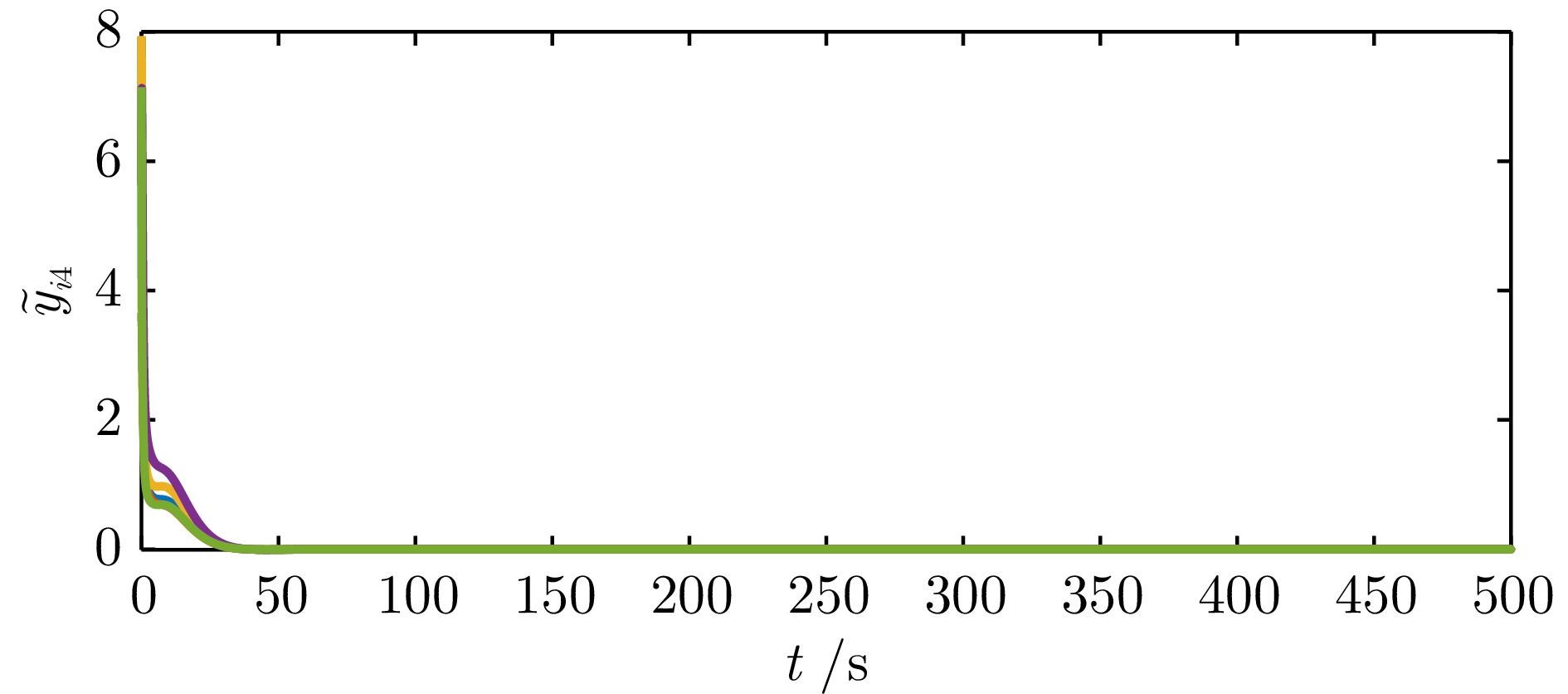
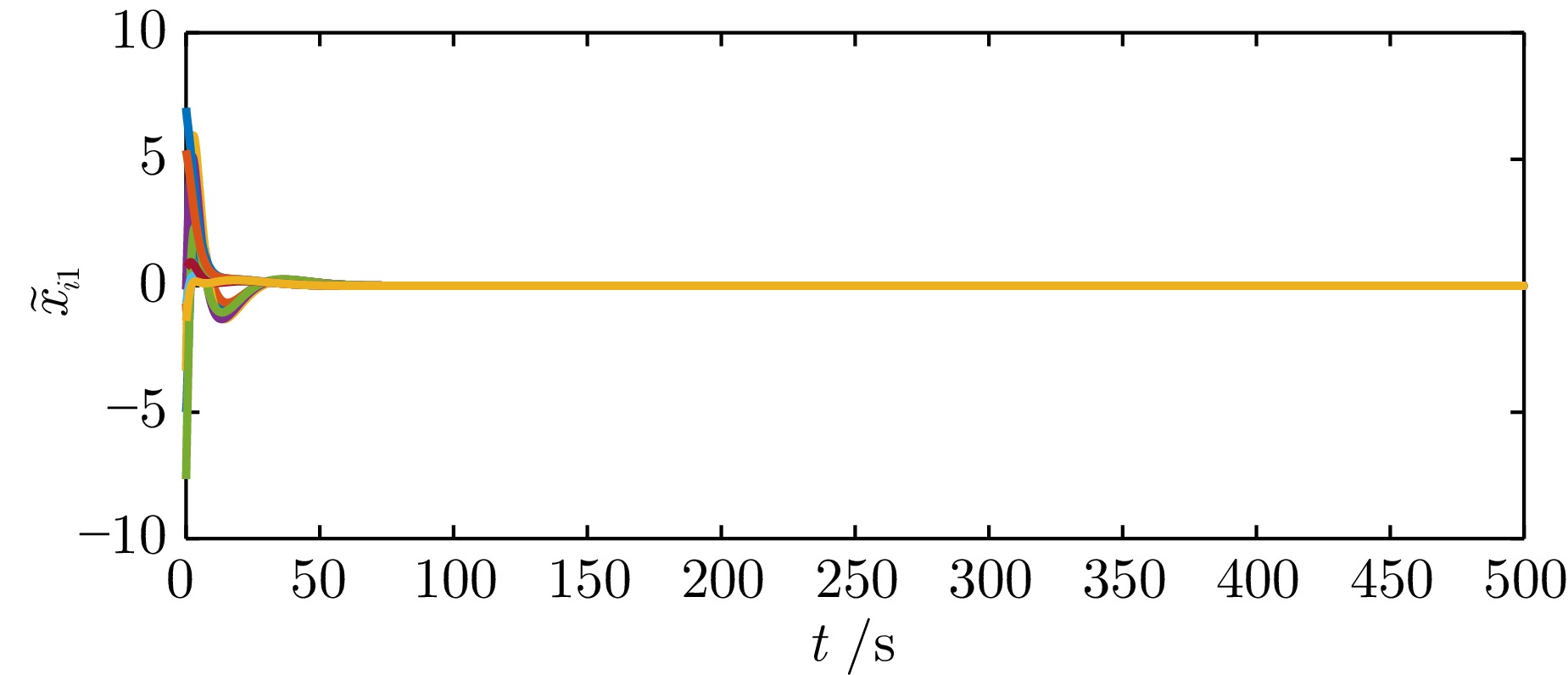
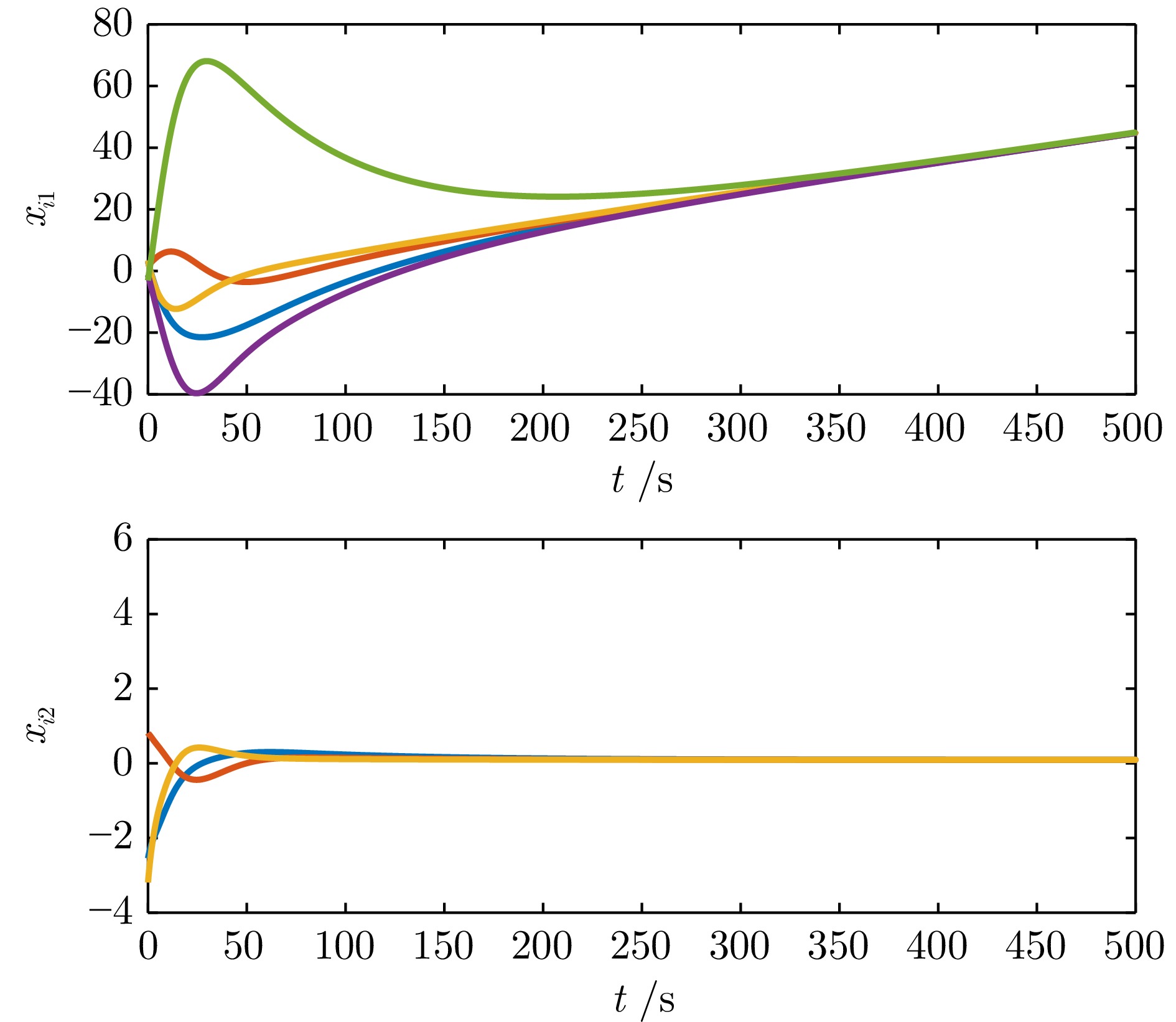
|
[1]
|
孙健, 邓方, 陈杰. 陆用运动体控制系统发展现状与趋势. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(11): 1985−1999Sun Jian, Deng Fang, Chen Jie. Control system of ground-based moving platforms: State of the art and future trends. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(11): 1985−1999
|
|
[2]
|
罗彪, 胡天萌, 周育豪, 黄廷文, 阳春华, 桂卫华. 多智能体强化学习控制与决策研究综述. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(3): 510−539Luo Biao, Hu Tian-Meng, Zhou Yu-Hao, Huang Ting-Wen, Yang Chun-Hua, Gui Wei-Hua. Survey on multi-agent reinforcement learning for control and decision-making. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(3): 510−539
|
|
[3]
|
Dorigo M, Theraulaz G, Trianni V. Swarm robotics: Past, present, and future. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2021, 109(7): 1152−1165 doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2021.3072740
|
|
[4]
|
Olfati-Saber R, Murray R M. Consensus problems in networks of agents with switching topology and time-delays. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2004, 49(9): 1520−1533 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2004.834113
|
|
[5]
|
Ren W, Beard R W. Consensus seeking in multiagent systems under dynamically changing interaction topologies. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2005, 50(5): 655−661 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2005.846556
|
|
[6]
|
Ren W, Sorensen N. Distributed coordination architecture for multi-robot formation control. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2008, 56(4): 324−333 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2007.08.005
|
|
[7]
|
Chung S J, Ahsun U, Slotine J J E. Application of synchronization to formation flying spacecraft: Lagrangian approach. Journal of Guidance, Control and Dynamics, 2009, 32(2): 512−526 doi: 10.2514/1.37261
|
|
[8]
|
Olfati-Saber R. Flocking for multi-agent dynamic systems: Algorithms and theory. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2006, 51(3): 401−420 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2005.864190
|
|
[9]
|
Zhang H T, Zhai C, Chen Z Y. A general alignment repulsion algorithm for flocking of multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2011, 56(2): 430−435 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2010.2089652
|
|
[10]
|
Li W, Cassandras C G. Distributed cooperative coverage control of sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Seville, Spain: IEEE, 2005. 2542−2547
|
|
[11]
|
Ren W. On consensus algorithms for double-integrator dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2008, 53(6): 1503−1509 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2008.924961
|
|
[12]
|
Seo J H, Shim H, Back J. Consensus of high-order linear systems using dynamic output feedback compensator: Low gain approach. Automatica, 2009, 45(11): 2659−2664 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.07.022
|
|
[13]
|
Li Z K, Duan Z S, Chen G R, Huang L. Consensus of multiagent systems and synchronization of complex networks: A unified viewpoint. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2010, 57(1): 213−224 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2009.2023937
|
|
[14]
|
Wen G H, Zhao Y, Duan Z S, Yu W W, Chen G R. Containment of higher-order multi-leader multi-agent systems: A dynamic output approach. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2016, 61(4): 1135−1140 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2465071
|
|
[15]
|
Movric K H, Lewis F L. Cooperative optimal control for multi-agent systems on directed graph topologies. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2014, 59(3): 769−774 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2013.2275670
|
|
[16]
|
Sarlette A, Sepulchre R, Leonard N E. Autonomous rigid body attitude synchronization. Automatica, 2009, 45(2): 572−577 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2008.09.020
|
|
[17]
|
Mei J, Ren W, Ma G F. Distributed coordinated tracking with a dynamic leader for multiple Euler-Lagrange systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2011, 56(6): 1415−1421 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2011.2109437
|
|
[18]
|
Ding Z T. Consensus control of a class of Lipschitz nonlinear systems. International Journal of Control, 2014, 87(11): 2372−2382
|
|
[19]
|
Zhang F, Trentelman H L, Scherpen J M A. Fully distributed robust synchronization of networked Lur'e systems with incremental nonlinearities. Automatica, 2014, 50(10): 2515−2526 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.08.033
|
|
[20]
|
Hu J P, Zheng W X. Adaptive tracking control of leader-follower systems with unknown dynamics and partial measurements. Automatica, 2014, 50(5): 1416−1423 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.02.037
|
|
[21]
|
Ghosh S, Lee J W. Optimal distributed finite-time consensus on unknown undirected graphs. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2015, 2(4): 323−334 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2015.2426751
|
|
[22]
|
Dominguez-Garcia A D, Hadjicostis C N. Distributed matrix scaling and application to average consensus in directed graphs. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2013, 58(3): 667−681 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2012.2219953
|
|
[23]
|
Hadjicostis C N, Charalambous T. Average consensus in the presence of delays in directed graph topologies. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2014, 59(3): 763−768 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2013.2275669
|
|
[24]
|
Saboori I, Khorasani K. ${H_{\infty}}$ consensus achievement of multi-agent systems with directed and switching topology networks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2014, 59(11): 3104−3109 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2014.2358071
|
|
[25]
|
Psillakis H E. Consensus in networks of agents with unknown high-frequency gain signs and switching topology. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(8): 3993−3998 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2016.2616645
|
|
[26]
|
Lv Y Z, Li Z K, Duan Z S, Chen J. Distributed adaptive output feedback consensus protocols for linear systems on directed graphs with a leader of bounded input. Automatica, 2016, 74: 308−314 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.07.041
|
|
[27]
|
Li Z K, Ren W, Liu X D, Xie L H. Distributed consensus of linear multi-agent systems with adaptive dynamic protocols. Automatica, 2013, 49(7): 1986−1995 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2013.03.015
|
|
[28]
|
Li Z K, Wen G H, Duan Z S, Ren W. Designing fully distributed consensus protocols for linear multi-agent systems with directed graphs. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(4): 1152−1157 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2014.2350391
|
|
[29]
|
Lv Y Z, Li Z K, Duan Z S, Feng G. Novel distributed robust adaptive consensus protocols for linear multi-agent systems with directed graphs and external disturbances. International Journal of Control, 2017, 90(2): 137−147 doi: 10.1080/00207179.2016.1172259
|
|
[30]
|
Lv Y Z, Fu J J, Wen G H, Huang T W, Yu X H. On consensus of multiagent systems with input saturation: Fully distributed adaptive antiwindup protocol design approach. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2020, 7(3): 1127−1139 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2020.2964146
|
|
[31]
|
Lv Y Z, Fu J J, Wen G H, Huang T W, Yu X H. Fully distributed anti-windup consensus protocols for linear MASs with input saturation: The case with directed topology. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(5): 2359−2371 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2977554
|
|
[32]
|
Lv Y Z, Fu J J, Wen G H, Huang T W, Yu X H. Distributed adaptive observer-based control for output consensus of heterogeneous MASs with input saturation constraint. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2020, 67(3): 995−1007 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2019.2955163
|
|
[33]
|
Cheng B, Li Z K. Fully distributed event-triggered protocols for linear multiagent networks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(4): 1655−1662 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2857723
|
|
[34]
|
Cheng B, Li Z K. Coordinated tracking control with asynchronous edge-based event-triggered communications. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(10): 4321−4328 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2895927
|
|
[35]
|
Cheng B, Lv Y Z, Li Z K, Duan Z S. Discrete communication and control updating in adaptive dynamic event-triggered consensus. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(1): 347−354 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3260681
|
|
[36]
|
Dimarogonas D V, Frazzoli E, Johansson K H. Distributed event-triggered control for multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(5): 1291−1297 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2011.2174666
|
|
[37]
|
Qian J C, Duan P H, Duan Z S. Fully distributed filtering with a stochastic event-triggered mechanism. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2022, 9(2): 753−762 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2021.3124257
|
|
[38]
|
Yi X L, Liu K, Dimarogonas D V, Johansson K H. Dynamic event-triggered and self-triggered control for multi-agent systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(8): 3300−3307 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2874703
|
|
[39]
|
de Persis C, Tesi P. Formulas for data-driven control: Stabilization, optimality, and robustness. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2020, 65(3): 909−924 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2959924
|
|
[40]
|
Liu W J, Sun J, Wang G, Bullo F, Chen J. Data-driven resilient predictive control under denial-of-service. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(8): 4722−4737 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2022.3209399
|
|
[41]
|
Liu W J, Sun J, Wang G, Bullo F, Chen J. Data-driven self-triggered control via trajectory prediction. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(11): 6951−6958 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3244116
|
|
[42]
|
Li Y F, Wang X, Sun J, Wang G, Chen J. Self-triggered consensus control of multiagent systems from data. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(7): 4702−4709 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2024.3351865
|
|
[43]
|
Duan P H, Liu T, Xing Y, Johansson K H. Robust data-driven Kalman filtering for unknown linear systems using maximum likelihood optimization. Automatica, 2025, 180: Article No. 112474 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2025.112474
|
|
[44]
|
Duan P H, Liu T, Lv Y Z, Wen G H. Cooperative control of multichannel linear systems with self-organizing private agents. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2024, 11(4): 1937−1948 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2024.3371549
|
|
[45]
|
Duan P H, Lv Y Z, Wen G H, Ogorzalek M. A framework on fully distributed state estimation and cooperative stabilization of LTI plants. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(10): 6746−6761 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2024.3376791
|
|
[46]
|
Rego F C, Pu Y, Alessandretti A, Aguiar A P, Pascoal A M, Jones C N. A distributed Luenberger observer for linear state feedback systems with quantized and rate-limited communications. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(9): 3922−3937 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.3027658
|
|
[47]
|
Duan P H, Duan Z S, Lv Y Z, Chen G R. Distributed finite-horizon extended Kalman filtering for uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(2): 512−520 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2919919
|
|
[48]
|
Slotine J J E, Li W. Applied Nonlinear Control. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall, 1991.
|
|
[49]
|
Zhou J, Shang J, Chen T W. Cybersecurity landscape on remote state estimation: A comprehensive review. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2014, 11(4): 851−865
|
|
[50]
|
Zhao D, Lv Y Z, Yu X H, Wen G H, Chen G R. Resilient consensus of higher order multiagent networks: An attack isolation-based approach. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2022, 67(2): 1001−1007 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2021.3075327
|
|
[51]
|
Zhao D, Lv Y Z, Wen G H, Gao Z W. Resilient consensus of high-order networks against collusive attacks. Automatica, 2023, 151: Article No. 110934 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2023.110934
|
|
[52]
|
Zhao D, Lv Y Z, Zhou J L, Wen G H, Huang T W. Attack-isolation-based resilient control of large-scale systems against collusive attacks. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2022, 9(4): 2857−2869 doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2022.3171219
|
|
[53]
|
Zhao D, Ho D W C, Wen G H. Generalized graph-dependent isolation of collusive attacks for interconnected systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2025, 70(4): 2274−2288 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2024.3474055
|
|
[54]
|
Wen G H, Lv Y Z, Zheng W X, Zhou J L, Fu J J. Joint robustness of time-varying networks and its applications to resilient consensus. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(11): 6466−6480 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3237493
|
|
[55]
|
Tang Y Y, Lv Y Z, Zhou J L, Ogorzalek M. Resilient consensus in open multi-agent systems. IEEE Control Systems Letters, 2025, 9: 1261−1266 doi: 10.1109/LCSYS.2025.3580518
|
|
[56]
|
Zhou J L, Lv Y Z, Wen G H, Yu X H. Resilient consensus of multiagent systems under malicious attacks: Appointed-time observer-based approach. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(10): 10187−10199 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3058094
|
|
[57]
|
Lv Y Z, Wen G H, Huang T W. Adaptive protocol design for distributed tracking with relative output information: A distributed fixed-time observer approach. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2020, 7(1): 118−128 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2019.2919855
|
|
[58]
|
Lv Y Z, Wen G H, Huang T W, Duan Z S. Adaptive attack-free protocol for consensus tracking with pure relative output information. Automatica, 2020, 117: Article No. 108998 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2020.108998
|
|
[59]
|
Lv Y Z, Zhou J L, Wen G H, Yu X H, Huang T W. Fully distributed adaptive NN-based consensus protocol for nonlinear MASs: An attack-free approach. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(4): 1561−1570 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3042821
|




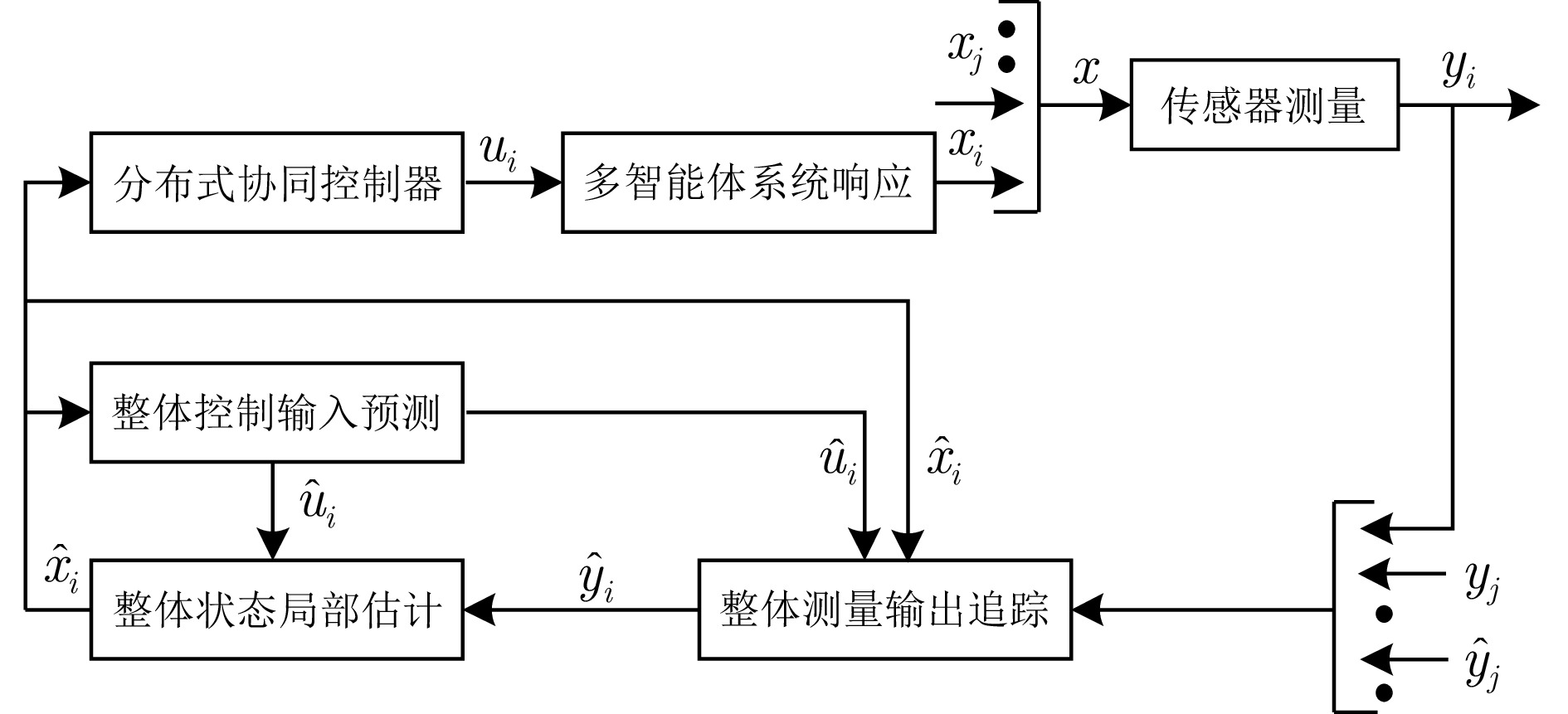
 下载:
下载: