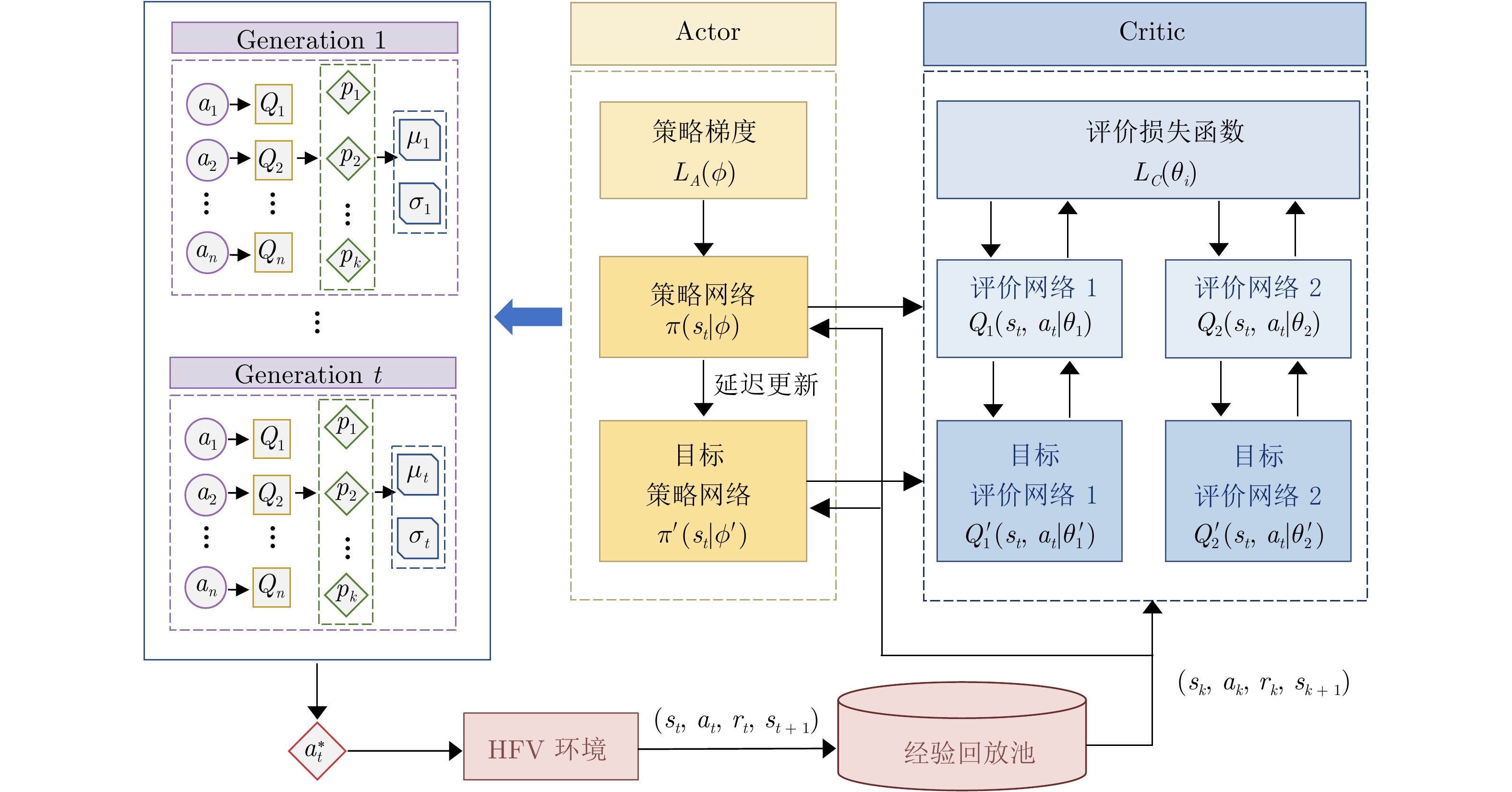
摘要: 针对高超声速飞行器在外界干扰与模型不确定性影响下的制导控制难题, 提出一种融合双延迟深度确定性策略梯度与交叉熵方法 (CEM) 的进化强化学习框架. 首先, 构建高超声速飞行器的运动模型与制导控制一体化模型; 其次, 将复杂干扰环境下的多约束控制问题转化为强化学习决策优化过程, 依托深度强化学习的无模型数据驱动特性, 建立从状态观测到舵偏角指令的端到端映射机制. 同时, 引入基于CEM的动作空间采样机制, 通过Q 值最大化准则筛选精英候选动作集, 利用价值函数引导进化搜索方向, 有效克服传统强化学习探索低效、盲目性强的缺陷, 提升样本利用效率. 最后, 仿真结果表明所提算法能够适应初始高度偏差 ±300 m、速度偏差 ±200 m/s及气动参数 ±40%不确定性等变任务飞行条件, 且在终端控制精度与鲁棒性等核心指标上显著优于传统控制方法.Abstract: Aiming at the challenging problem of guidance and control for hypersonic flight vehicles under external disturbances and model uncertainties, this paper proposes an evolutionary reinforcement learning framework that integrates the twin delayed deep deterministic policy gradient and cross-entropy method (CEM). First, the motion model and integrated guidance and control model of the hypersonic flight vehicle are constructed. Second, the multi-constraint control problem in complex disturbed environments is transformed into a reinforcement learning decision optimization process. Leveraging the model-free, data-driven nature of deep reinforcement learning, an end-to-end mapping mechanism from state observations to rudder deflection commands is established. Meanwhile, a CEM-based action space sampling mechanism is introduced, which screens elite candidate action sets through the Q-value maximization criterion and uses the value function to guide the direction of evolutionary search. This effectively overcomes the defects of inefficient and highly blind exploration in traditional reinforcement learning and improves sample utilization efficiency. Finally, simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can adapt to variable mission flight conditions such as initial altitude deviations of ±300 m, velocity deviations of ±200 m/s, and aerodynamic parameter uncertainties of ±40%. It also significantly outperforms traditional control methods in core indicators such as terminal control accuracy and robustness.
-
表 1 神经网络结构参数
Table 1 Parameters of neural network structure
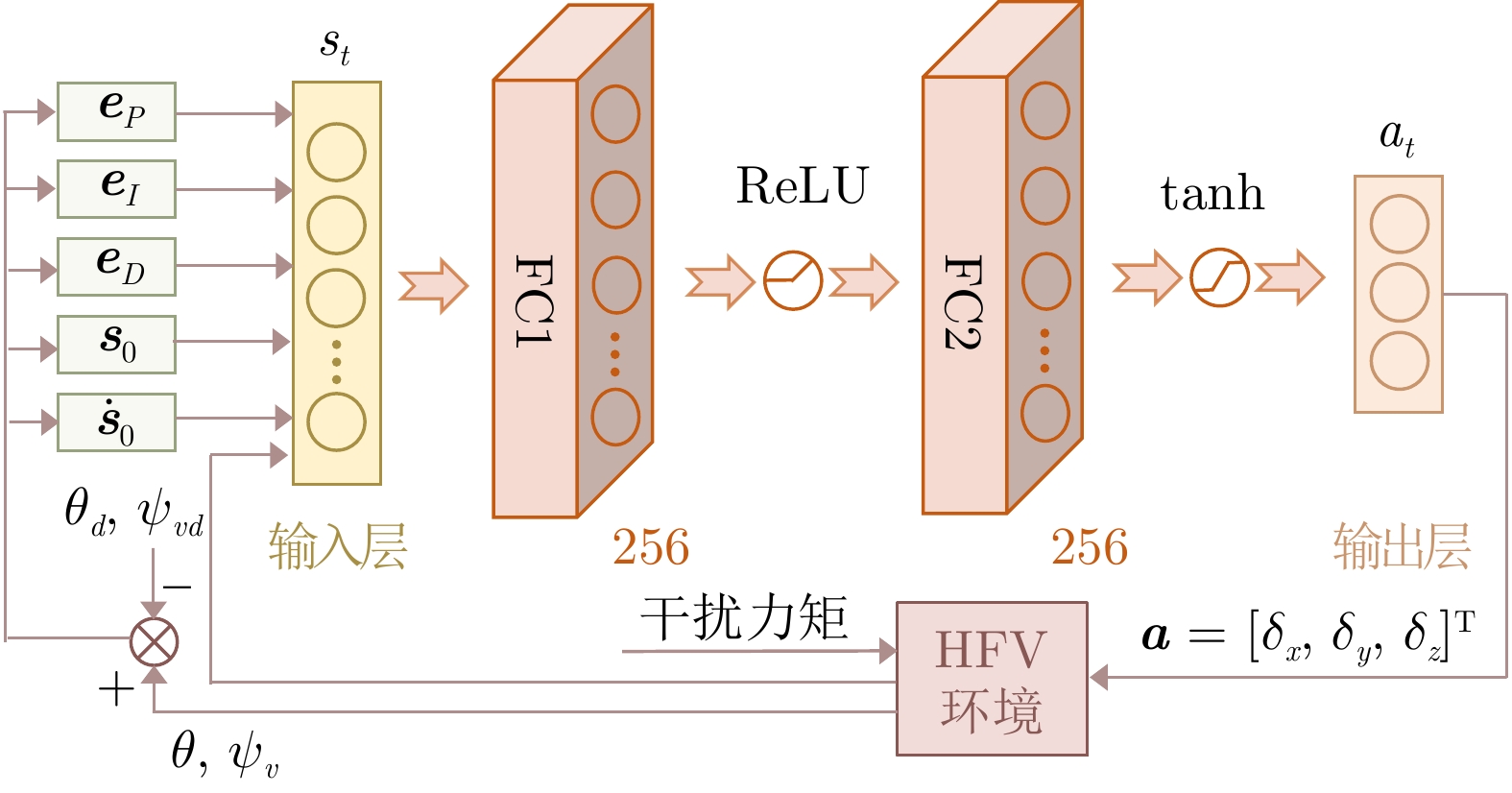
网络层 策略网络 价值网络 神经元数 激活函数 神经元数 激活函数 输入层 18 none 21 none 隐藏层1 256 ReLU 256 ReLU 隐藏层2 256 ReLU 256 ReLU 输出层 3 tanh 1 Linear 表 2 训练超参数
Table 2 Training hyperparameters
训练超参数 数值 训练超参数 数值 训练回合数$ M $ 500 经验回放池容量$ N_{\text{max}} $ $ 10^{6} $ 单回合最大时间步$ T $ — 策略网络噪声标准差$\varepsilon_1$ 0.1 批学习数$ N_{b} $ 128 目标网络噪声标准差$\varepsilon_2$ 0.2 折扣因子$ \gamma $ 0.99 价值网络1学习率$ \alpha_1 $ $ 5.0 \times 10^{-4} $ 策略网络学习率$ \beta $ $ 1.0 \times 10^{-4} $ 价值网络2学习率$ \alpha_2 $ $ 5.0 \times 10^{-4} $ 目标网络更新系数$ \kappa $ $ 5.0 \times 10^{-3} $ 延迟策略更新$ k $ 2 表 3 模拟外部干扰的参数域设置
Table 3 Parameter domain settings for simulated external disturbances
参数项 单位 参数域 干扰力矩$ \Delta d_{x} $ N·m $ \tilde{D}_{x} (-\cos (\pi t/40)+\sin (\pi t/20)) $, $\tilde{D}_{x} \in [40,\;60]$ 干扰力矩$ \Delta d_{y} $ N·m $ \tilde{D}_{y} (-\cos (\pi t/30)+\sin (\pi t/60)) $, $\tilde{D}_{y} \in [400,\;600]$ 干扰力矩$ \Delta d_{z} $ N·m $ \tilde{D}_{z} \cos (\pi t/30) \sin (\pi t/20) $, $\tilde{D}_{z} \in [800,\;1\;200]$ 注: $ \tilde{*} $表示参数“$ * $”从参数域中随机选择. 表 4 每回合初始状态量的参数域设置
Table 4 Parameter domain settings for initial state variables in each episode
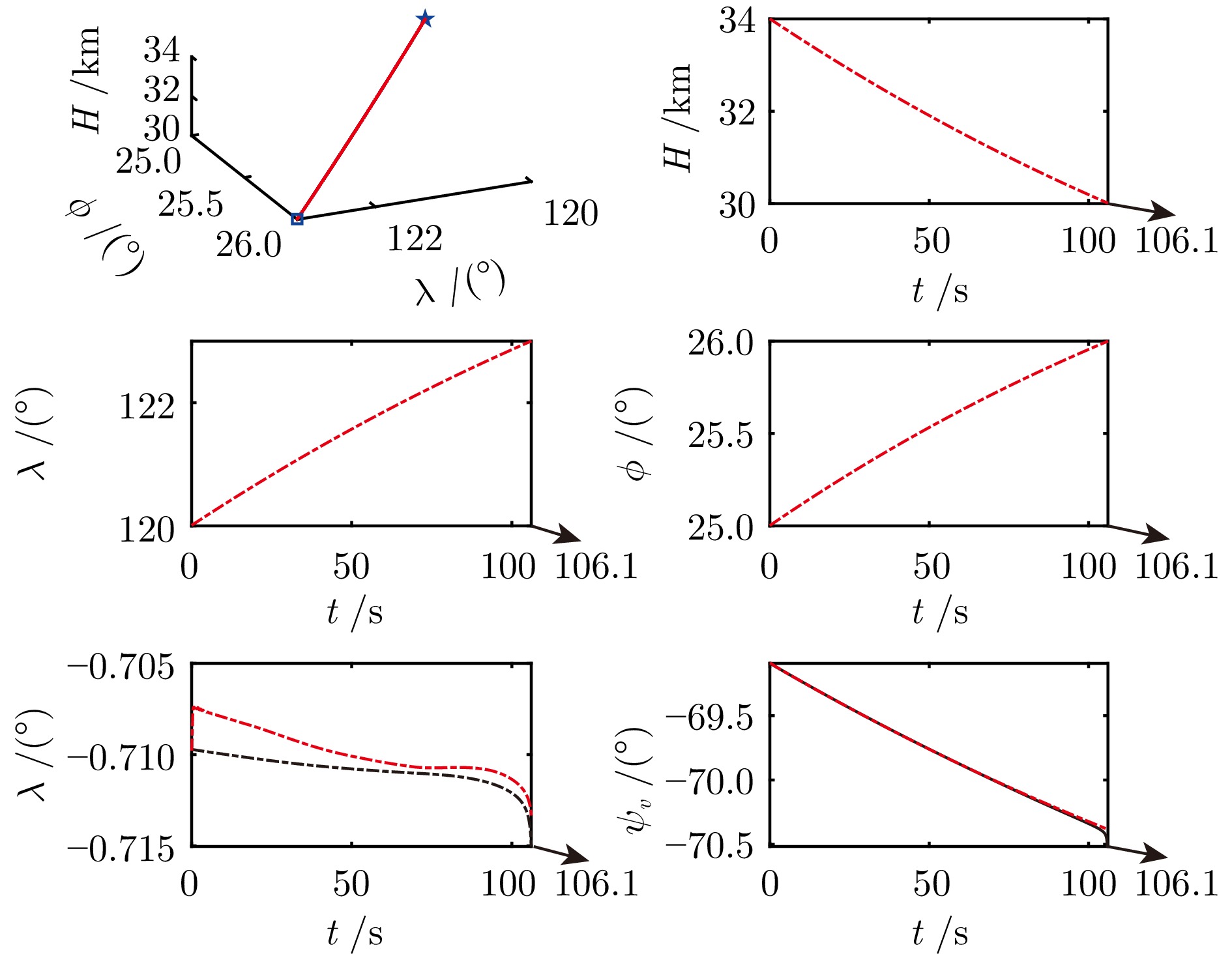
状态量 单位 数学形式 偏差带$ 3\sigma $ 高度$\tilde{H}_0$ m $34\;000 + \mathrm{N}(0,\; \sigma_H^2)$ 300 速度$\tilde{V}_0$ m/s $3\;700 + \mathrm{N}(0,\; \sigma_V^2)$ 200 经度$\tilde{\lambda}_0$ ° $120 + \mathrm{N}(0,\; \sigma_\lambda^2)$ 0.1 纬度$\tilde{\phi}_0$ ° $25 + \mathrm{N}(0,\; \sigma_\phi^2)$ 0.1 轨迹倾角$\tilde{\theta}_0$ ° $\theta_0 + \mathrm{N}(0,\; \sigma_\theta^2)$ 1.0 轨迹偏角$\tilde{\psi}_{v_0}$ ° $\psi_{v_0} + \mathrm{N}(0,\; \sigma_{\psi_v}^2)$ 1.0 表 5 模拟气动参数不确定性的参数域设置
Table 5 Parameter domain settings for simulated aerodynamic parameter uncertainties
参数项 数学形式 偏差带$3\sigma$ 气动力系数偏差$ \Delta \tilde{C}_{L},\; \Delta \tilde{C}_{D},\; \Delta \tilde{C}_{Y}$ $\mathrm{N}(0,\; \sigma^2)$ 40% 气动力矩系数偏差$ \Delta \tilde{C}_{mx},\;\Delta \tilde{C}_{my},\;\Delta \tilde{C}_{mz} $ $\mathrm{N}(0,\; \sigma^2)$ 40% 大气密度$ \tilde{\rho} $ $\mathrm{N}(0,\; \sigma^2)$ 40% -
[1] 张绍芳, 叶蕾. 国外高超声速飞行器及技术发展综述. 中国航天, 2016, 12: 16−20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7742.2016.12.008Zhang Shao-Fang, Ye Lei. Summary of foreign hypersonic vehicles and technology development. China Aerospace, 2016, 12: 16−20 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7742.2016.12.008 [2] 杨浩东, 王剑颖, 吴志刚, 刘佳琪, 梁海朝. 面向动态禁飞区的自适应触角探测机动制导方法. 宇航学报, 2024, 45(2): 192−202 doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2024.02.004Yang Hao-Dong, Wang Jian-Ying, Wu Zhi-Gang, Liu Jia-Qi, Liang Hai-Chao. Adaptive antenna detection maneuver guidance method for dynamic no-fly zone. Journal of Astronautics, 2024, 45(2): 192−202 doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2024.02.004 [3] 顾攀飞, 齐瑞云, 郭小平. 高超声速飞行器再入自适应容错制导控制一体化设计. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 50(6): 763−775 doi: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2018.06.005Gu Pan-Fei, Qi Rui-Yun, Guo Xiao-Ping. Integrated design of reentry adaptive fault-tolerant guidance and control for hypersonic vehicle. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 50(6): 763−775 doi: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2018.06.005 [4] Song H T, Zhang T. Fast robust integrated guidance and control design of interceptors. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2015, 24(1): 349−356 [5] Wang W H, Xiong S F, Wang S, Song S Y, Lai C. Three dimensional impact angle constrained integrated guidance and control for missiles with input saturation and actuator failure. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2016, 53: 169−187 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2016.03.015 [6] Chang J, Guo Z Y, Cieslak J, Chen W S. Integrated guidance and control design for the hypersonic interceptor based on adaptive incremental backstepping technique. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, 89: 318−332 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2019.03.058 [7] Xu B. Robust adaptive neural control of flexible hypersonic flight vehicle with dead-zone input nonlinearity. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2015, 80: 1509−1520 doi: 10.1007/s11071-015-1958-8 [8] Luo Y X, Song J, Zhao M F, Li W L, Wei M J. Integrated guidance and control for hypersonic vehicle with disturbance and measurement noise suppression. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(5): 7172−7184 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3412070 [9] Chong Z Y, Guo J G, Zhao B, Guo Z, Lu X D. Finite-time integrated guidance and control system for hypersonic vehicles. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2021, 43(4): 842−853 doi: 10.1177/0142331220941934 [10] 何昊, 王鹏. 高速变形飞行器制导控制一体化设计方法. 航空学报, 2024, 45(S1): 299−312He Hao, Wang Peng. Integrated design method of guidance and control for high-speed deformable aircraft. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2024, 45(S1): 299−312 [11] 赖超, 王卫红, 熊少锋. 拦截大机动目标的三维制导控制一体化设计. 宇航学报, 2017, 38(7): 714−722 doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2017.07.006Lai Chao, Wang Wei-Hong, Xiong Shao-Feng. Integrated design of three-dimensional guidance and control for intercepting highly maneuvering targets. Journal of Astronautics, 2017, 38(7): 714−722 doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2017.07.006 [12] Kim B S, Calise A J, Sattigeri R J. Adaptive, integrated guidance and control design for line-of-sight-based formation flight. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2007, 30(5): 1386−1399 doi: 10.2514/1.27758 [13] Wang Y L, Wang C C, Han Q L, Wang X F. Networked and deep reinforcement learning-based control for autonomous marine vehicles: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 55(1): 4−17 [14] Wang Y D, Sun J, He H B, Sun C Y. Deterministic policy gradient with integral compensator for robust quadrotor control. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 50(10): 3713−3725 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2018.2884725 [15] Zhu J W, Zhang H, Zhao S B, Bao W M. Multi-constrained intelligent gliding guidance via optimal control and DQN. Science China Information Sciences, 2023, 66(3): Article No. 132202 doi: 10.1007/s11432-022-3543-4 [16] Li X, Wang X G, Zhou H Y, Li Y. A novel evasion guidance for hypersonic morphing vehicle via intelligent maneuver strategy. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2024, 37(5): 441−461 doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2024.02.024 [17] Cao C Y, Li F B, Xie Q C, Liao Y X, Huang T W, Yang C H. Integrated guidance and control of morphing flight vehicle via sliding mode based robust reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2025, 55(5): 3350−3362 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2025.3540262 [18] Cao C Y, Li F B, Ding R, Huang C H, Gui W H. Intelligent attitude control for morphing flight vehicle: A deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 74(6): 8851−8865 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2025.3541606 [19] Salimans T, Ho J, Chen X, Sidor S, Sutskever I. Evolution strategies as a scalable alternative to reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1703.03864, 2017. [20] Such F P, Madhavan V, Conti E, Lehman J, Stanley K O, Clune J. Deep neuroevolution: Genetic algorithms are a competitive alternative for training deep neural networks for reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1712.06567, 2017. [21] Majid A Y, Saaybi S, Francois-Lavet V, Prasad R V, Verhoeven C. Deep reinforcement learning versus evolution strategies: A comparative survey. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 35(9): 11939−11957 [22] Schulman J, Wolski F, Dhariwal P, Radford A, Klimov O. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1707.06347, 2017. [23] Sigaud O. Combining evolution and deep reinforcement learning for policy search: A survey. ACM Transactions on Evolutionary Learning, 2023, 3(3): 1−20 [24] Khadka S, Tumer K. Evolution-guided policy gradient in reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1805.07917, 2018. [25] Marchesini E, Corsi D, Farinelli A. Genetic soft updates for policy evolution in deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Virtual Event: OpenReview.net, 2021. [26] Khadka S, Majumdar S, Nassar T, Dwiel Z, Tumer E, Miret S, et al. Collaborative evolutionary reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). California, America: PMLR, 2019. 3341−3350 [27] Pourchot A, Sigaud O. CEM-RL: Combining evolutionary and gradient-based methods for policy search. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1810.01222, 2018. [28] de Boer P T, Kroese D P, Mannor S, Rubinstein R Y. A tutorial on the cross-entropy method. Annals of Operations Research, 2005, 134: 19−67 doi: 10.1007/s10479-005-5724-z [29] 李惠峰, 肖进, 林平. 基于参数化外形的通用大气飞行器建模与分析. 宇航学报, 2011, 32(11): 2305−2311 doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2011.11.001Li Hui-Feng, Xiao Jin, Lin Ping. Modeling and analysis of general atmospheric aircraft based on parametric shape. Journal of Astronautics, 2011, 32(11): 2305−2311 doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2011.11.001 [30] 曹承钰, 李繁飙, 廖宇新, 殷泽阳, 桂卫华. 高超声速变外形飞行器建模与固定时间预设性能控制. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(3): 486−504 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230240Cao Cheng-Yu, Li Fan-Biao, Liao Yu-Xin, Yin Ze-Yang, Gui Wei-Hua. Modeling and fixed-time prescribed performance control for hypersonic morphing vehicle. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(3): 486−504 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230240 [31] 孙长银, 穆朝絮, 余瑶. 近空间高超声速飞行器控制的几个科学问题研究. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(11): 1901−1913 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01901Sun Chang-Yin, Mu Chao-Xu, Yu Yao. Some control problems for near space hypersonic vehicles. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(11): 1901−1913 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01901 [32] 张迎雪, 管萍, 戈新生. 高超声速飞行器的模糊分数阶PID控制. 航天控制, 2020, 38(6): 31−37 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3242.2020.06.006Zhang Ying-Xue, Guan Ping, Ge Xin-Sheng. Fuzzy fractional PID control of hypersonic vehicles. Aerospace Control, 2020, 38(6): 31−37 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3242.2020.06.006 [33] 黄绍洧, 都延丽, 刘燕斌, 王跃萍, 刘武. 有限时间收敛的自适应滑模协同末制导. 系统工程与电子技术, 2025, 47(3): 961−969Huang Shao-Wei, Du Yan-Li, Liu Yan-Bin, Wang Yue-Ping, Liu Wu. Adaptive sliding mode cooperative terminal guidance with finite-time convergence. Systems Engineering and Electronics Technology, 2025, 47(3): 961−969 [34] 唐建, 齐瑞云, 姜斌. 考虑约束的高超声速飞行器制导与控制一体化设计. 宇航学报, 2022, 43(5): 649−664Tang Jian, Qi Rui-Yun, Jiang-Bin. Integrated design of guidance and control for hypersonic vehicles considering constraints. Journal of Astronautics, 2022, 43(5): 649−664 [35] Bao C Y, Wang P, Tang G J. Integrated method of guidance, control and morphing for hypersonic morphing vehicle in glide phase. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2021, 34(5): 535−553 doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2020.11.009 -




 下载:
下载: