A decision method for orbital game based on behavior prediction and strategy fusion
-
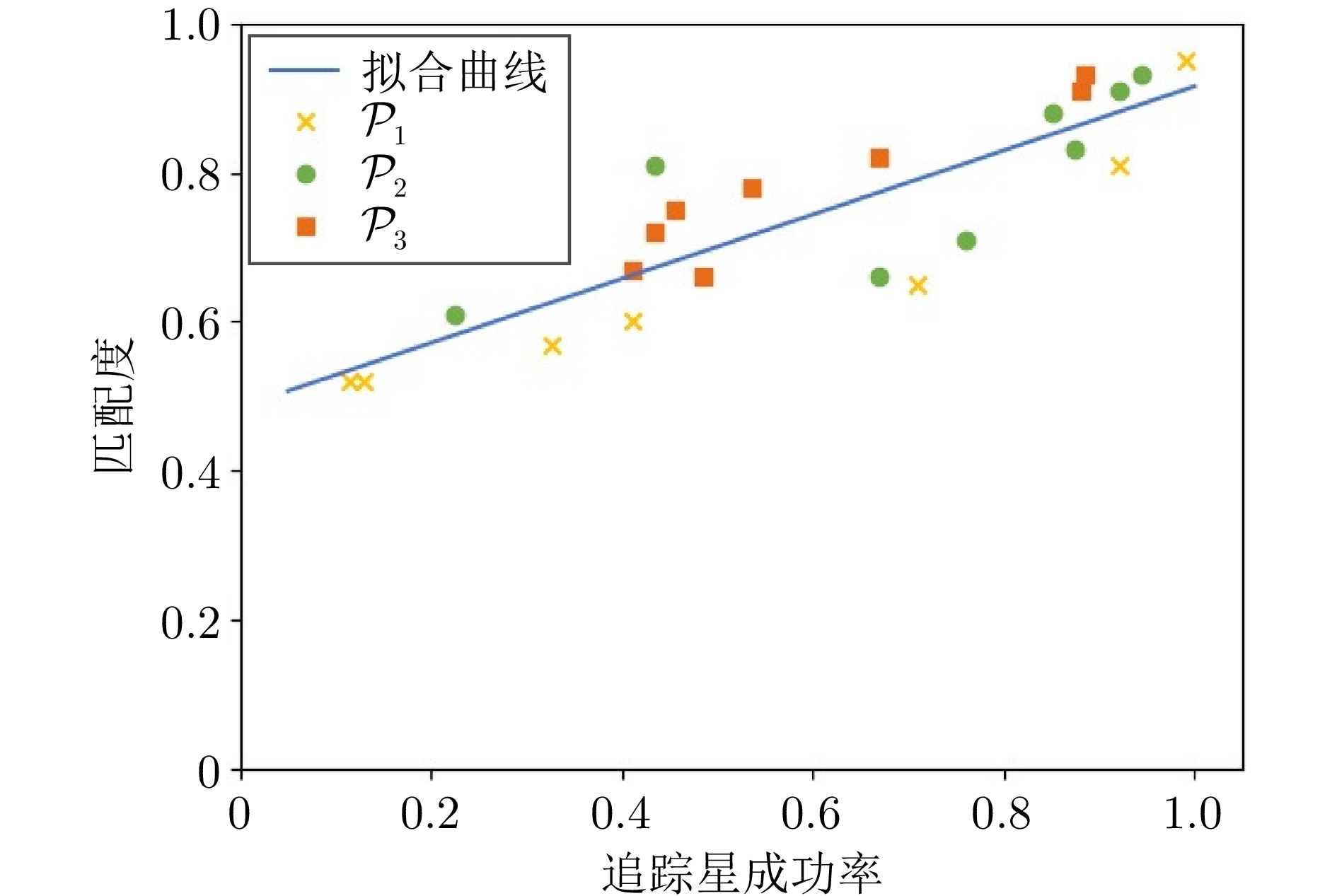
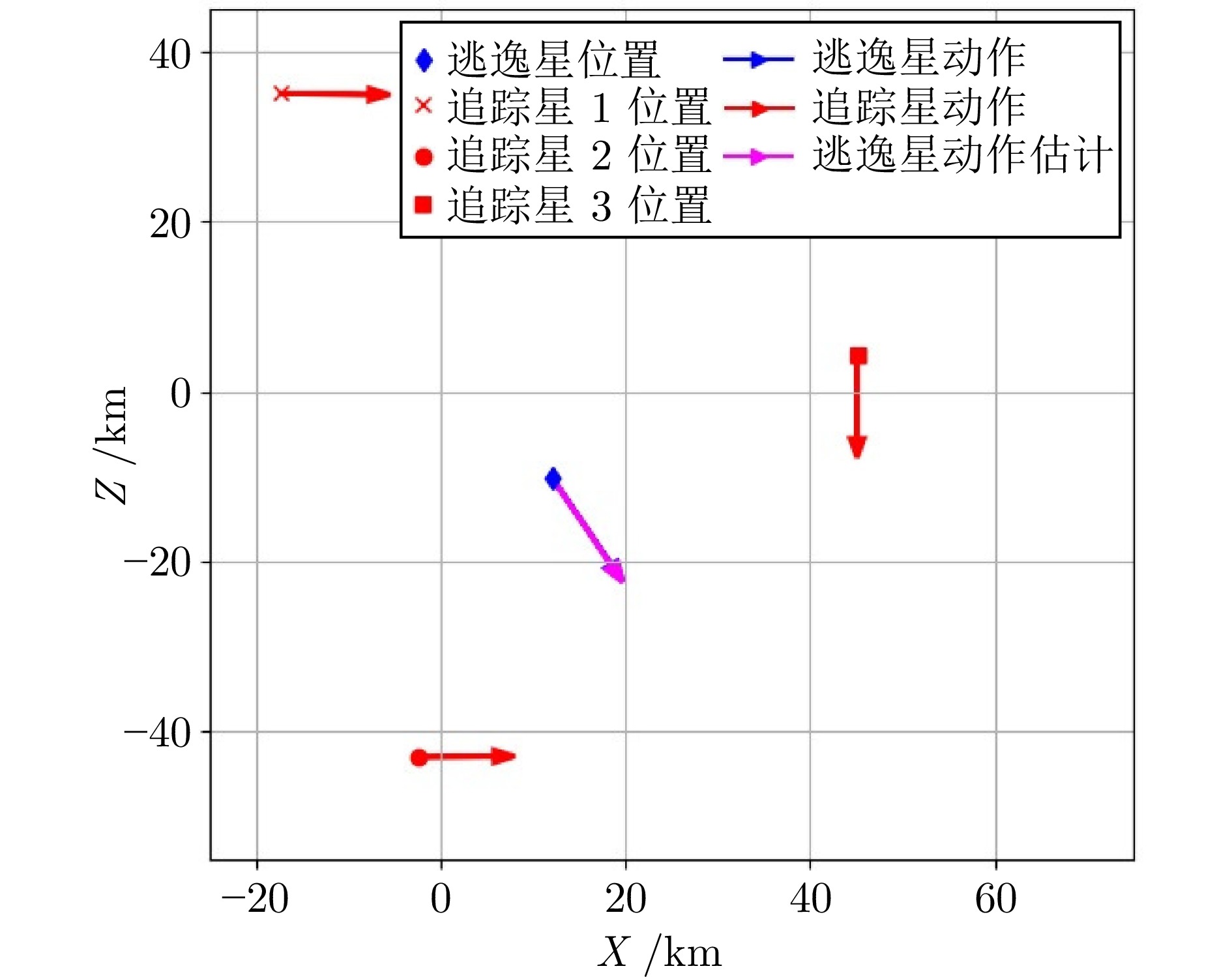
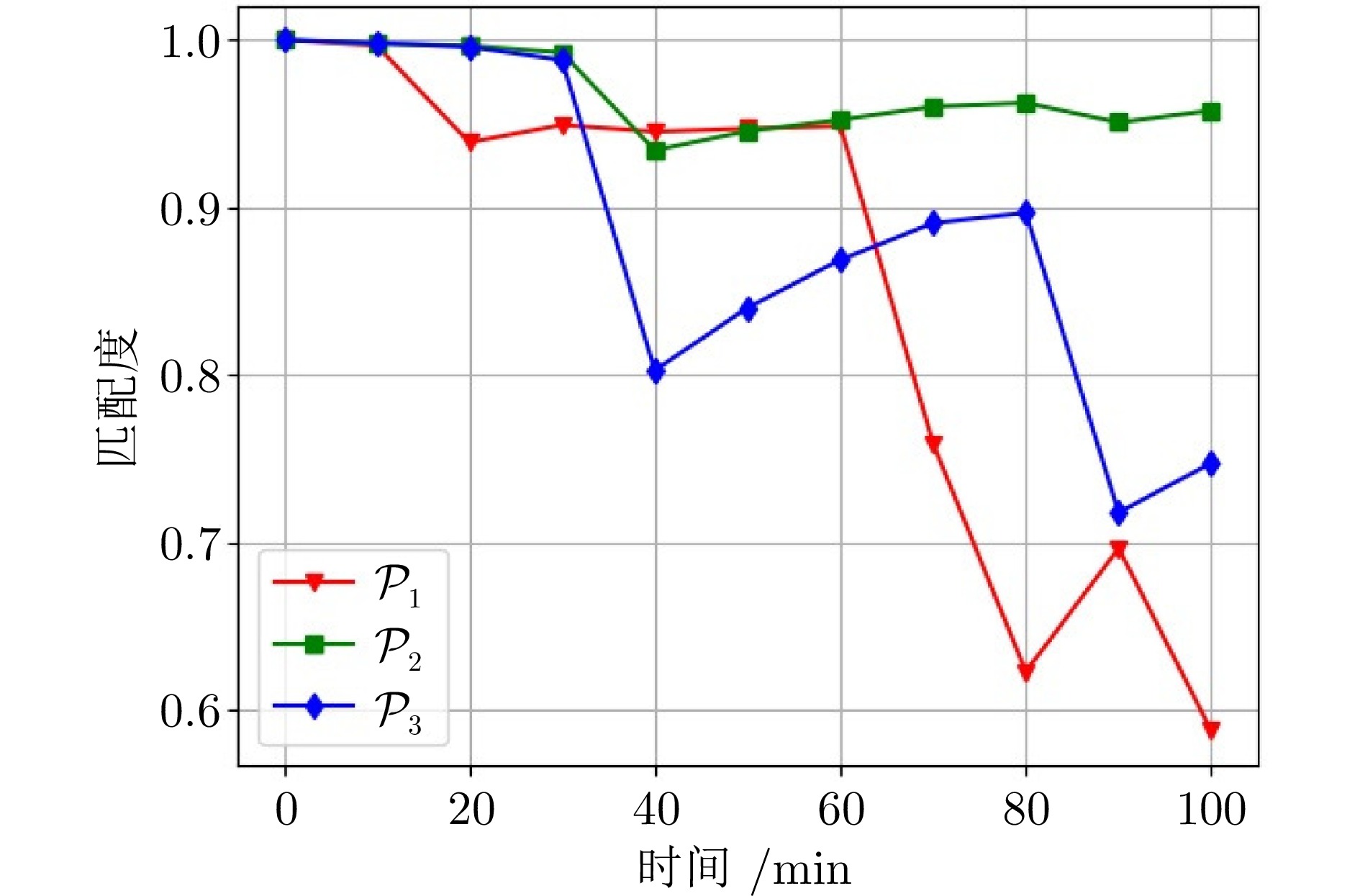
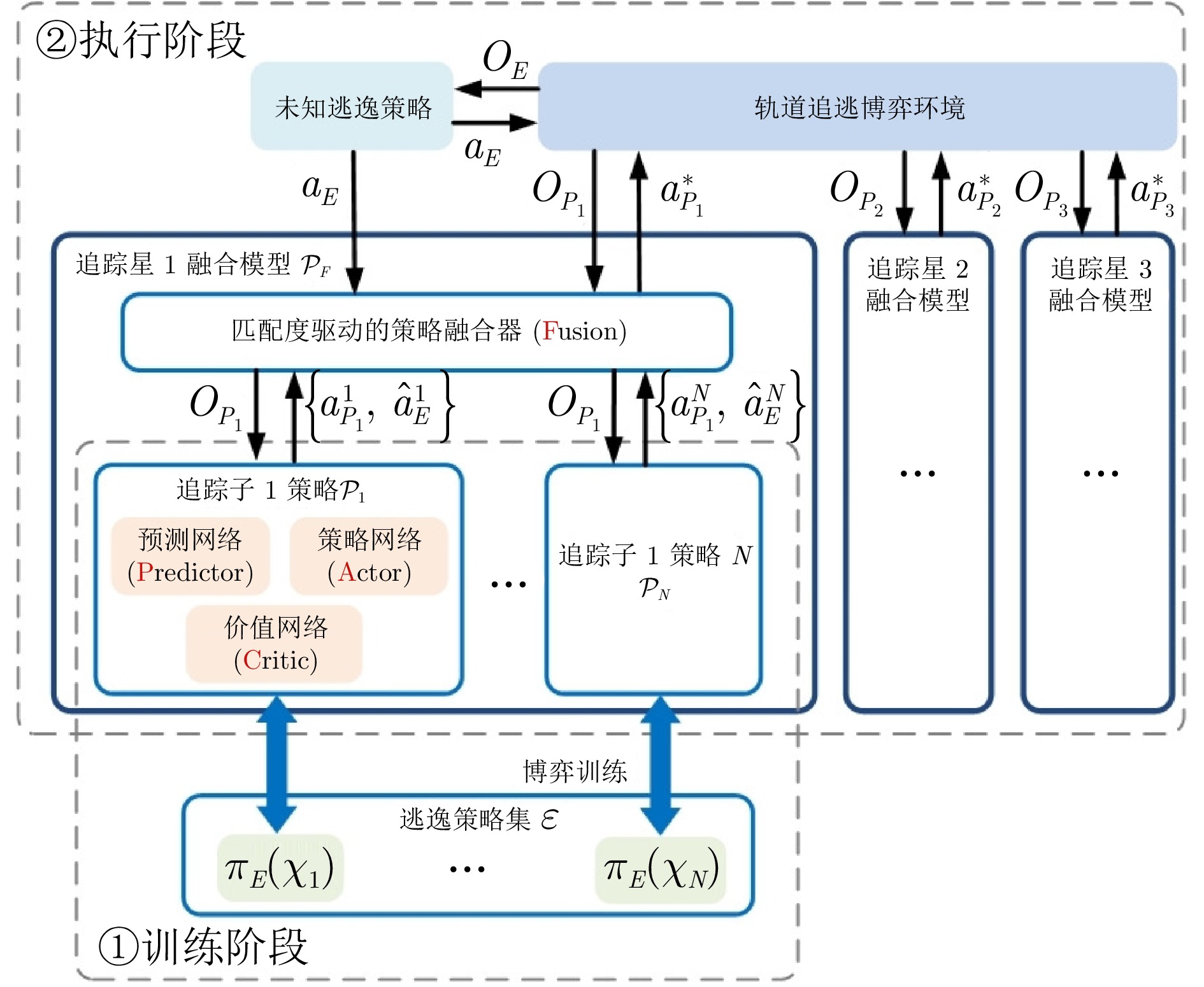
摘要: 轨道追逃博弈中逃逸策略的高度未知性与行为多样性, 给追踪策略的泛化能力带来了严峻挑战. 深度强化学习虽可提升追踪星的博弈效能, 但当逃逸策略偏离训练分布时, 策略网络易产生次优甚至失效的决策. 为此, 本文提出一种基于行为预测和策略融合的轨道博弈决策方法. 在训练阶段, 首先采用“预测制导+人工势场法”构建多样化逃逸策略集. 随后在传统演员−评论家训练框架基础上, 通过引入预测网络构建预测器−演员−评论家算法, 针对每类逃逸策略分别训练以获得对应的追踪子策略. 其中预测网络用于估计逃逸星动作, 并通过预测结果与真实动作的相似性衡量子策略与未知逃逸策略的匹配度. 在执行阶段, 策略融合器以逃逸星历史动作与各追踪子策略的预测结果为输入, 动态计算匹配度并选择最优子策略进行博弈决策. 实验结果表明, 预测网络能有效评估追踪子策略对未知逃逸策略的适应性, 策略融合器可显著提升追踪星面对多样化逃逸策略的泛化能力与可靠性.Abstract: The high uncertainty and behavioral diversity of evasion strategies in orbital pursuit-evasion game pose significant challenges to the generalization capability of pursuit strategies. Although deep reinforcement learning can enhance the pursuit agent's performance, the policy network often produces suboptimal or even invalid decisions when facing evasion behaviors that deviate from the training distribution. To address this issue, this paper proposes a decision method based on behavior prediction and strategy fusion, named predictor-actor-critic with fusion. During the training phase, a set of diverse evasion strategies is modeled using a prediction-guided approach combined with the artificial potential field method. Based on the traditional actor-critic framework, a predictor-actor-critic algorithm is developed by introducing a prediction network, and a corresponding pursuit sub-policy is trained for each type of evasion strategy. The prediction network estimates the evader's actions, and the similarity between predicted and actual actions is used to quantify the matching degree between each sub-policy and the unknown evasion strategy. During the execution phase, the fusion module takes the evaders historical actions and sub-policies' prediction outputs as input, dynamically evaluates matching degree, and selects the most appropriate sub-policy for decision-making. Experimental results demonstrate that the prediction network effectively evaluates adaptability of sub-policy to unknown evasion behaviors, and the fusion module significantly enhances the generalization capability and reliability of the pursuit agent when confronted with diverse evasion strategies.
-
表 1 场景参数
Table 1 Parameters of scenario
场景参数 数值 最大博弈时间 ${t_{\max }} = 250$ min 脉冲控制周期 $T=600$ s 逃逸星安全距离 $r_c=3$ km 追踪星单步最大脉冲控制约束 $\Delta {V_P} = 2.0$ m/s 逃逸星单步最大脉冲控制约束 $\Delta {V_E} = 2.4$ m/s 表 2 PAC算法训练参数
Table 2 Training parameters of PAC algorithm
训练参数 数值 策略网络学习率 $\alpha _a = 0.001$ 价值网络学习率 $\alpha _c = 0.001$ 预测网络学习率 $\alpha _p = 0.010$ 折扣率 ${\gamma } = 0.97$ 软更新速率 ${\tau } = 0.01$ 延迟策略更新频率 $d = 2$ mini-batch大小 $b = 1\;256$ 经验回放池大小 $B = 100\;000$ 奖励函数系数 $\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} \alpha_1 = 0.01,\; \alpha_2 = 0.02,\; \alpha_3 = 1.00 \end{array}$ 终端奖励 $C = 15$ 表 3 追踪模型平均与最低成功率统计表
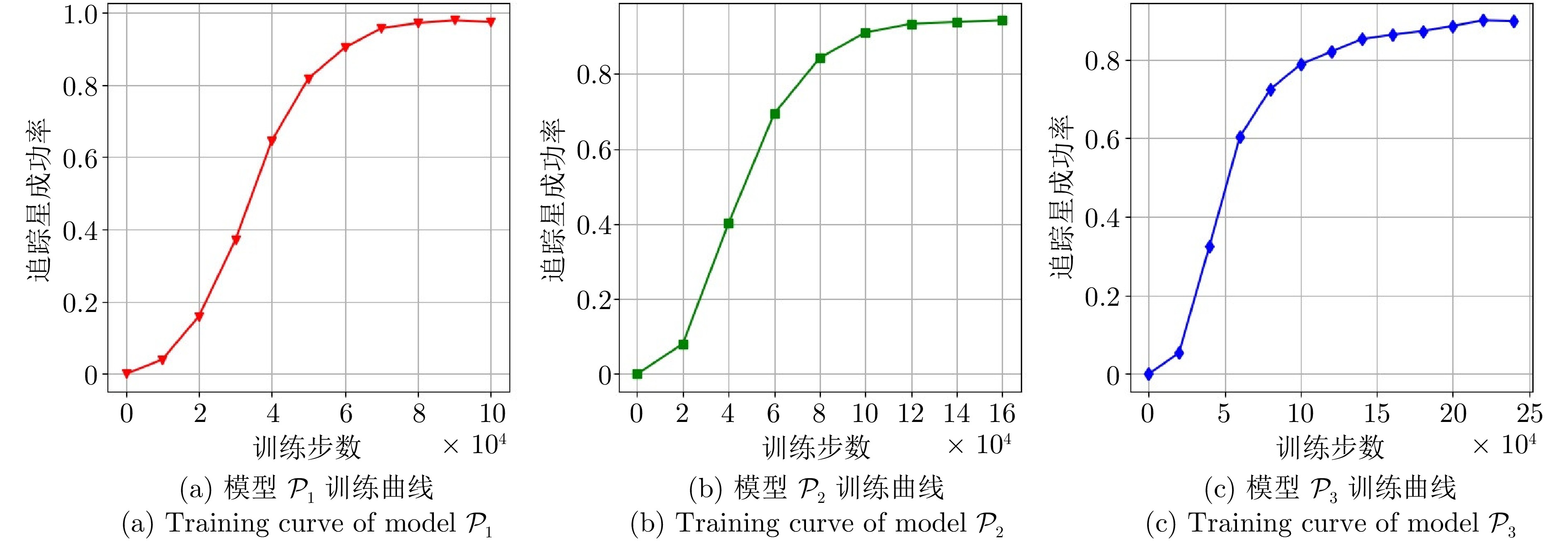
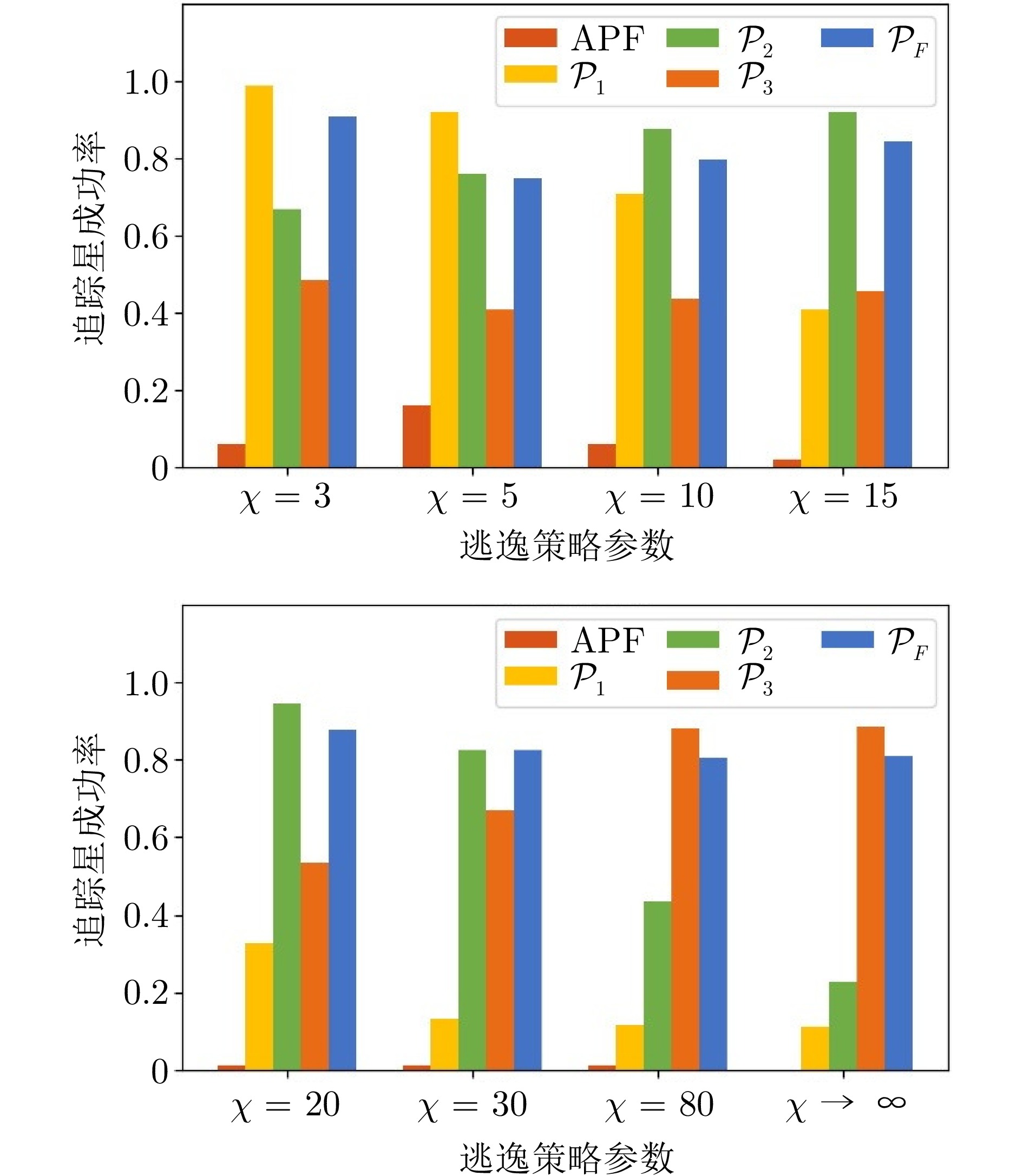
Table 3 Statistical table of average and minimum success rates of pursuit models
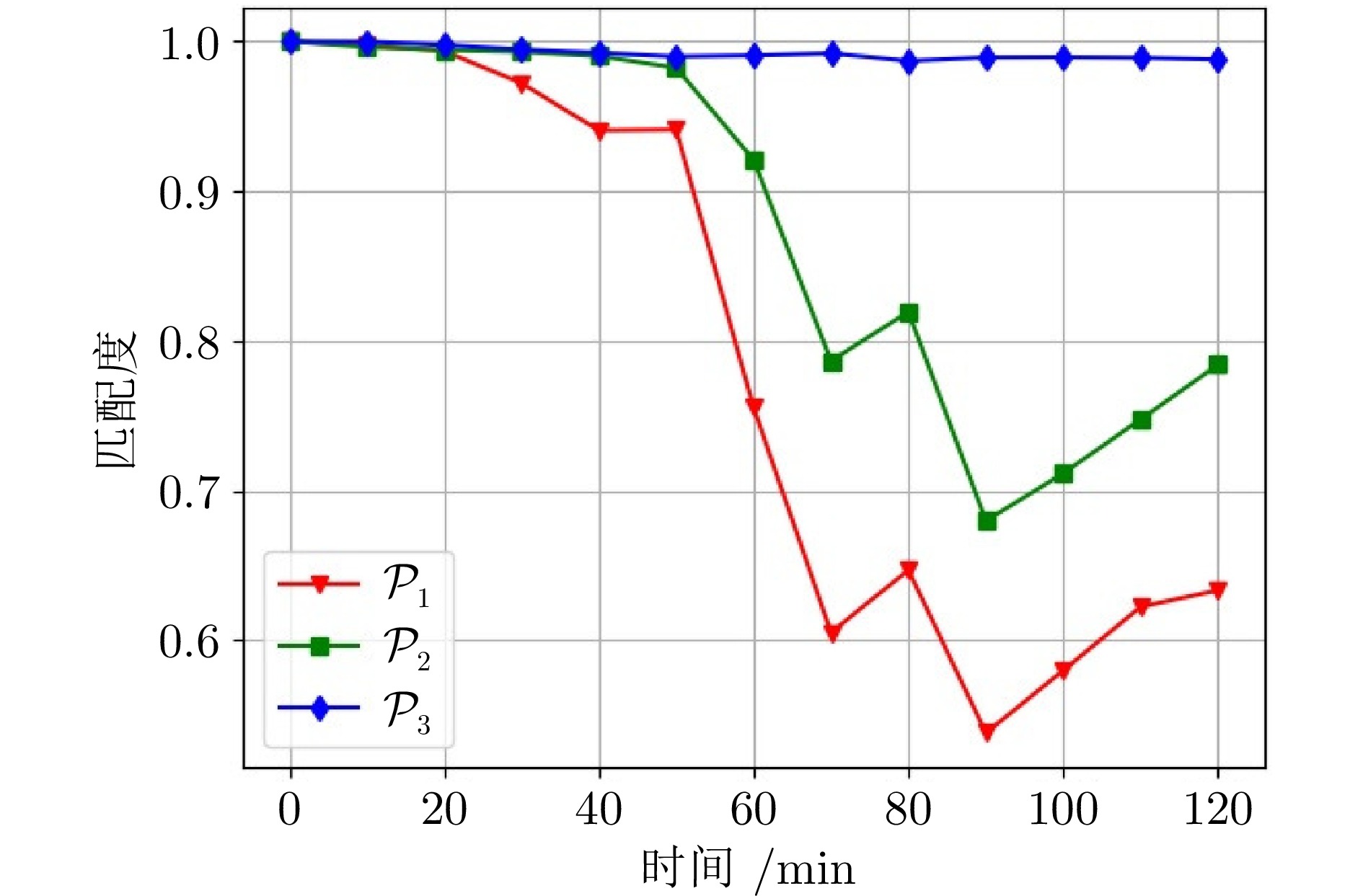
追踪策略模型 平均追踪成功率 最低追踪成功率 ${\mathcal{P}_1}$ 46.4% 11.0% ${\mathcal{P}_2}$ 70.7% 22.5% ${\mathcal{P}_3}$ 59.4% 41.0% ${\mathcal{P}_F}$ 82.8% 75.0% 表 4 不同平滑系数$\lambda$的追踪成功率统计表
Table 4 Statistical table of success rate for different smoothing factors $\lambda$
$\chi$ $\lambda$ $\lambda=0.2$ $\lambda=0.5$ $\lambda=0.8$ $\chi = 3$ 92% 91% 92% $\chi = 10$ 76% 80% 80% $\chi = 30$ 78% 83% 82% $\chi = 80$ 81% 84% 79% $\chi \to \infty $ 73% 81% 81% -
[1] 高婉莹, 吴健发, 魏春岭. 航天器威胁规避自主决策规划方法研究综述. 中国空间科学技术(中英文), 2024, 44(4): 71−89Gao Wan Ying, Wu Jian Fa, Wei Chun Ling. Review on spacecraft autonomous decision-making and planning for orbital threat avoidance. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2024, 44(4): 71−89 [2] 袁利, 姜甜甜. 航天器威胁规避智能自主控制技术研究综述. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(2): 229−245Yuan Li, Jiang Tian Tian. Review on intelligent autonomous control for spacecraft confronting orbital threats. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(2): 229−245 [3] 罗亚中, 李振瑜, 祝海. 航天器轨道追逃微分对策研究综述. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2020, 50(12): 1533−1545 doi: 10.1360/SST-2019-0174Luo Ya Zhong, Li Zhen Yu, Zhu Hai. Survey on spacecraft orbital pursuit-evasion differential games. Sci Sin Tech, 2020, 50(12): 1533−1545 doi: 10.1360/SST-2019-0174 [4] Zhang J R, Zhang K P, Zhang Y, Shi H, Tang L, Li M. Near-optimal interception strategy for orbital pursuit-evasion using deep reinforcement learning. Acta Astronautica, 2022, 198: 9−25 doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2022.05.057 [5] Li Z Y, Zhu H, Luo Y Z. An escape strategy in orbital pursuit-evasion games with incomplete information. Science China Technological Sciences, 2021, 64(3): 559−570 doi: 10.1007/s11431-020-1662-0 [6] Chen Q, Qiao D, Shang H B, Liu X F. A new method for solving reachable domain of spacecraft with a single impulse. Acta Astronautica, 2018, 145: 153−164 doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2018.01.040 [7] 李靖林, 姜中英, 师鹏, 李文龙. 基于相对可达域的航天器博弈均衡求解方法. 飞行力学, 2024, 42(5): 34−41Li Jing Lin, Jiang Zhong Ying, Shi Peng, Li Wen Long. Nash equilibrium solution method of spacecraft game based on the relative motion reachable set. Flight Dynamics, 2024, 42(5): 34−41 [8] Zhang K P, Zhang Y, Shi H, Huang H, Ye J, Wang H B. Escape-zone-based optimal evasion guidance against multiple orbital pursuers. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(6): 7698−7714 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3292072 [9] 耿远卓, 袁利, 黄煌, 汤亮. 基于终端诱导强化学习的航天器轨道追逃博弈. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(5): 974−984Geng Yuan Zhuo, Yuan Li, Huang Huang, Tang Liang. Terminal-guidance based reinforcement-learning for orbital pursuit-evasion game of the spacecraft. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(5): 974−984 [10] Wang H B, Zhang Y. Impulsive maneuver strategy for multi-agent orbital pursuit-evasion game under sparse rewards. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2024, 155: 109618 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2024.109618 [11] Zhao L R, Zhang Y L, Dang Z H. PRD-MADDPG: An efficient learning-based algorithm for orbital pursuit-evasion game with impulsive maneuvers. Advances in Space Research, 2023, 72(2): 211−230 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2023.03.014 [12] Geng Y Z, Yuan L, Guo Y N, Tang L, Huang H. Impulsive guidance of optimal pursuit with conical imaging zone for the evader. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2023, 142(108604): 1−12 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2023.108604 [13] Yang B, Liu P X, Feng J L, Li S. Two-stage pursuit strategy for incomplete-information impulsive space pursuit-evasion mission using reinforcement learning. Aerospace, 2021, 8(10): 299 doi: 10.3390/aerospace8100299 [14] 王英杰, 袁利, 汤亮, 黄煌, 耿远卓. 信息非完备下多航天器轨道博弈强化学习方法. 宇航学报, 2023, 44(10): 1522−1533Wang Ying Jie, Yuan Li, Tang Liang, Huang Huang, Geng Yuan Zhuo. Reinforcement learning method for multi-spacecraft orbital game with incomplete information. Journal of Astronautics, 2023, 44(10): 1522−1533 [15] 许旭升, 党朝辉, 宋斌, 袁秋帆, 肖余之. 基于多智能体强化学习的轨道追逃博弈方法. 上海航天(中英文), 2022, 39(2): 24−31 doi: 10.19328/j.cnki.2096‑8655.2022.02.004Xu Xu Sheng, Dang Zhao Hui, Song Bin, Yuan Qiu Fan, Xiao Yu Zhi. Method for cluster satellite orbit pursuit-evasion game based on multi-agent deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm. Aerospace Shanghai (Chinese & English), 2022, 39(2): 24−31 doi: 10.19328/j.cnki.2096‑8655.2022.02.004 [16] Li Z Y, Chen S, Zhou C, Sun W. Orbital multi-player pursuit-evasion game with deep reinforcement learning. The Journal of the Astronautical Sciences, 2025, 72(1): 1−29 doi: 10.1007/s40295-024-00474-3 [17] 曹宏业, 刘潇, 董绍康, 杨尚东, 霍静, 李文斌, 等. 面向强化学习的可解释性研究综述. 计算机学报, 2024, 47(8): 1853−1882Cao Hong Ye, Liu Xiao, Dong Shao Kang, Yang Shang Dong, Huo Jing, Li Wen Bin, et al. A survey of interpretability research methods for reinforcement learning. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2024, 47(8): 1853−1882 [18] 杨书恒, 张栋, 熊威, 任智, 唐硕. 基于可解释性强化学习的空战机动决策方法. 航空学报, 2024, 45(18): 257−274Yang Shu Heng, Zhang Dong, Xiong Wei, Ren Zhi, Tang Shuo. Decision-making method for air combat maneuver based on explainable reinforcement learning. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2024, 45(18): 257−274 [19] Greydanus S, Koul A, Dodge J, Fern A. Visualizing and understanding atari agents. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm, Sweden: PMLR, 2018. 1792-1801 [20] Bastani O, Pu Y, Solar-Lezama A. Verifiable reinforcement learning via policy extraction. In: Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montréal, Canada: Curran Associates, Inc., 2018. [21] Zhu Y Y, Xiao Y, Chen C L. Extracting decision tree from trained deep reinforcement learning in traffic signal control. IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, 2022, 10(4): 1997−2007 doi: 10.1109/iccsi53130.2021.9736263 [22] Soares E, Angelov P P, Costa B, Castro M P G, Filev D. Explaining deep learning models through rule-based approximation and visualization. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, 29(8): 2399−2407 doi: 10.1109/tfuzz.2020.2999776 [23] Danesh M H, Koul A, Fern A, Khorram S. Re-understanding finite-state representations of recurrent policy networks. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning. Virtual Event: PMLR, 2021. 2388-2397 [24] Konda V R, Tsitsiklis J N. Actor-critic algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 12th Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Denver, USA, 1999. [25] Lillicrap T P, Hunt J J, Pritzel A, Heess N, Erez T, Tassa Y, et al. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations. San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2016. [26] Fujimoto S, Hoof H, Meger D. Addressing function approximation error in actor-critic methods. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm, Sweden. PMLR, 2018: 1587-1596 [27] Zappulla R, Park H, Virgili-Llop J, Romano M. Real-time autonomous spacecraft proximity maneuvers and docking using an adaptive artificial potential field approach. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2018, 27(6): 2598−2605 doi: 10.1109/tcst.2018.2866963 [28] 高婉莹, 李克行. 基于人工势场的星群松散编队控制. 空间控制技术与应用, 2021, 47(3): 33−39Gao Wan Ying, Li Ke Hang. Loose formation control of satellite clusters based on artificial potential field. Aerospace Control and Application, 2021, 47(3): 33−39 [29] Hwang J, Lee J, Park C. Collision avoidance control for formation flying of multiple spacecraft using artificial potential field. Advances in Space Research, 2022, 69(5): 2197−2209 doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2021.12.015 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 101
- HTML全文浏览量: 105
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: