Dynamic Event-triggered Fixed-time Consensus Control for Nonlinear Multi-agent Systems
-
摘要: 研究通信拓扑固定下受有界扰动影响的非线性多智能体系统固定时间一致性问题. 针对现有事件触发控制方法存在的收敛时间依赖初值、扰动下触发可靠性低, 控制参数缺乏理论设计依据等挑战, 提出一种动态事件触发固定时间一致性控制方法. 首先, 设计融合非线性增益与双曲正切扰动补偿的固定时间控制器, 在消除抖振的同时保证收敛时间上界严格独立于系统初始状态. 其次, 构造基于动态变量自适应调节的事件触发机制, 显著降低通信频率并严格证明系统不存在Zeno行为. 进一步, 通过建立新型Lyapunov稳定性分析框架, 显式给出收敛时间上界与事件触发间隔下界. 仿真结果表明, 所提方法在保证固定时间收敛性能的同时, 有效实现通信效率的优化提升.Abstract: This paper investigates the fixed-time consensus problem for nonlinear multi-agent systems under bounded disturbances and a fixed communication topology. Addressing the challenges in existing event-triggered control methods, such as convergence time dependence on initial conditions, low triggering reliability under disturbances, and lack of theoretical basis for control parameter design, a dynamic event-triggered fixed-time consensus control method is proposed. Firstly, a fixed-time controller integrating nonlinear gain and disturbance compensation is designed, which uses hyperbolic tangent functions instead of sign functions to eliminate chattering and achieve smooth control signals, ensuring the upper bound of convergence time is strictly independent of initial states. Secondly, an event-triggering mechanism based on adaptive dynamic variables is constructed, significantly reducing communication frequency and rigorously excludes Zeno behavior. Furthermore, through the construction of a novel Lyapunov stability analysis framework, explicit expressions for the upper bound of convergence time and the lower bound of event-triggering intervals are derived. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method ensures fixed-time convergence while adaptively regulating communication through the dynamic event-triggering mechanism, significantly reducing the total number of triggering events compared to static strategies over the same period, thereby achieving co-optimization of convergence performance and communication efficiency.
-
表 1 动态事件触发固定时间一致性算法主要参数
Table 1 Main parameters of dynamic event-triggered fixed-time consensus algorithm
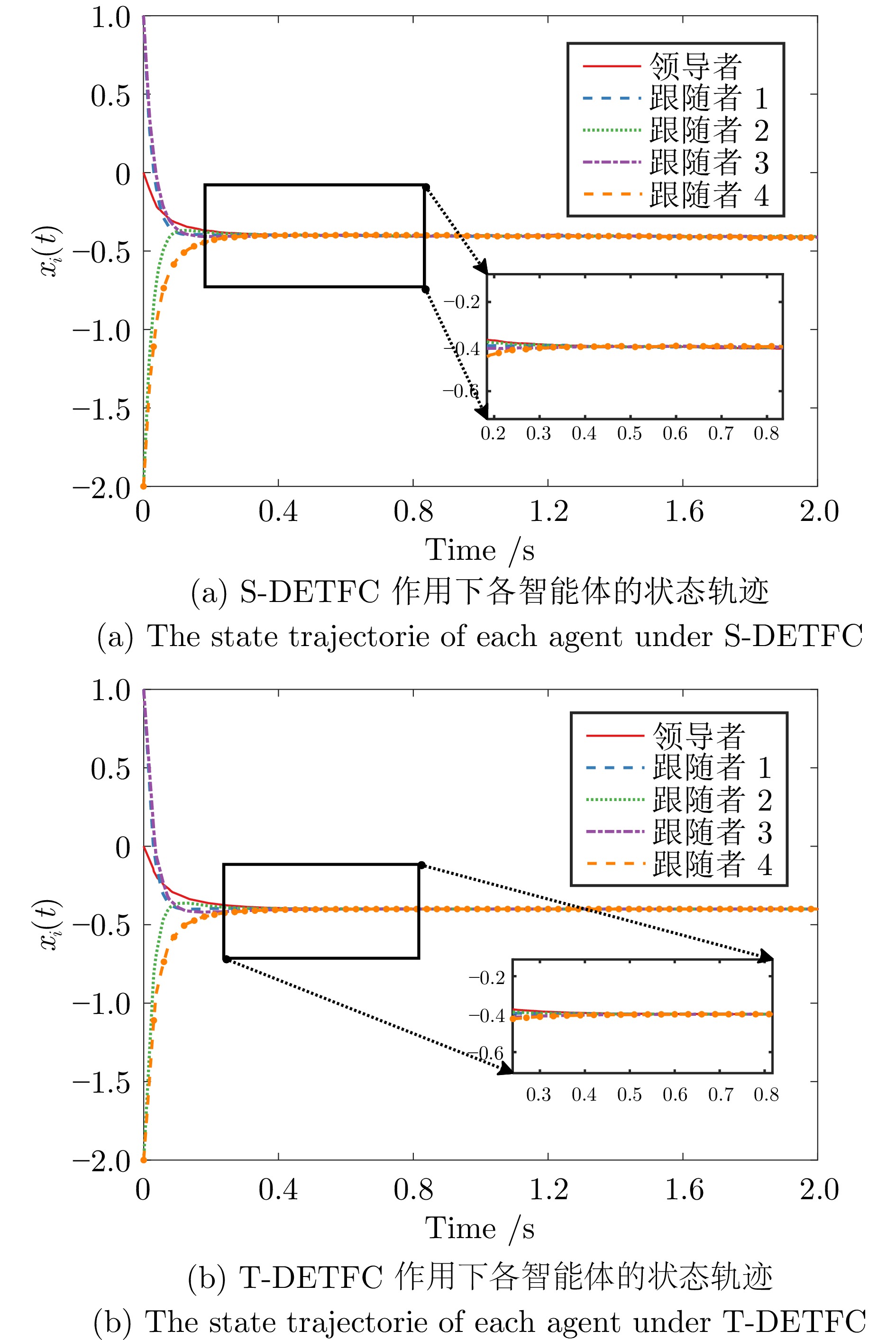
参数 值 $ \lambda $ $ 1.4 $ $ \overset\frown{u} $ $ 3.0 $ $ \rho $ $ 5.0 $ $ \sigma $ $ 3.0 $ $ \varepsilon $ $ 0.006 $ $ \delta $ $ 0.4 $ $ K $ $ 5.0 $ $ a $ $ 2.0 $ $ b $ $ 1.0 $ $ q $ $ 1.4 $ $ p $ $ 0.4 $ 表 2 不同控制策略下智能体触发次数统计
Table 2 Trigger count statistic for agents under different control strategies
控制策略 跟随者1 跟随者2 跟随者3 跟随者4 总数 S-DETFC 231 529 509 496 1765 T-DETFC 63 74 67 57 261 SETFC 566 556 553 577 2252 表 3 不同控制策略下智能体触发间隔统计
Table 3 Trigger interval statistics for agents under different control strategies (s)
控制策略 跟随者1 跟随者2 跟随者3 跟随者4 均值 S-DETFC 0.0206 0.0168 0.0182 0.0198 0.0188 T-DETFC 0.0477 0.0525 0.0636 0.0641 0.0569 SETFC 0.0059 0.0050 0.0060 0.0049 0.0054 -
[1] Wei H, Hu B B, Wang Y, Lv C. Scalable and constrained consensus in multiagent systems: distributed model predictive control-based approaches. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(4): 5969−5978 doi: 10.1109/TII.2023.3342364 [2] Khalid M. Smart grids and renewable energy systems: perspectives and grid integration challenges. Energy Strategy Reviews, 2024, 51: 101299 doi: 10.1016/j.esr.2024.101299 [3] Farooq A, Xiang Z, Chang W J, Aslam M S. Recent advancement in formation control of multi-agent systems: a review. Computers, Materials & Continua, 2025, 83(3): 3623−3674 [4] Doostmohammadian M, et al. Survey of distributed algorithms for resource allocation over multi-agent systems. Annual Reviews in Control, 2025, 59: 100983 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2024.100983 [5] Olfati-Saber R, Fax J A, Murray R M. Consensus and cooperation in networked multi-agent systems. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2007, 95(1): 215−233 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2006.887293 [6] Zhang M, Yang W, Sun W, Yu D, Chen C L P. Nonsingular practical fixed-time adaptive fuzzy consensus control of nonstrict-feedback nonlinear multiagent systems with actuator fault. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2025, 55(4): 2834−2845 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2025.3526980 [7] Li J R, Li S, Liu Y J, Liu L, Li D P, Wang H. Adaptive dynamic event-triggered control strategy for nonlinear multi-agent systems. In: Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Unmanned Systems. Nanjing, China: IEEE, 2024. 1790-1795. [8] Pedroso L, Batista P, Heemels W M. Distributed design of ultra large-scale control systems: progress, challenges, and prospects. Annual Reviews in Control, 2025, 59: 100987 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2025.100987 [9] Wang G L, Li Y Q. Distributed finite-time consensus control of multi-agent systems with communication topology switching. In: Proceedings of the 2024 6th International Conference on Industrial Artificial Intelligence. Shenyang, China: IEEE, 2024. 1-6. [10] Sun Y, Ji Z, Shi Y, Liu Y. Event-based finite time stabilizability and formation control of multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025, 22: 7887−7896 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2024.3473972 [11] Zuo Z, Tang J, Ke R, Han Q L. Hyperbolic tangent function-based protocols for global/semi-global finite-time consensus of multi-agent systems. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2024, 11(6): 1381−1397 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2024.124485 [12] Ma C, Dong D. Finite-time prescribed performance time-varying formation control for second-order multi-agent systems with non-strict feedback based on a neural network observer. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2024, 11(4): 1039−1050 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123615 [13] Long S, Huang W, Wang J, Liu J, Gu Y, Wang Z. A fixed-time consensus control with prescribed performance for multi-agent systems under full-state constraints. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025, 22: 6398−6407 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2024.3445135 [14] Fang X, Wen G H. Distributed optimal coordination of multi-agent systems with coupled objective functions: a fixed-time estimation-based approach. Automatica, 2025, 175: 112213 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2025.112213 [15] Luo S, Xu G. Fixed-time consensus control for general linear multi-agent systems. In: Proceedings of the 2024 36th Chinese Control and Decision Conference. Xi'an, China: IEEE, 2024. 2981-2985. [16] Firouzbahrami M, Nobakhti A. Cooperative fixed-time/finite-time distributed robust optimization of multi-agent systems. Automatica, 2022, 142: 110358 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2022.110358 [17] Yang Y, Xin B, Dou L, Gan M. Event-triggered fixed-time sliding mode control for leader-follower consensus of nonlinear multi-agent systems. In: Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 18th International Conference on Control & Automation. Reykjavik, Iceland: IEEE, 2024. 319-325. [18] Kalyva D, Psillakis H E. Distributed control of a mobile robot multi-agent system for Nash equilibrium seeking with sampled neighbor information. Automatica, 2024, 166: 111712 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2024.111712 [19] Wang Y, Zong G, Zhao X, et al. Adaptive practical fixed-time synchronized tracking control of ASV with prescribed performance. Automatica, 2024, 166: 111716 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2024.111716 [20] Zuo Z, Ke R, Han Q L. Fully distributed adaptive practical fixed-time consensus protocols for multi-agent systems. Automatica, 2023, 157: 111248 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2023.111248 [21] Qin D, Ong C, Liu A, Zhang W A, Yu L. Event-triggered distributed predictive control for multi-agent systems with stability constraints. Automatica, 2025, 178: 112358 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2025.112358 [22] Yue S, Xu N, Zhang L, Zhao N. Observer-based event-triggered adaptive fuzzy hierarchical sliding mode fault-tolerant control for uncertain under-actuated nonlinear systems. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 20241−18 [23] Xiang K, Yu Z, Jiang H. Fixed-time bipartite output consensus of heterogeneous multi-agent systems with event-triggered observation. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 31188−31198 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3262284 [24] Zheng W, Dong Y, Wang H. Dynamic event-triggered fixed-time consensus control of multi-agent systems with unknown bounded disturbances. International Journal of Control, 2023, 97(5): 1037−1048 [25] 陈世明, 邵赛, 江青龙. 基于事件触发控制的二阶多智能体系统固定时间比例一致性. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 261−270 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190128Chen S M, Shao S, Jiang G L. Fixed-time proportional consensus of second-order multi-agent systems via event-triggered control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 261−270 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190128 [26] Ma X L, Tan Y B, Mei H. Predefined-time consensus of nonlinear multi-agent input delay/dynamic event-triggered under switching topology. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 29883−29895 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3258547 [27] Kim H J, Yoo S J. Adaptive fixed-time containment control of MIMO nonlinear multiagent systems via dynamic event-triggered communication. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2024, 112: 11127−11145 doi: 10.1007/s11071-024-09621-9 [28] Wang J H, Wang C, Chen K R, Chen Z T. Distributed fixed-time event-triggered consensus control for uncertain nonlinear multiagent systems with actuator failures. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2023, 2023: 8818233 doi: 10.1155/2023/8818233 [29] Chen X, Dong J, Wang Y, Zhou G. A new event-triggered distributed fixed-time consensus strategy for multi-agent systems with nonlinear dynamics and uncertain disturbances. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 30416−30426 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3368806 [30] Chai J, Lu Q, Tao X, Peng D, Zhang B. Dynamic event-triggered fixed-time consensus control and its applications to magnetic map construction. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2023, 10(10): 2000−2013 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123444 [31] Hao Y, Liu L. A new event-triggered internal model-based observer method for cooperative robust output regulation. Automatica, 2025, 177: 112293 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2025.112293 [32] Mao S, Mishra Y, Tian Y C, Perc M, Tang Y. Distributed online optimization with edge-based event-triggered communication. Automatica, 2025, 173: 112068 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2024.112068 [33] Hung N T, Pascoal A M. Consensus/synchronisation of networked nonlinear multiple agent systems with event-triggered communications. International Journal of Control, 2022, 95(5): 1305−1314 doi: 10.1080/00207179.2020.1849806 [34] Zhao X W, Wang J Y, Lai Q, et al. Team-based fixed-time containment control for multi-agent systems with disturbances. Chinese Physics B, 2023, 32(12): 311−323 [35] Yang P, Li W, Xuan Y. Fixed-time group consensus control of multi-agent systems with actuator faults based on dynamic event triggering. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 22892−22903 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3364763 [36] Zhou D, Zhang A, Yang P. Fixed-time event-triggered consensus of second-order multi-agent systems with fully continuous communication free. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2020, 14(16): 2385−2394 doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2020.0401 [37] Du H, Wen G, Wu D, Cheng Y, Lu J. Distributed fixed-time consensus for nonlinear heterogeneous multi-agent systems. Automatica, 2020, 113: 108797 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.108797 [38] 陈世明, 邵赛. 基于事件触发非线性多智能体系统的固定时间一致性. 控制理论与应用, 2019, 36(10): 1606−1614 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.80742Chen S M, Shao S. Fixed-time consensus of nonlinear multi-agent systems based on event-triggered. Control Theory & Applications, 2019, 36(10): 1606−1614 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2019.80742 [39] 陈世明, 叶舒康, 马旭阳, 邹钰彬, 刘江. 不确定多智能体系统的事件触发自适应一致性控制. 控制理论与应用, 2025, 42(1): 33−40Chen S M, Ye S K, Ma X Y, Zou Y B, Liu J. Event-triggered adaptive consensus control for uncertain multi-agent systems. Control Theory & Applications, 2025, 42(1): 33−40 [40] 孙梦薇, 任璐, 刘剑, 孙长银. 切换拓扑下多智能体系统的动态事件触发固定时间一致性控制. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(6): 1295−1305Sun M W, Ren L, Liu J, Sun C Y. Dynamic event-triggered fixed-time consensus control of multi-agent systems under switching topologies. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(6): 1295−1305 [41] Farooq A, Xiang Z, Chang W J, Aslam M S. Recent advancement in formation control of multi-agent systems: a review. Computers, Materials & Continua, 2025, 83(3): 3623−3674 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 300
- HTML全文浏览量: 301
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载: