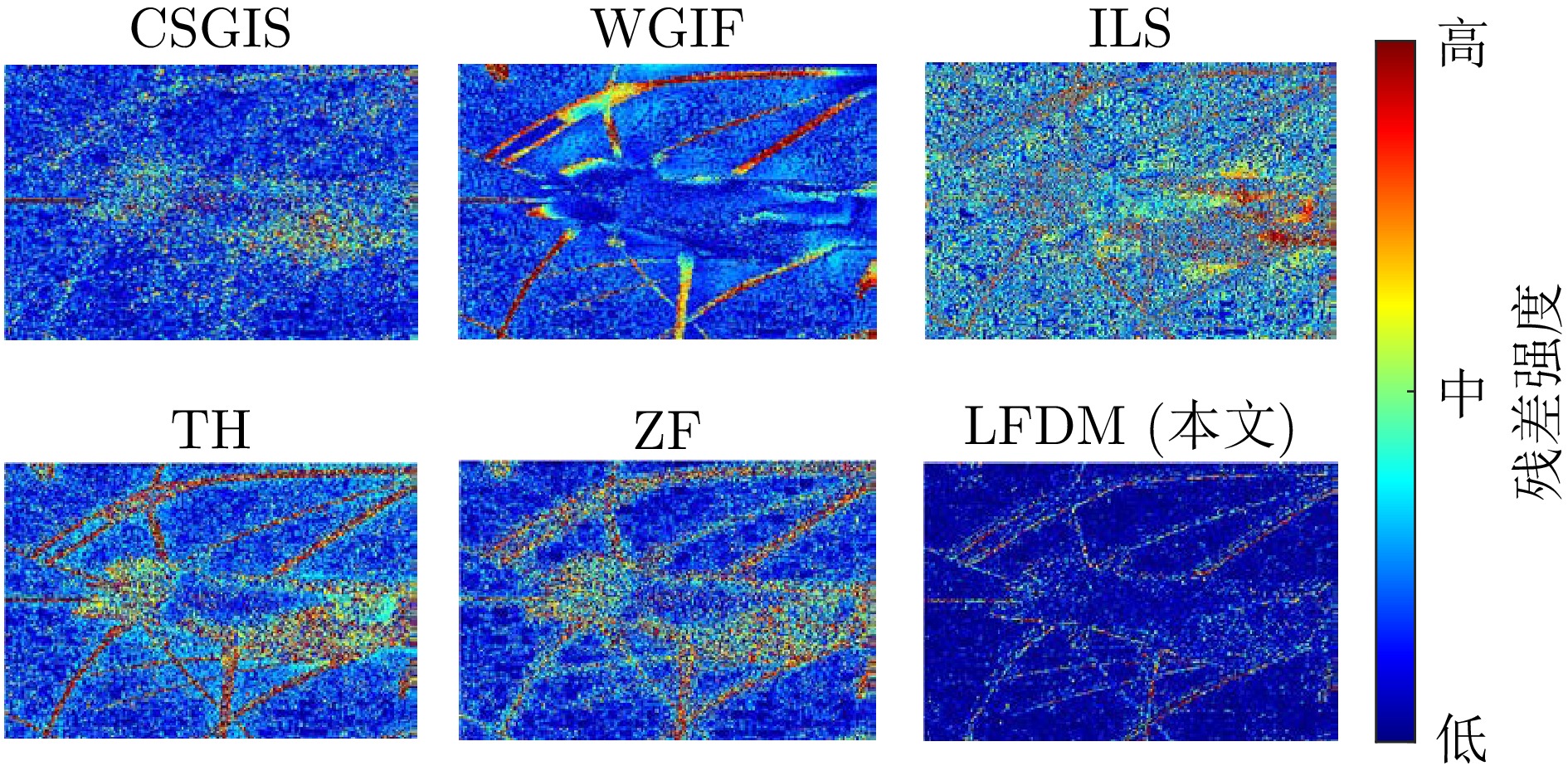
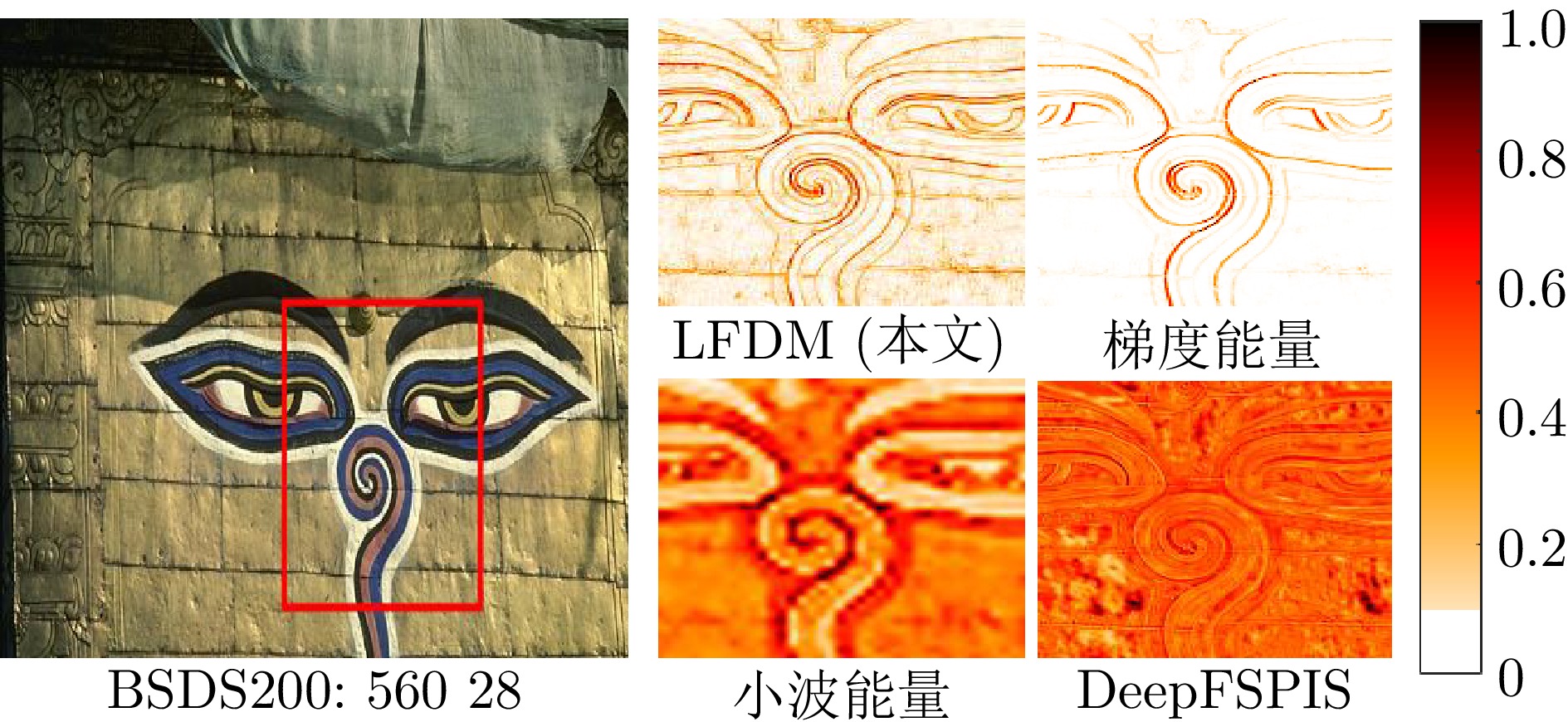
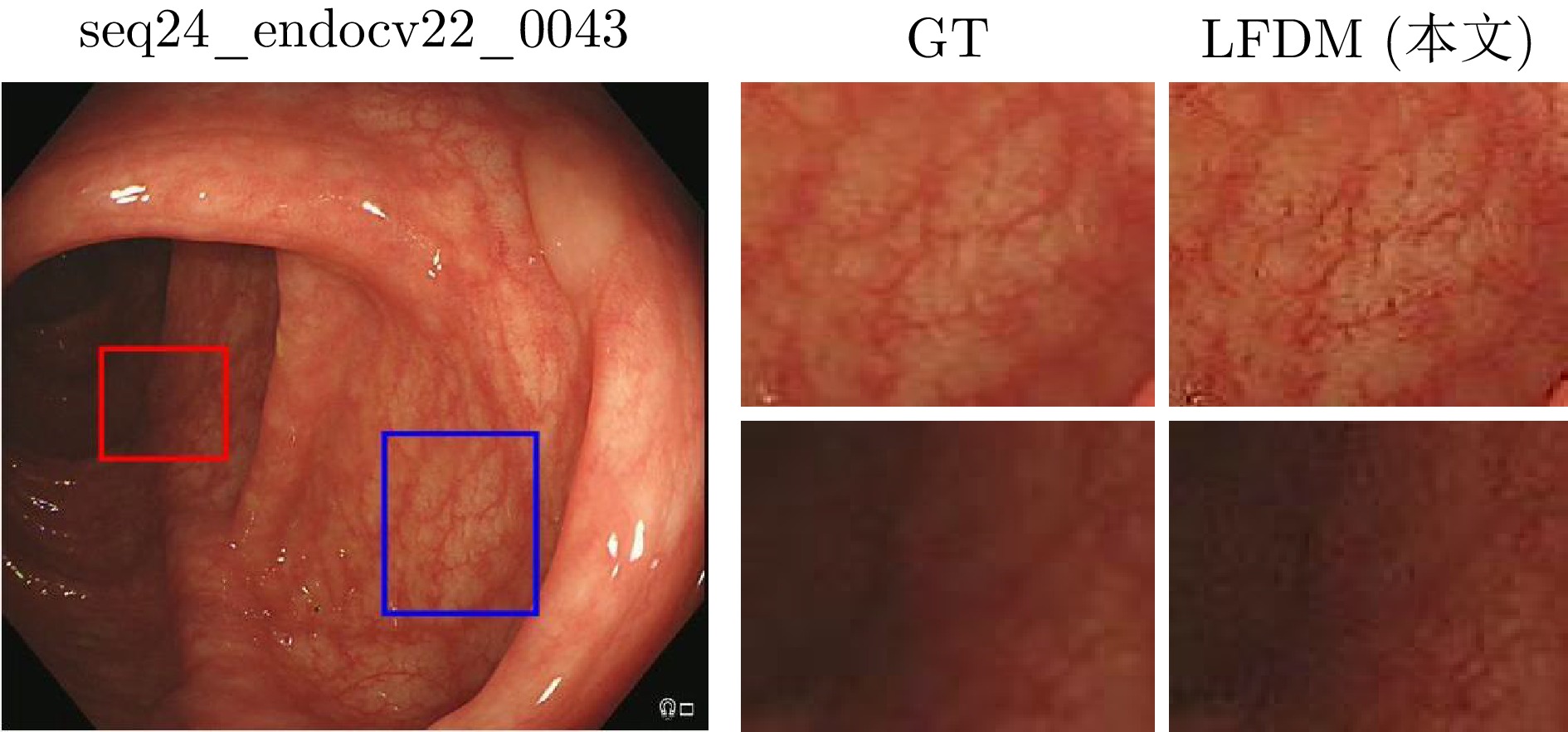
-
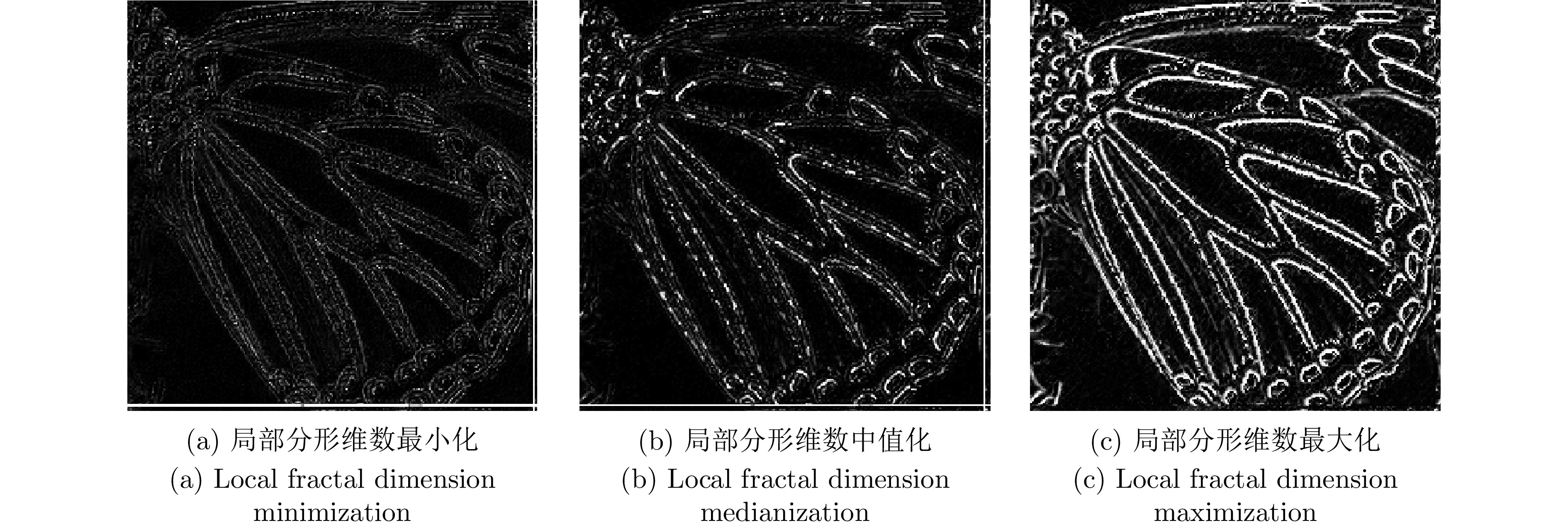
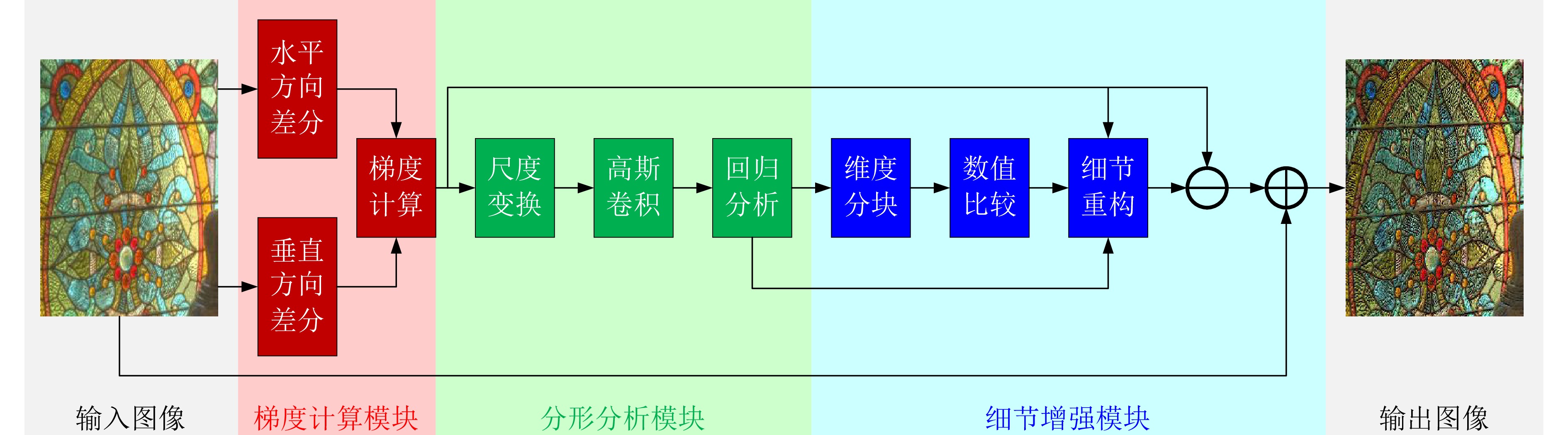
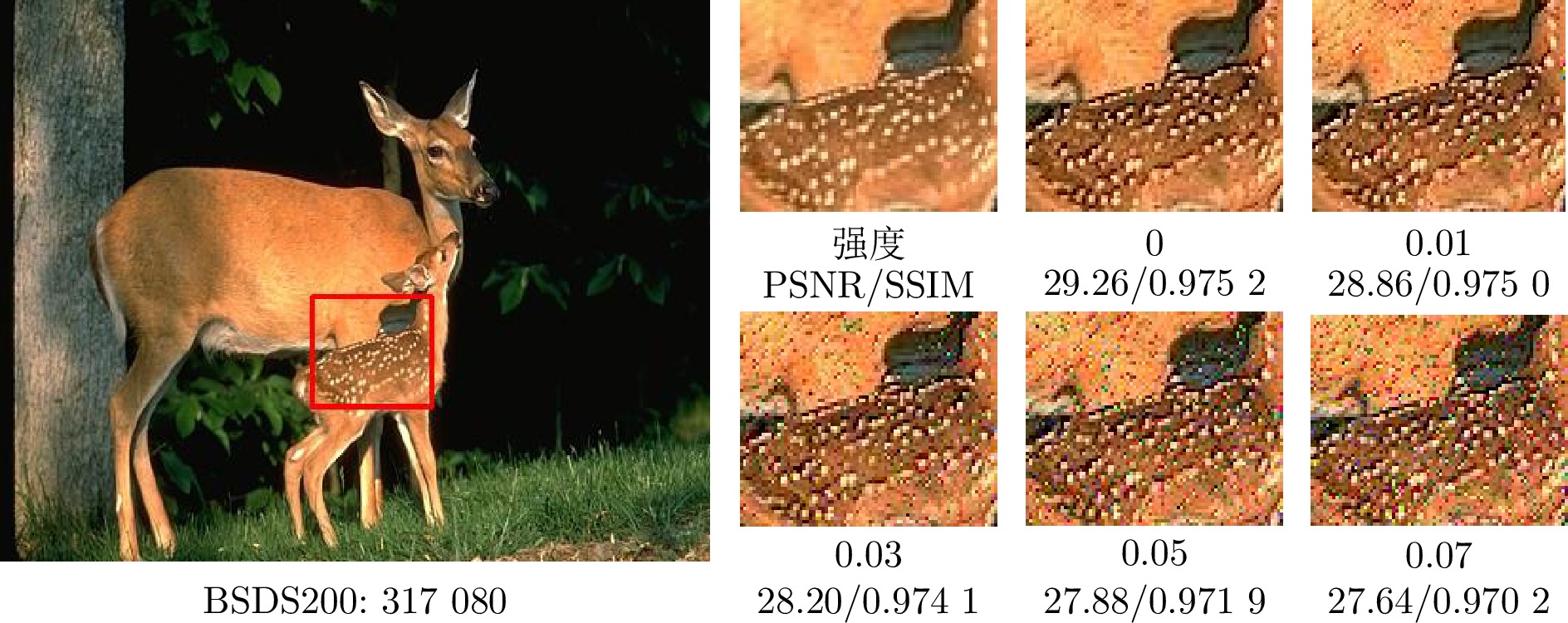
摘要: 随着人们对图像画质要求的不断提高, 各类图像细节增强技术不断涌现. 然而, 基于局部滤波器速度较快, 但其细节增强效果往往有限; 全局滤波器效果突出, 但计算开销较大; 深度学习方法高度依赖人工标注数据, 且其缺乏可解释性; 基于残差学习的策略则容易陷入局部最优, 难以充分挖掘潜在的全局最优特征. 针对上述挑战, 提出了一种基于局部分形维数最大化的图像细节增强算法. 研究发现, 图像的分形维数在一定程度上能够有效刻画图像纹理结构, 其空间分布呈现出一定规律: 边缘区域通常具有较高的分形维数, 纹理区域次之, 平坦区域则最低. 基于上述特性, 构建图像纹理特征与分形维数之间的映射关系, 并进一步探讨了分形维数与图像细节层之间的内在关联机制. 该方法在保持整体结构一致性的前提下, 通过提升局部分形维数, 实现了图像细节的有效增强, 进而为图像增强提供了一种具有理论依据的新思路. 大量实验结果表明, 该方法在主观视觉感受和客观评价指标上具有竞争力的表现. 如在BSDS200数据集上进行4倍增强因子的测试中, 所提方法在PSNR和SSIM指标上相较于当前流行方法QWLS分别提升了5.20 dB和
0.1456 , 充分展示了其在图像细节增强任务中的优势与算法良好的泛化特性.Abstract: With the increasing demand for higher image quality, various image detail enhancement techniques have continuously emerged. However, local filter–based methods, while fast, often provide only limited detail enhancement; global filter–based methods yield stronger enhancement but incur large computational costs; deep learning–based methods rely heavily on manually annotated data and lack interpretability; and residual learning–based strategies tend to fall into local optima, making it difficult to fully mine potential global-optimal features. To address these challenges, an image detail enhancement algorithm based on local fractal dimension maximization is proposed. The study finds that the fractal dimension of an image can effectively characterize its texture structure to a certain extent, and its spatial distribution exhibits a certain pattern: edge regions generally have the highest fractal dimension, textured regions follow, and smooth regions the lowest. Based on this characteristic, a mapping between image texture features and fractal dimension is established, and the intrinsic correlation mechanism between fractal dimension and image detail layers is further investigated. Under the premise of maintaining overall structural consistency, the proposed method achieves effective detail enhancement by increasing local fractal dimensions, thereby providing a theoretically grounded new approach to image enhancement. Extensive experimental results show that the method is competitive in both subjective visual perception and objective evaluation metrics. For example, in ×4 enhancement tests on the BSDS200 dataset, the proposed method improves PSNR and SSIM by 5.20 dB and0.1456 over the currently popular QWLS method, thereby demonstrating its advantages and strong generalization capability in image detail enhancement tasks.-
Key words:
- Single image detail enhancement /
- fractal dimension /
- fractal length /
- interpretability /
- image texture
-
表 1 增强因子为2和4时在基准数据集下的指标对比
Table 1 Comparison of indicators under the benchmark dataset when the enhancement factor is 2 and 4
模型 增强因子 RealSRSet[39] BSDS200[40] T91[41] PSNR(dB) SSIM PSNR(dB) SSIM PSNR(dB) SSIM WLS[16] ×2 20.16 0.8235 17.74 0.7439 18.63 0.7693 GIF[12] 24.45 0.8908 23.89 0.8344 23.82 0.8444 WGIF[13] 25.66 0.8867 27.91 0.8816 24.85 0.8517 GGIF[14] 27.35 0.9256 27.41 0.8865 26.95 0.8955 ZF[29] 20.65 0.7731 22.56 0.7966 24.09 0.9237 BFLS[42] 22.51 0.8318 23.06 0.7965 21.63 0.7659 ILS[19] 26.16 0.8761 25.09 0.8313 23.48 0.8093 DIP[43] 23.00 0.7970 23.75 0.7657 25.87 0.8232 IPRH[30] 26.30 0.9147 24.97 0.8629 28.48 0.9102 TH[44] 20.70 0.7872 21.32 0.7620 21.43 0.7616 DeepFSPIS[45] 26.13 0.8640 27.05 0.8640 25.67 0.8260 CSGIS[46] 24.50 0.8340 25.32 0.8355 25.18 0.8216 PTF[47] 18.43 0.7365 19.12 0.7116 18.76 0.6939 MGPNet[48] 20.56 0.6953 23.38 0.8430 21.18 0.7489 QWLS[20] 24.54 0.8894 26.83 0.9099 27.50 0.9153 PMN[49] 26.87 0.8377 29.53 0.8820 27.85 0.8869 ALSP[50] 19.18 0.7324 17.15 0.6285 17.58 0.6899 LLF-LUT++[51] 19.96 0.4715 20.16 0.5810 20.69 0.3256 NCC-PLM[52] 23.52 0.9290 22.86 0.9098 23.56 0.9370 LFDM(本文) 29.46 0.9687 31.59 0.9754 32.52 0.9826 WLS[16] ×4 – – – – – – GIF[12] 19.53 0.7638 18.71 0.6637 18.73 0.6862 WGIF[13] 20.87 0.7781 22.54 0.7517 19.77 0.7081 GGIF[14] 22.09 0.8294 21.90 0.7517 21.53 0.7699 ZF[29] 16.60 0.6038 18.07 0.6218 19.36 0.6081 BFLS[42] 18.70 0.6982 18.07 0.6174 16.95 0.5898 ILS[19] 21.10 0.7491 19.81 0.6636 18.49 0.6432 DIP[43] 19.69 0.6988 21.16 0.6860 22.71 0.7285 IPRH[30] 21.47 0.8039 20.14 0.7105 23.30 0.7782 TH[44] 16.72 0.6354 16.77 0.5786 16.91 0.5822 DeepFSPIS[45] 20.88 0.7220 21.59 0.7030 20.47 0.6510 CSGIS[46] 19.16 0.6651 19.82 0.6523 19.77 0.6344 PTF[47] 15.09 0.5777 15.17 0.5244 14.89 0.5080 MGPNet[48] 16.86 0.5422 19.47 0.7070 18.02 0.6018 QWLS[20] 20.27 0.7721 21.83 0.7906 22.88 0.7950 PMN[49] 21.37 0.6691 23.79 0.9095 22.27 0.7325 ALSP[50] 15.81 0.5469 14.11 0.4274 14.36 0.5076 LLF-LUT++[51] 12.37 0.2977 13.58 0.3122 13.20 0.2407 NCC-PLM[52] 24.43 0.9237 24.20 0.9100 23.46 0.9312 LFDM(本文) 25.12 0.9230 27.03 0.9362 27.81 0.9545 注: 表中加粗显示的是最优值, 下划线标记的是次优值 表 2 MOS测试前三名结果
Table 2 Top three MOS test results
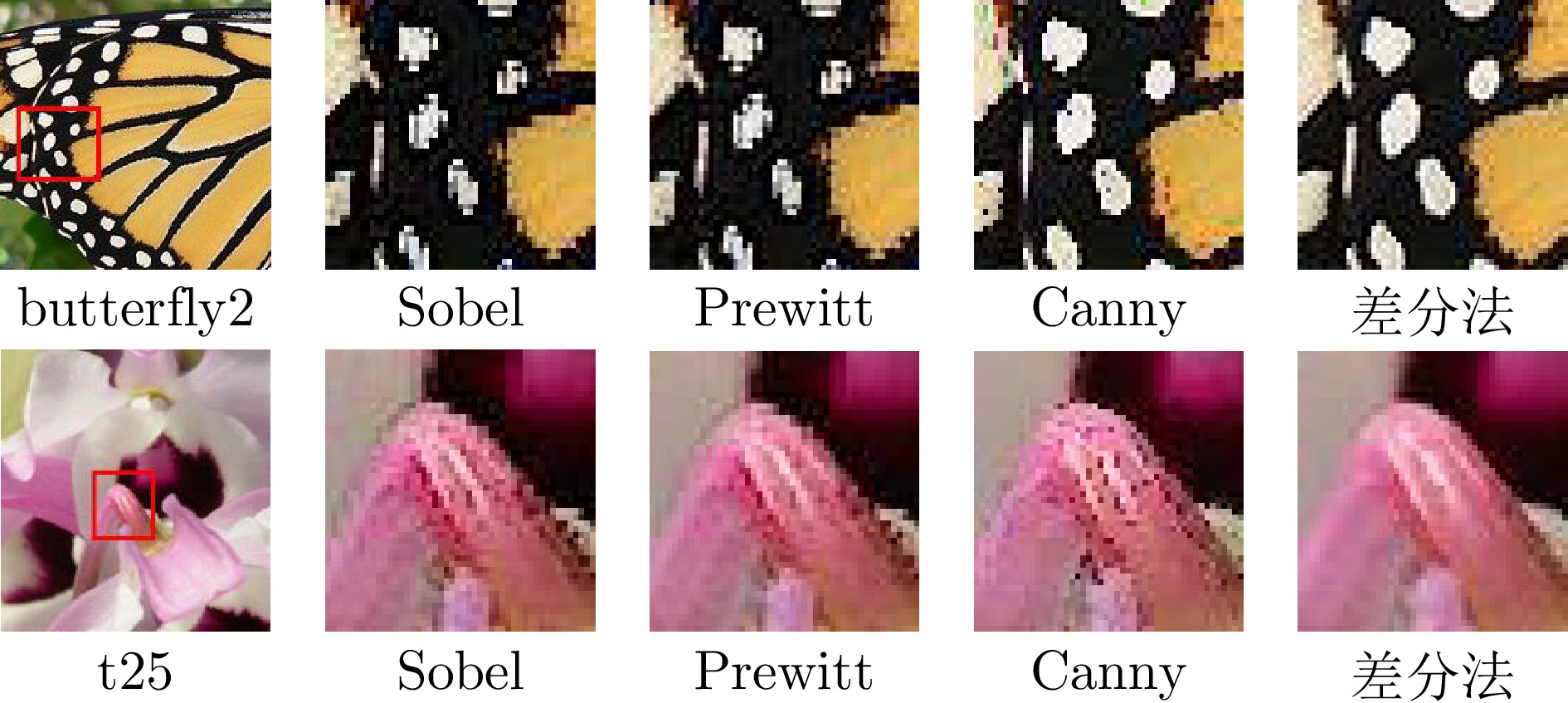
表 3 不同边缘检测算法在测试数据集上的性能比较
Table 3 Performance comparison of various edge detection algorithms on the test dataset
表 4 不同边缘检测算法在测试数据集上的性能指标比较
Table 4 Performance metrics comparison of various edge detection algorithms on the test dataset
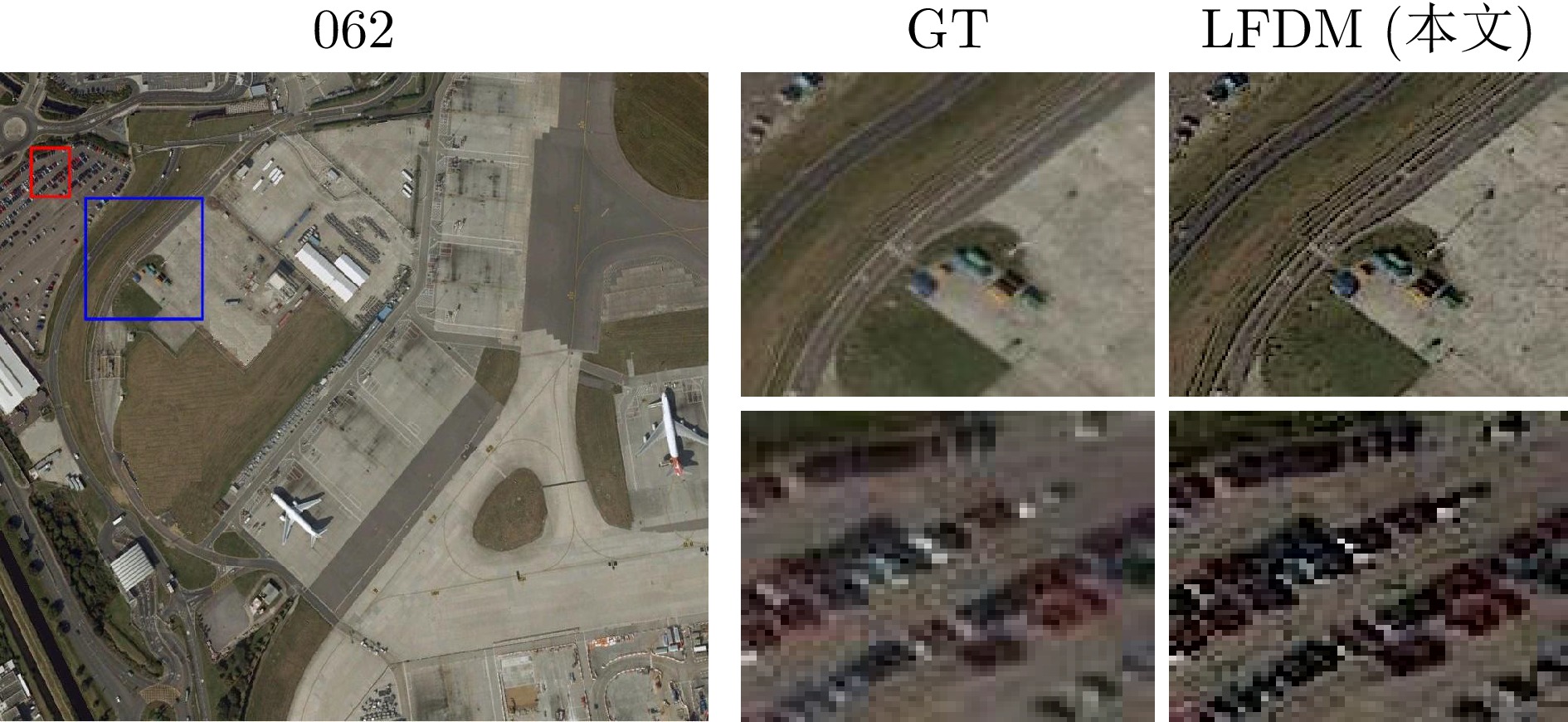
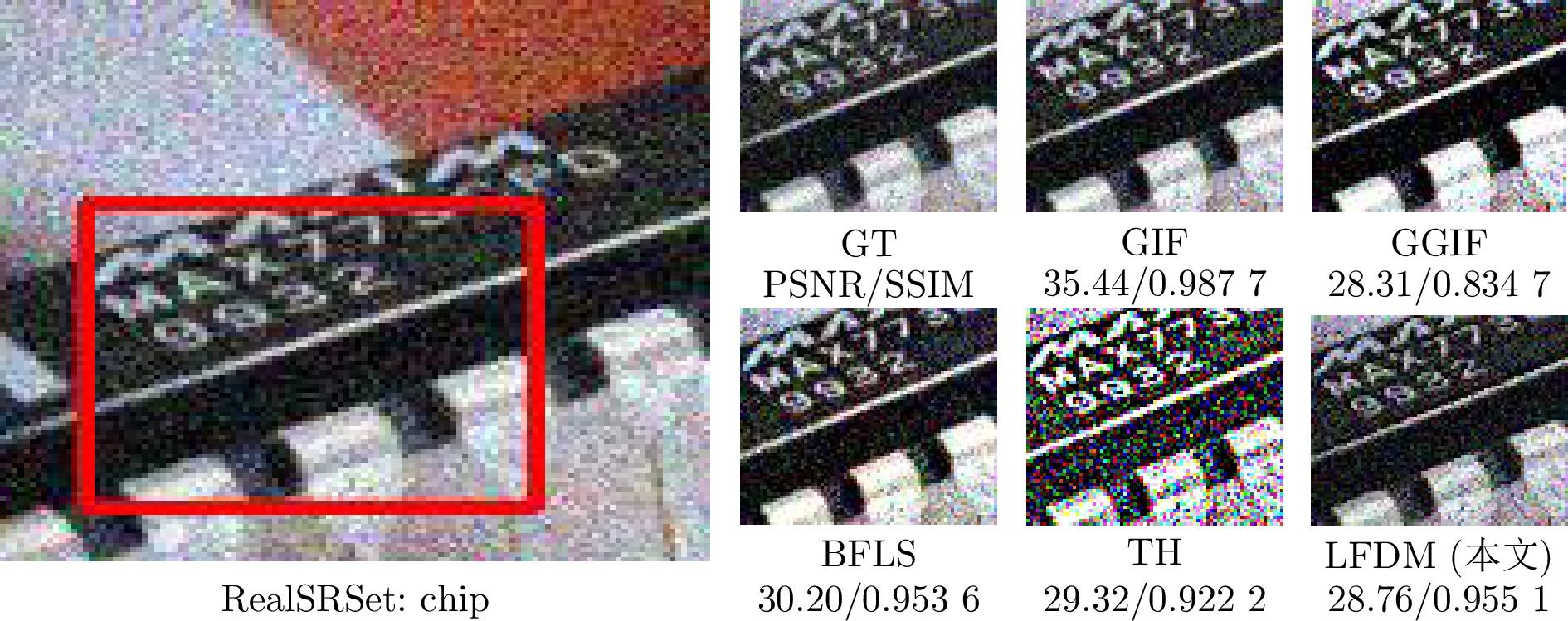
表 5 不同算法在RealSRSet[39]数据集上的平均运行速度及PSNR
Table 5 Performance comparison of different algorithms on the RealSRSet dataset in terms of average running speed and PSNR
模型 速度(s) PSNR(dB) GIF[12] 0.04 19.53 WGIF[13] 0.08 20.87 GGIF[14] 0.08 22.09 ZF[29] 0.04 16.60 BFLS[42] 0.52 18.70 ILS[19] 0.44 21.10 DIP[43] 4.01 19.69 IPRH[30] 0.03 21.47 TH[44] 0.39 16.72 DeepFSPIS[45] 0.52 20.88 CSGIS[46] 0.34 19.16 PTF[47] 7.64 15.09 MGPNet[48] 0.36 16.86 QWLS[20] 0.19 20.27 PMN[49] 0.26 21.37 ALSP[50] 0.04 15.81 LLF-LUT++[51] 0.18 12.37 NCC-PLM[52] 0.07 24.43 LFDM (本文) 1.39 25.12 -
[1] 王云涛, 赵蔺, 刘李漫, 陶文兵. 基于组–信息蒸馏残差网络的轻量级图像超分辨率重建. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(10): 2063−2078 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c211089Wang Yun-Tao, Zhao Lin, Liu Li-Man, and Tao Wen-Bing. G-idrn: a group-information distillation residual network for lightweight image super-resolution. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(10): 2063−2078 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c211089 [2] 李嫣, 任文琦, 张长青, 张金刚, 聂云峰. 基于真实退化估计与高频引导的内窥镜图像超分辨率重建. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(2): 334−347 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230070Li Yan, Ren Wen-Qi, Zhang Chang-Qing, Zhang Jin-Gang, and Nie Yun-Feng. Super-resolution of endoscopic images based on real degradation estimation and high-frequency guidance. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(2): 334−347 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230070 [3] 廖苗, 杨睿新, 赵于前, 邸拴虎, 杨振. 基于CE TransNet的腹部CT图像多器官分割. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(6): 1371−1387 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240489Liao Miao, Yang Rui-Xin, Zhao Yu-Qian, Di Shuan-Hu, and Yang Zhen. Multi-organ segmentation from abdominal ct images based on ce transnet. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(6): 1371−1387 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240489 [4] Dong S W and Lu C H. Dynamically activated de-glaring and detail-recovery for low-light image enhancement directly on smart cameras. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2024, 13(1): 222−233 [5] 何磊, 易遵辉, 谢永芳, 陈超洋, 卢明. 基于Retinex先验引导的低光照图像快速增强方法. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(5): 1035−1046 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230585He Lei, Yi Zun-Hui, Xie Yong-Fang, Chen Chao-Yang, and Lu Ming. Fast enhancement method for low light images guided by retinex prior. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(5): 1035−1046 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230585 [6] Xie H, Qian K, et al. Research on low-light image enhancement algorithm based on attention mechanism. Journal of Advanced Computing Systems, 2025, 5(5): 1−14 [7] Xu L T, Hu C H, Hu Y, Jing X Y, Cai Z Y, and Lu X B. Upt-flow: multi-scale transformer-guided normalizing flow for low-light image enhancement. Pattern Recognition, 2025, 158: 111076 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2024.111076 [8] 罗小同, 杨汶锦, 曲延云, 谢源. 基于全局局部协同的非均匀图像去雾方法. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(7): 1333−1344 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230567Luo Xiao-Tong, Yang Wen-Jin, Qu Yan-Yun, and Xie Yuan. Dehazeformer: nonhomogeneous image dehazing with collaborative global-local network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(7): 1333−1344 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230567 [9] Cui Y N, Wang Q, Li C P, Ren W Q, and Knoll A. Eenet: an effective and efficient network for single image dehazing. Pattern Recognition, 2025, 158: 111074 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2024.111074 [10] Chen J Y, Ren W Q, Zhao H H, Xia Q B, and Yang G B. You only need clear images: self-supervised single image dehazing. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2025, 27: 5800−5814 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2025.3542999 [11] Ye Z H, Cho J H, and Oh C J. Improving image de-raining using reference-guided transformers. In: Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates: IEEE, 2024. 1629-1634 [12] He K, Sun J, and Tang X. Guided image filtering. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 35(6): 1397−1409 [13] Li Z, Zheng J, Zhu Z, Yao W, and Wu S. Weighted guided image filtering. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 24(1): 120−129 [14] Kou F, Chen W, Wen C, and Li Z. Gradient domain guided image filtering. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 4528−4539 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2468183 [15] Lu Z, Long B, Li K, and Lu F. Effective guided image filtering for contrast enhancement. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(10): 1585−1589 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2867896 [16] Rudin L I, Osher S, and Fatemi E. Nonlinear total variation based noise removal algorithms. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1992, 60(1-4): 259−268 doi: 10.1016/0167-2789(92)90242-F [17] Xu L, Lu C, Xu Y, and Jia J. Image smoothing via l 0 gradient minimization. In: Proceedings of the SIGGRAPH Asia Conference 2011. Hong Kong: ACM, 2011. 1-12 [18] Li J, Han Y, Gao Y, Li Q, and Wang S. An enhance relative total variation with bf model for edge-preserving image smoothing. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2023, 33(10): 5420−5432 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2023.3255208 [19] Liu W, Zhang P, Huang X, Yang J, Shen C, and Reid I. Real-time image smoothing via iterative least squares. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2020, 39(3): 1−24 [20] Liu W, Zhang P, Qin H, Huang X, Yang J, and Ng M. Fast global image smoothing via quasi weighted least squares. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2024, 132(12): 6039−6068 doi: 10.1007/s11263-024-02105-8 [21] 陈超洋, 胡盼, 何磊, 易遵辉, 桂卫华. 基于相对总变差统计线的水下图像快速增强方法. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(8): 1−14 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240794Chen Chao-Yang, Hu Pan, He Lei, Yi Zun-Hui, and Gui Wei-Hua. Fast enhancement method for underwater images based on relative total variation statistical line. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(8): 1−14 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240794 [22] Xu L, Ren J, Yan Q, Liao R, and Jia J. Deep edge-aware filters. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille: PMLR, 2015. 1669-1678 [23] Liu S, Pan J, and Yang M H. Learning recursive filters for low-level vision via a hybrid neural network. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam: Springer, 2016. 560-576 [24] Fan Q, Yang J, Hua G, Chen B, and Wipf D. A generic deep architecture for single image reflection removal and image smoothing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice: IEEE, 2017. 3238-3247 [25] Yang Y, Tang L, Yan T, Zeng L, Shen X, and Zhan Y. Parameterized L0 image smoothing with unsupervised learning. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2024, 8(2): 1938−1951 doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2024.3359060 [26] Zhang F, Tian M, Li Z, Xu B, Lu Q, Gao C, et al. Lookup table meets local laplacian filter: pyramid reconstruction network for tone mapping. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2023, 36: 57558−57569 [27] Qi H, Tan S, and Luo X. Self-supervised dual generative networks for edge-preserving image smoothing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Seoul: IEEE, 2024. 7215-7219 [28] Kim D, Park J, Jung J, Kim T, and Paik J. Lens distortion correction and enhancement based on local self-similarity for high-quality consumer imaging systems. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2014, 60(1): 18−22 doi: 10.1109/TCE.2014.6780920 [29] Tao X, Zhou C, Shen X, Wang J, and Jia J. Zero-order reverse filtering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice: IEEE, 2017. 222-230 [30] Jiang H, Asad M, Huang X, and Yang J. Learning in-place residual homogeneity for single image detail enhancement. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2020, 29(4): 043016−043016 [31] Varma M and Garg R. Locally invariant fractal features for statistical texture classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Rio de Janeiro: IEEE, 2007. 1-8 [32] Xu Y, Ji H, and Fermüller C. Viewpoint invariant texture description using fractal analysis. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2009, 83(1): 85−100 doi: 10.1007/s11263-009-0220-6 [33] Pentland A P. Fractal-based description of natural scenes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1984, 6: 661−674 [34] Zeyde R, Elad M, and Protter M. On single image scale-up using sparse-representations. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Curves and Surfaces. Avignon: Springer, 2010. 711-730 [35] Xu Y, Ji H, and Fermuller C. A projective invariant for textures. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York: IEEE, 2006. 1932-1939 [36] Xu Y, Quan Y, Ling H, and Ji H. Dynamic texture classification using dynamic fractal analysis. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona: IEEE, 2011. 1219-1226 [37] Cannon J W. The fractal geometry of nature. by benoit b. mandelbrot. The American Mathematical Monthly, 1984, 91(9): 594−598 [38] Falconer K. Fractal Geometry: Mathematical Foundations and Applications. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2013. [39] Zhang K, Liang J, Van Gool L, and Timofte R. Designing a practical degradation model for deep blind image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Montreal: IEEE, 2021. 4791-4800 [40] Arbelaez P, Maire M, Fowlkes C, and Malik J. Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 33(5): 898−916 [41] Dong C, Loy C C, He K, and Tang X. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich: Springer, 2014. 184-199 [42] Liu W, Zhang P, Chen X, Shen C, Huang X, and Yang J. Embedding bilateral filter in least squares for efficient edge-preserving image smoothing. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2018, 30(1): 23−35 [43] Ulyanov D, Vedaldi A, and Lempitsky V. Deep image prior. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(7): 1867−1888 doi: 10.1007/s11263-020-01303-4 [44] Liu W, Zhang P, Lei Y, Huang X, Yang J, and Ng M. A generalized framework for edge-preserving and structure-preserving image smoothing. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 44(10): 6631−6648 [45] Li M, Fu Y, Li X, and Guo X. Deep flexible structure preserving image smoothing. In: Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Lisbon: ACM, 2022. 1875-1883 [46] Wang J, Wang Y, Feng Y, Gong L, Yan X, Xie H, et al. Contrastive semantic-guided image smoothing network. In: Proceedings of the Computer Graphics Forum. London: Wiley Online Library, 2022. 335-346 [47] Zhang Q, Jiang H, Nie Y, and Zheng W S. Pyramid texture filtering. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2023, 42(4): 1−11 [48] He X, Quan Y, Xu Y, and Xu R. Image smoothing via multiscale global perception. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2024, 31: 411−415 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2024.3354549 [49] Feng H, Wang L, Wang Y, Fan H, and Huang H. Learnability enhancement for low-light raw image denoising: a data perspective. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(1): 370−387 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3301502 [50] He L, Yi Z, Liu J, Chen C, Lu M, and Chen Z. Alsp+: fast scene recovery via ambient light similarity prior. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2025, 34: 4470−4484 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2025.3586514 [51] Zhang F, Deng H, Li Z, Li L, Xu B, Lu Q, et al. High-resolution photo enhancement in real-time: a laplacian pyramid network. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 20251−15 [52] Kucuk S, Severoglu N, Demir Y, and Kaplan N H. New color channel driven physical lighting model for low-light image enhancement. Digital Signal Processing, 2025, 156: 104757 doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2024.104757 [53] Li X, Zhou F, Tan H, Zhang W, and Zhao C. Multimodal medical image fusion based on joint bilateral filter and local gradient energy. Information Sciences, 2021, 569: 302−325 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.04.052 [54] Pun C M, Lee M C. Log-polar wavelet energy signatures for rotation and scale invariant texture classification. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2003, 25(5): 590−603 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2003.1195993 [55] Cheng G, Han J, Zhou P, and Guo L. Multi-class geospatial object detection and geographic image classification based on collection of part detectors. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2014, 98: 119−132 doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.10.002 [56] Garcia-Vega A, Ochoa G, and Espinosa R. Endoscopic real-synthetic over-and underexposed frames for image enhancement. Mendeley Data, 2022, 1 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 261
- HTML全文浏览量: 212
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载: