An Exploration of a New Paradigm for Constructing Industrial Domain-specific Embodied Intelligent Control Large Models
-
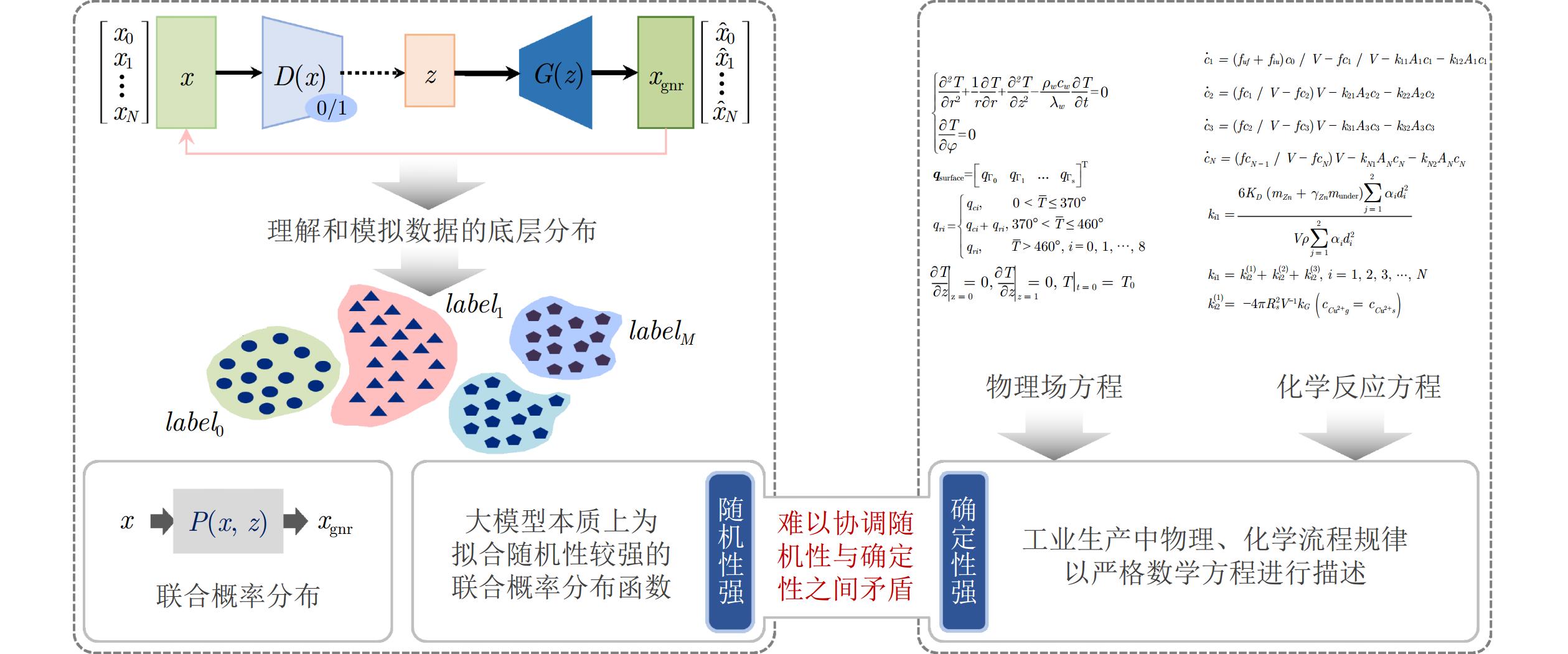
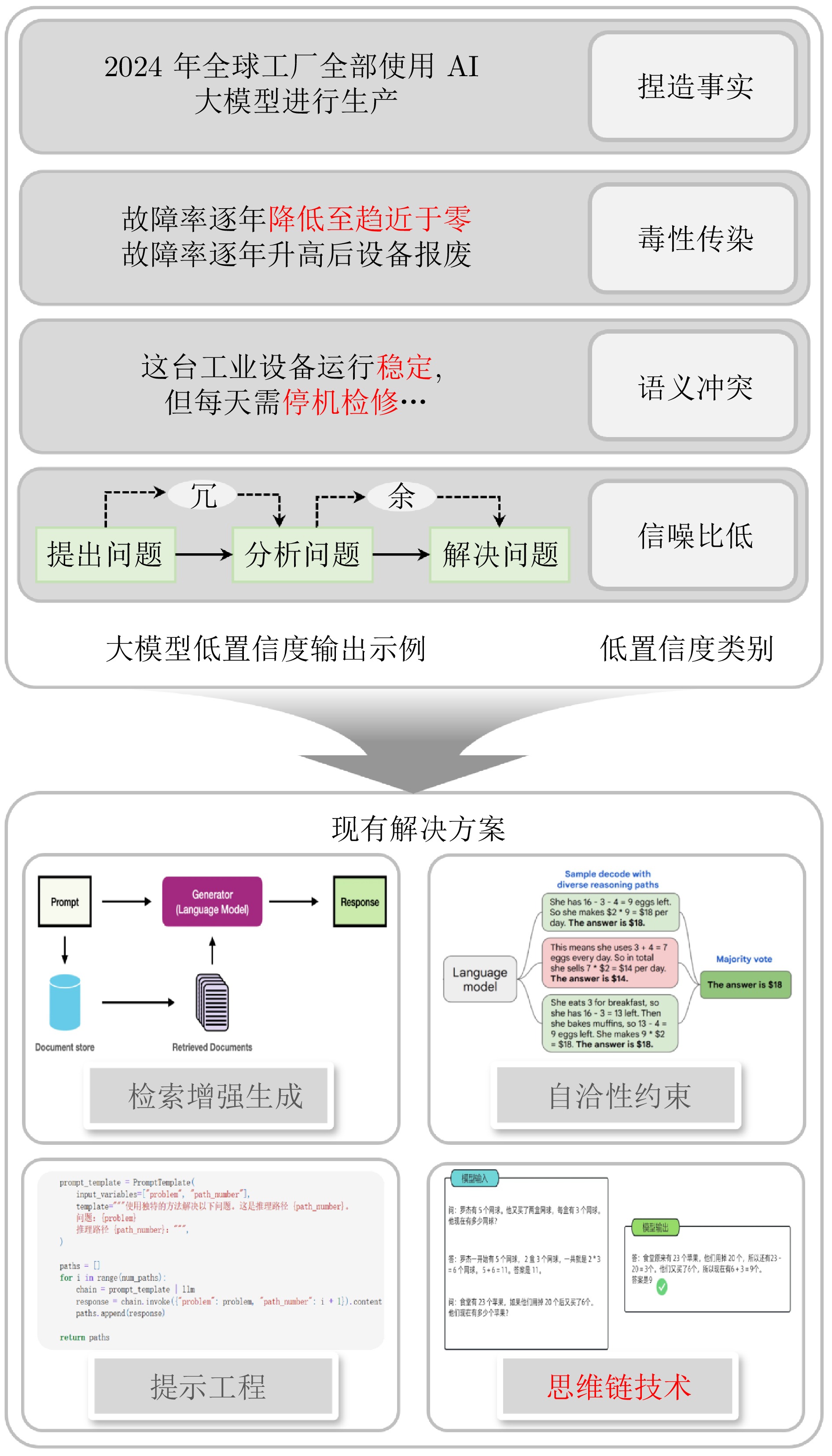
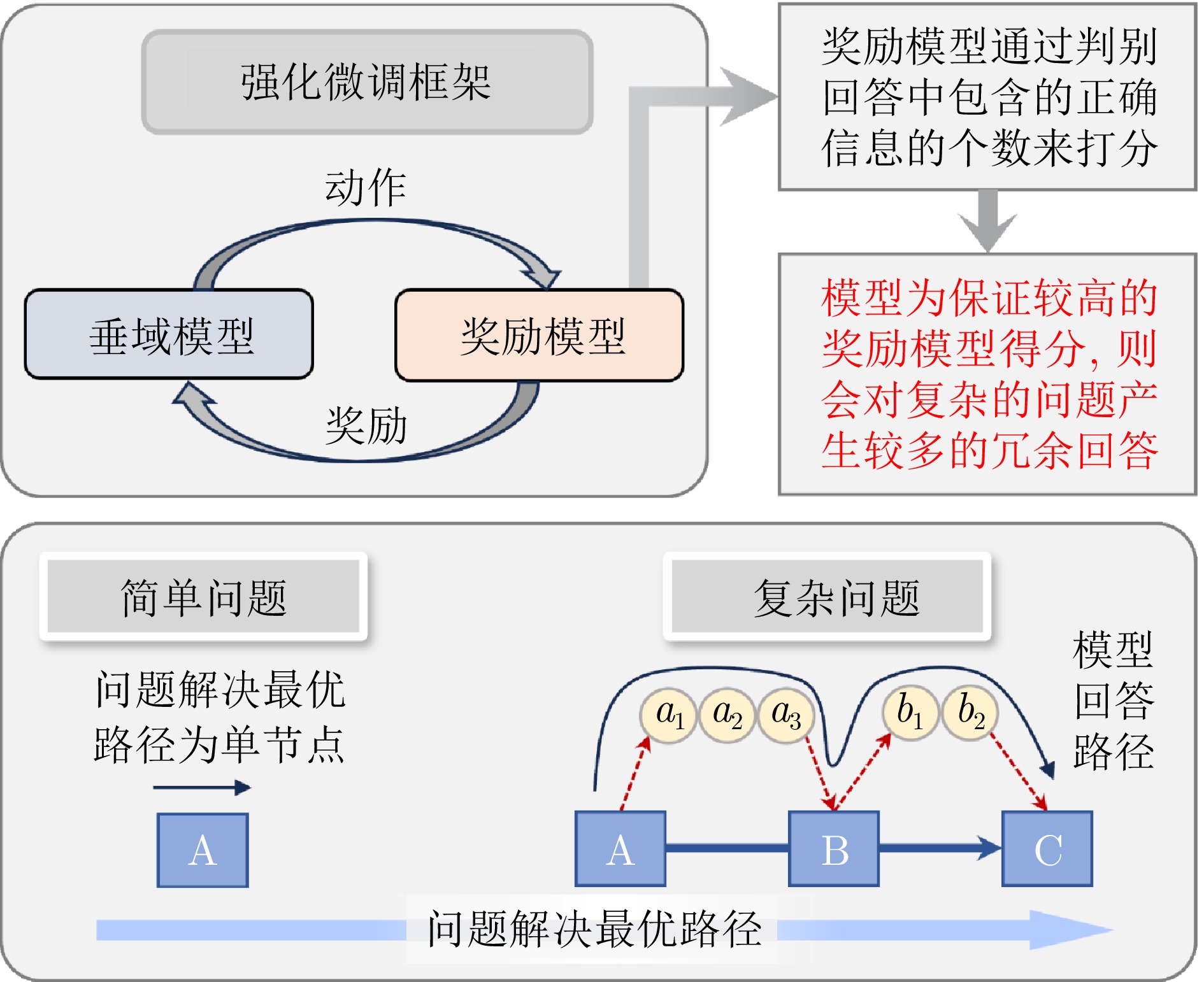
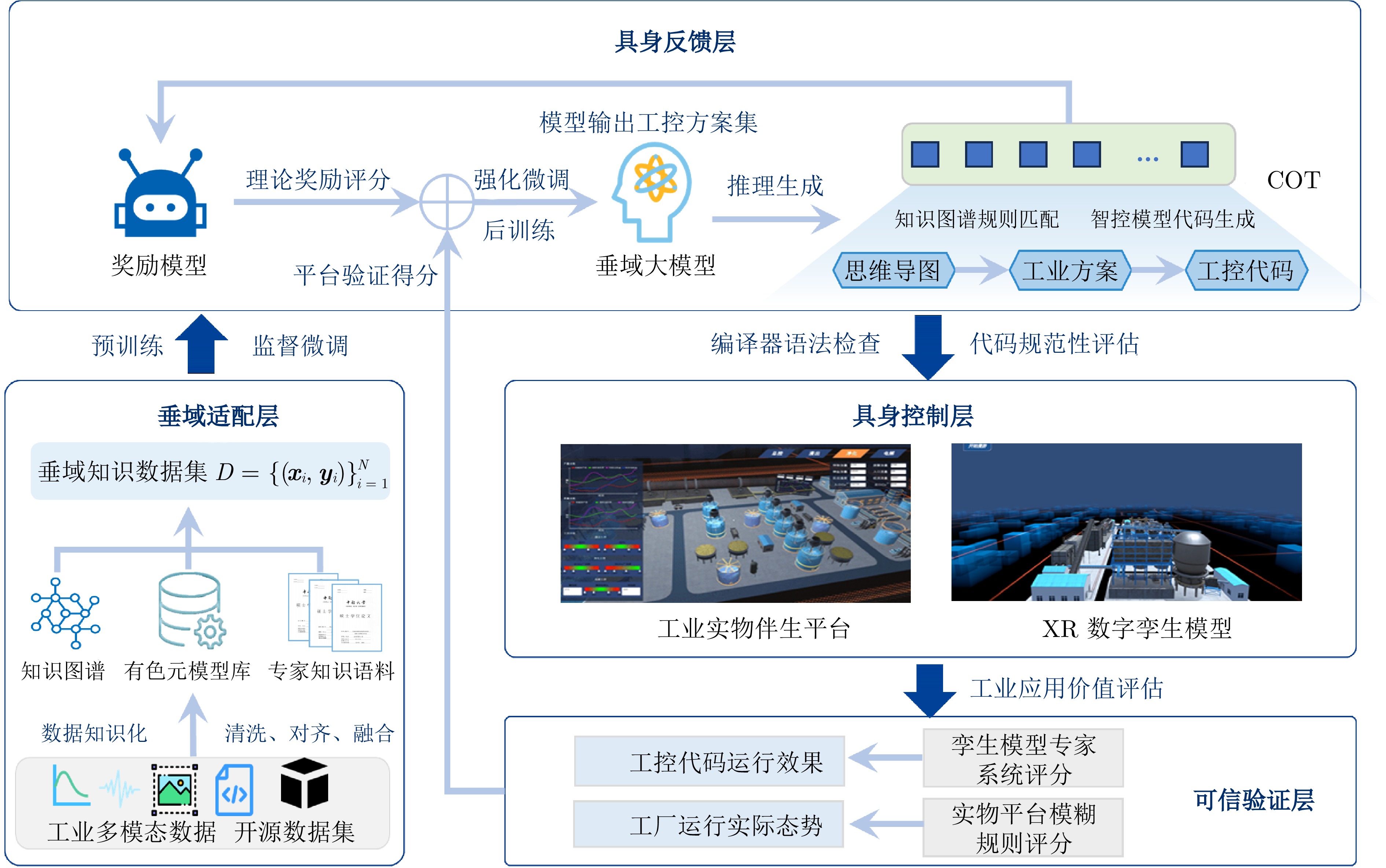
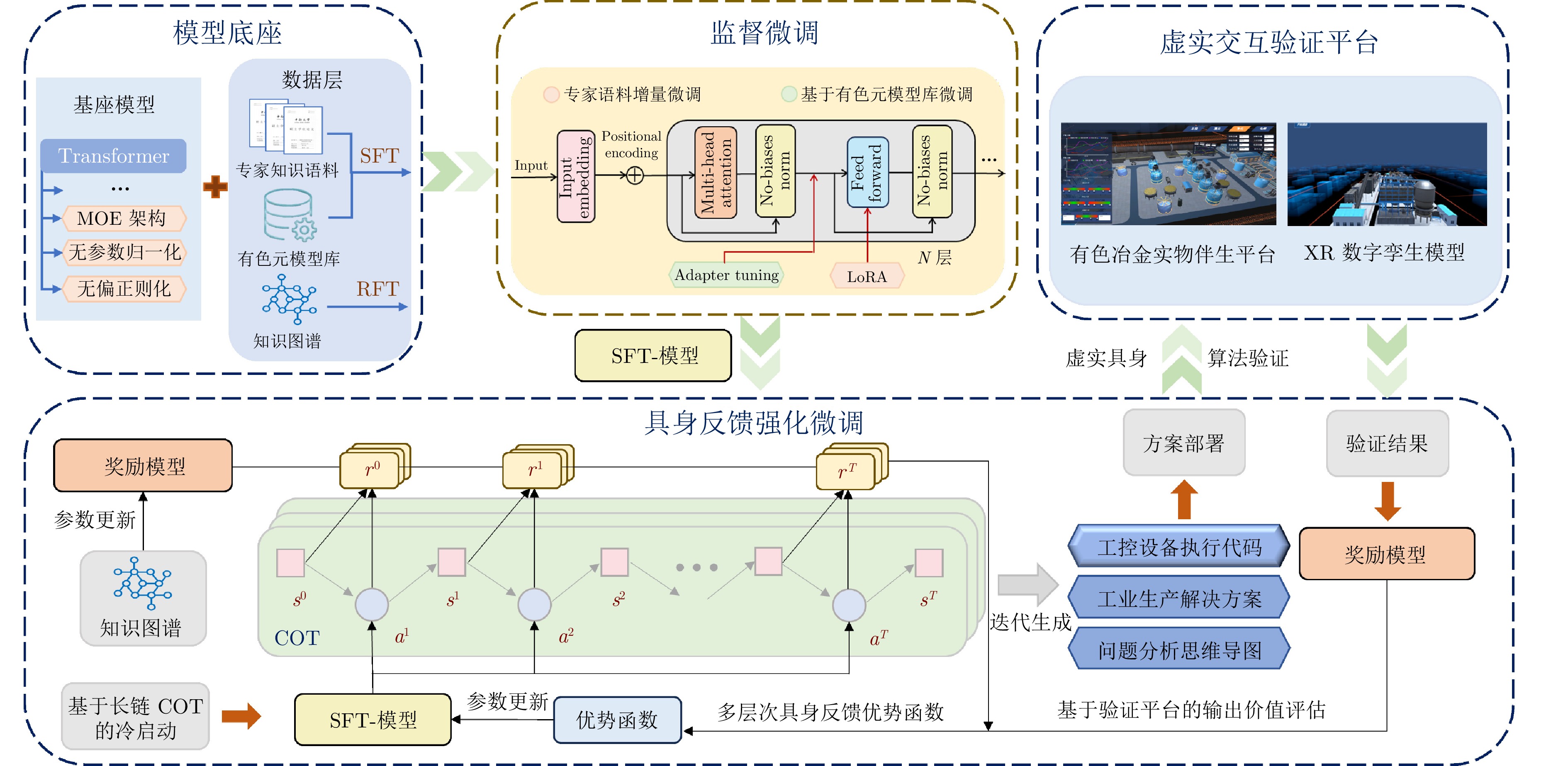
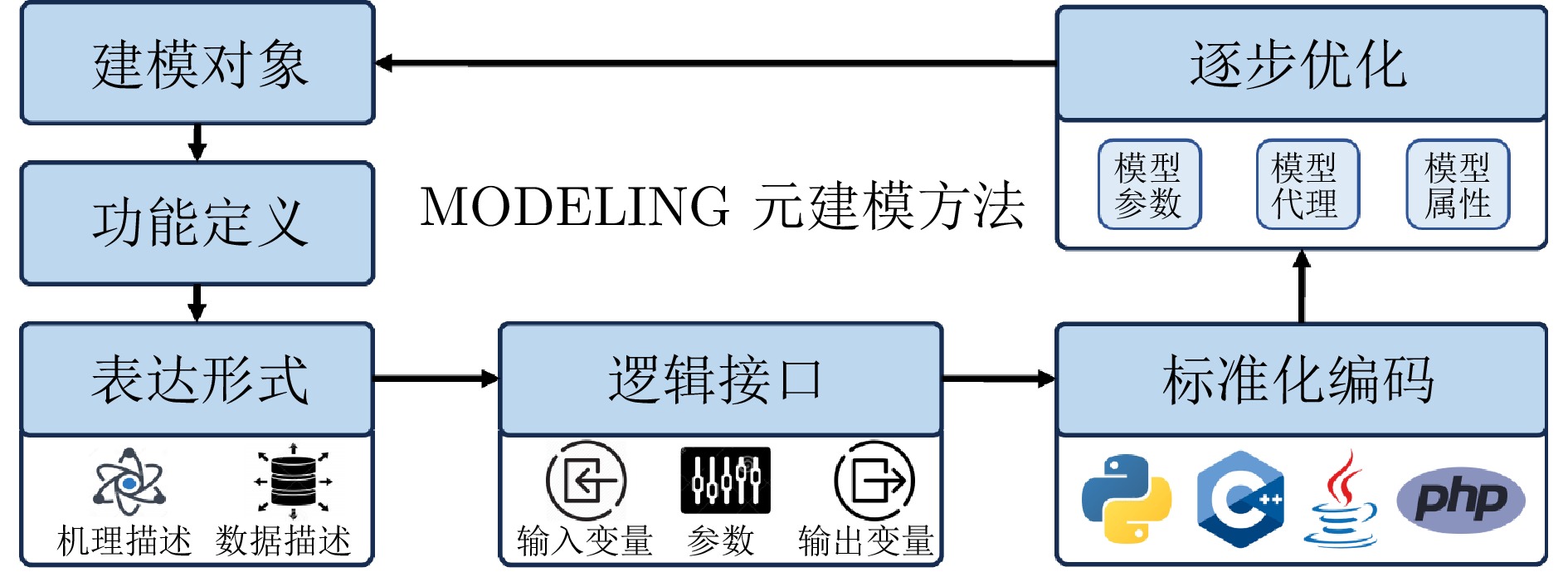
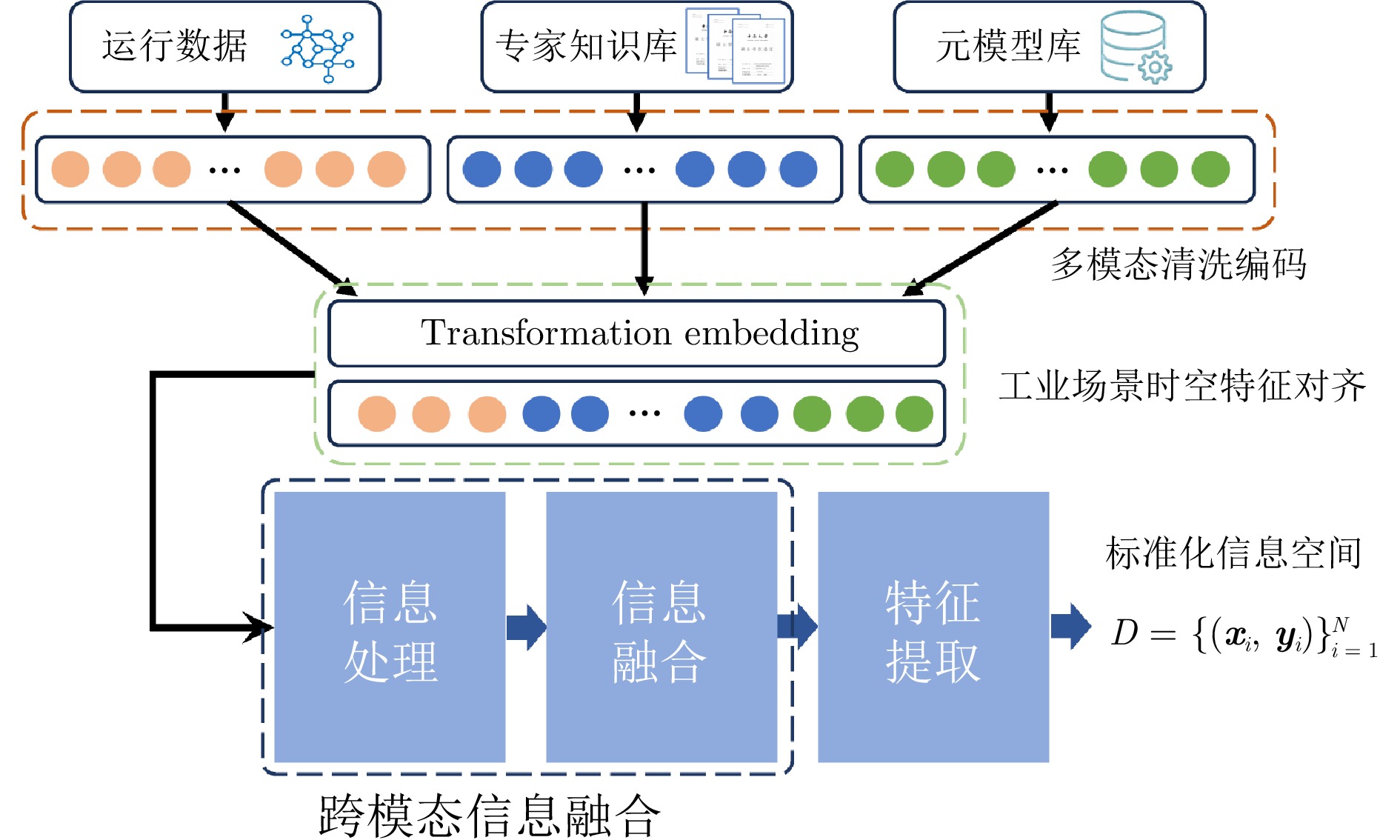
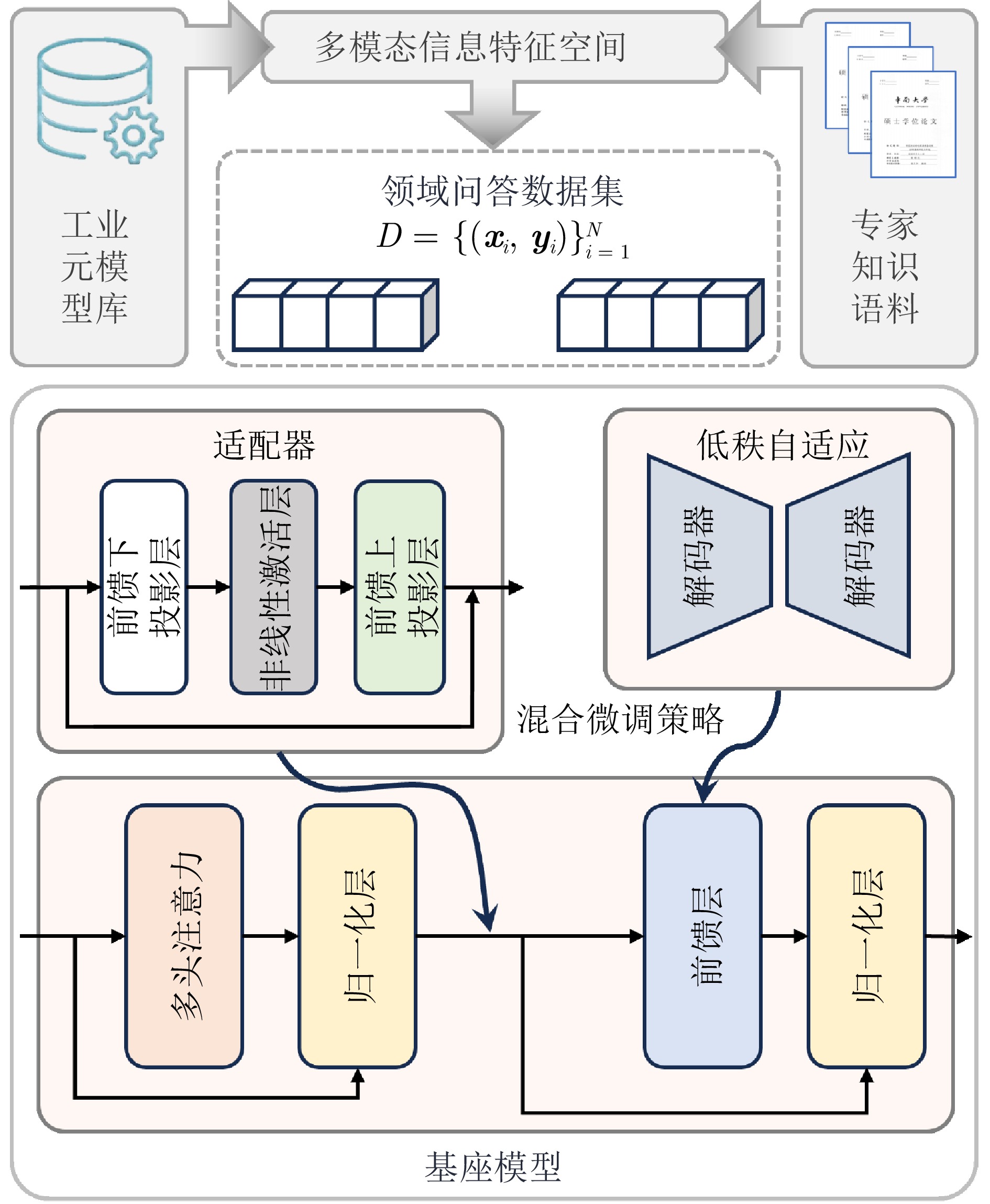
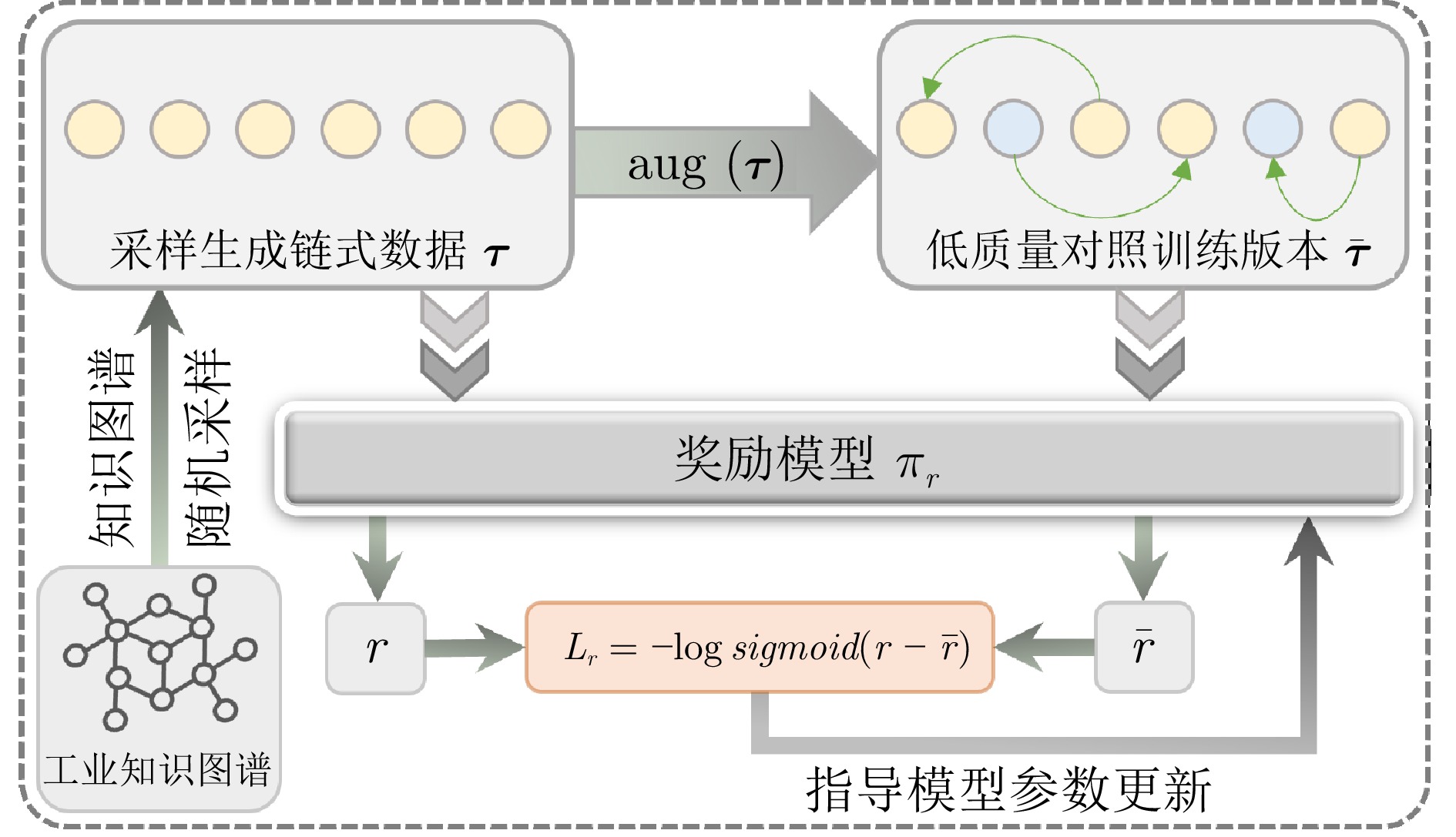
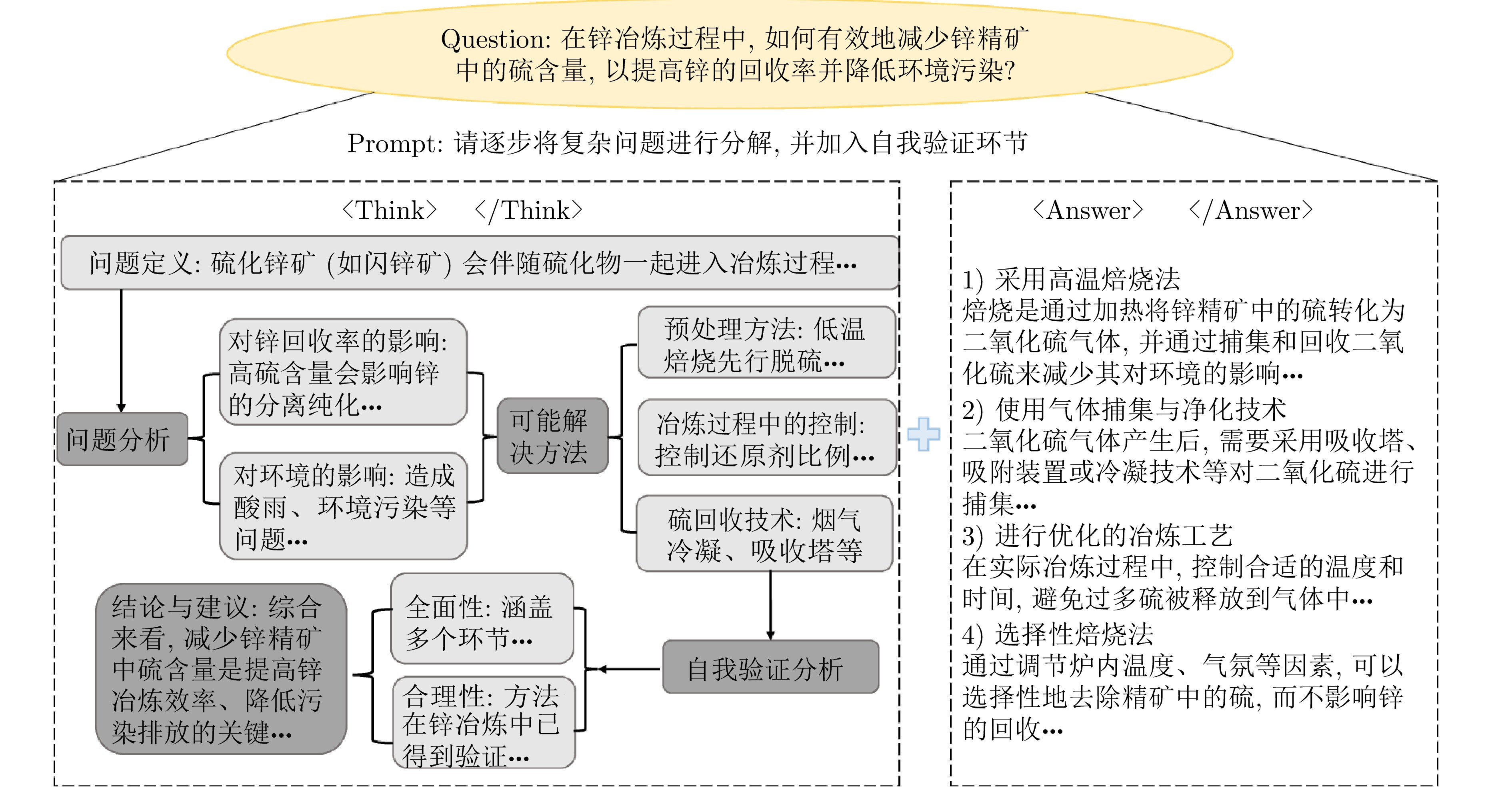
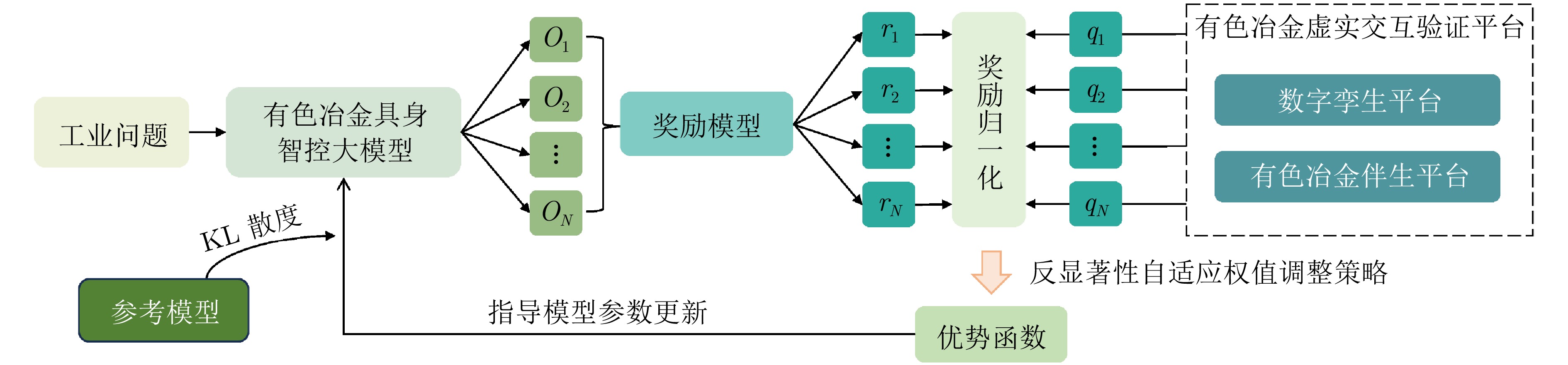
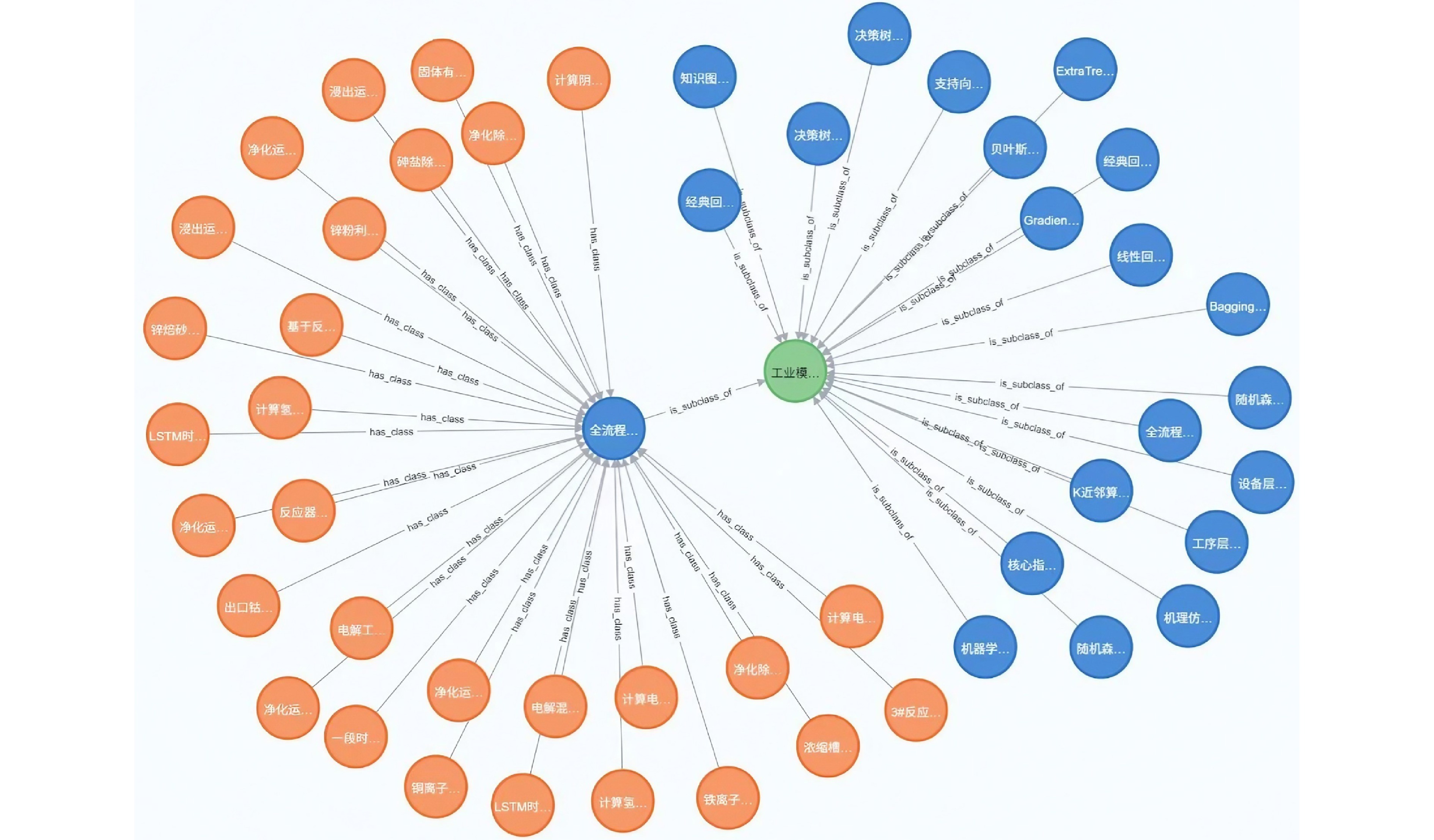
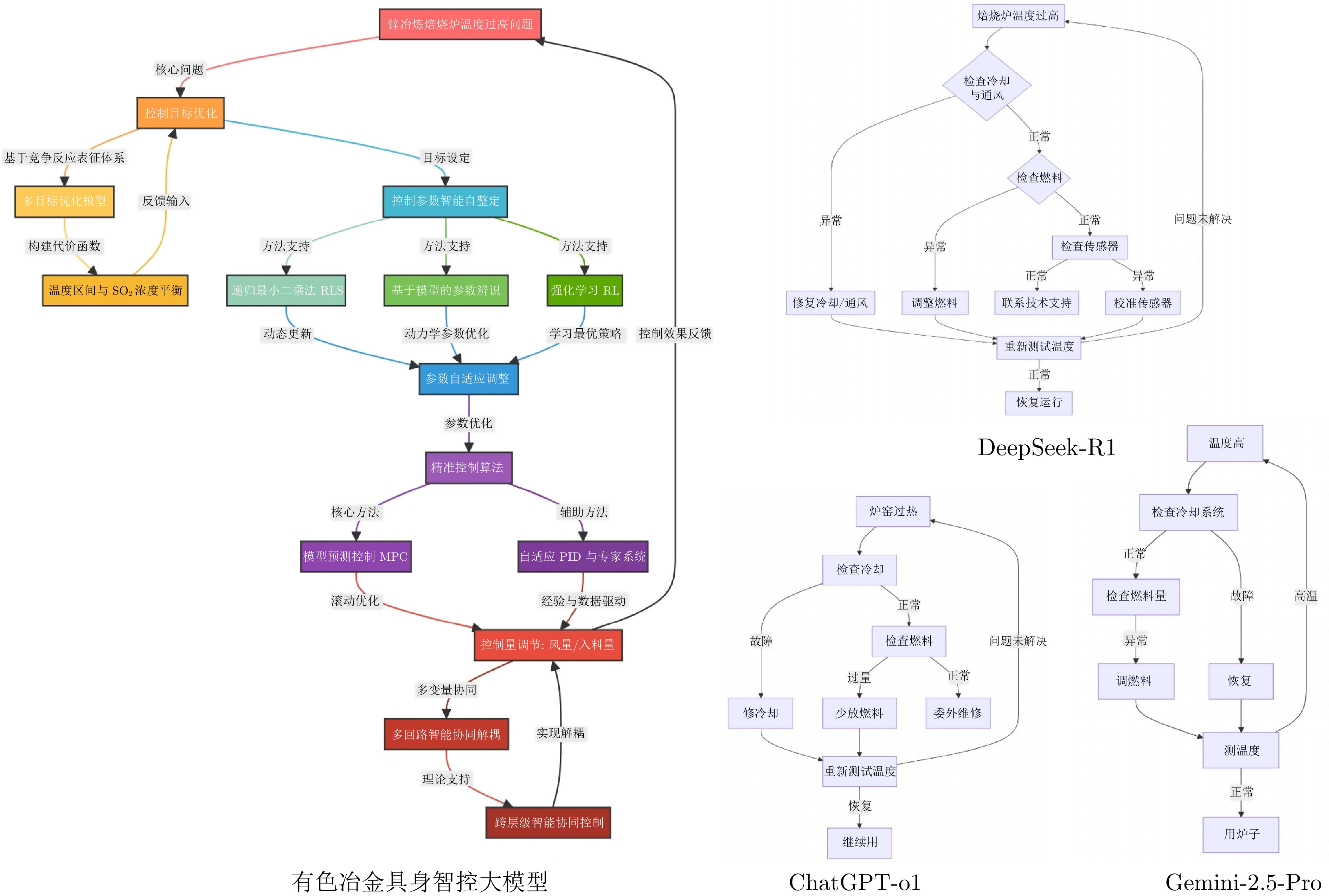
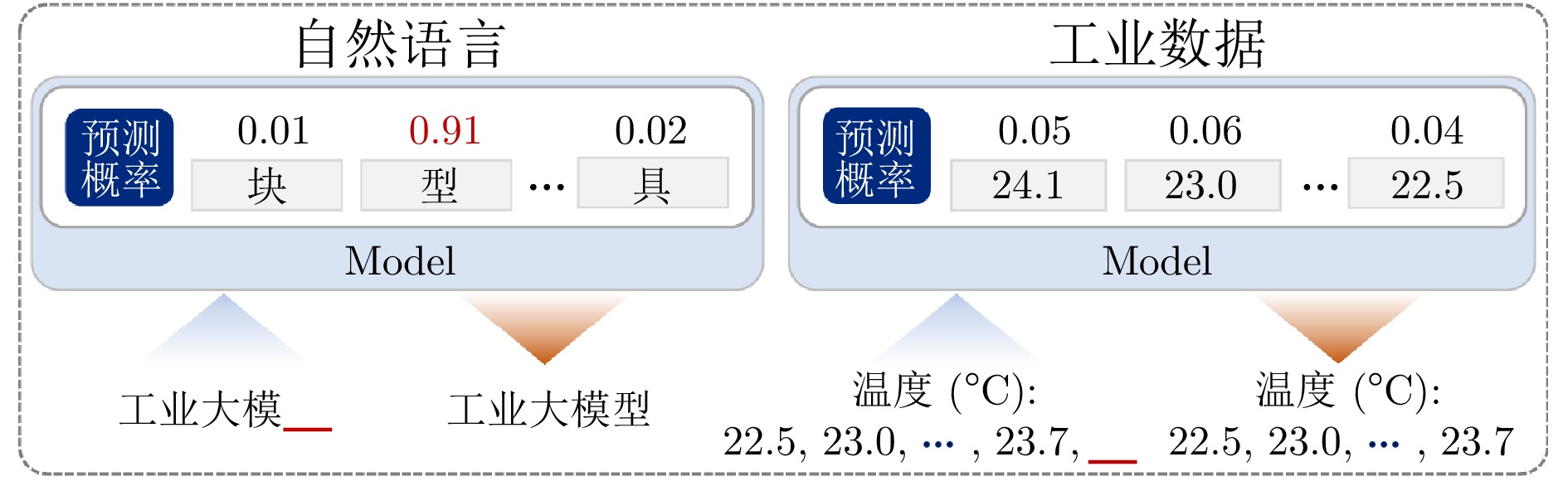
摘要: 大模型工业垂域化是通用智能迈向专业化应用的必然趋势, 更是驱动工业智能化转型的核心引擎. 然而, 大模型在工业领域应用中, 面临难以洞察工业时序数据内涵、难以嵌入工业物理化学规律、难以确保模型输出可信度以及难以解决复杂工业问题等挑战. 针对上述瓶颈, 提出工业垂域具身智控大模型构建范式: 创新性引入时序数据元模型化方法, 将工业时序数据转换为代码语义, 提升大模型对时序数据的理解与推理能力; 借助元模型构建工业规律知识图谱, 并将其嵌入大模型生成过程, 以确定性科学原理抑制生成随机性; 构建数字孪生与实物伴生的双轨验证平台, 通过虚实具身反馈机制、实时强化学习, 优化模型输出的可信度; 设计融合知识图谱规则评分与虚实验证专家评分的混合奖励函数, 结合自适应学习与长度正则化策略, 克服大模型解决复杂工业问题时“趋易畏难”倾向. 最终形成一个集垂域适配、具身控制、可信验证和具身反馈于一体的四层闭环架构. 应用于有色冶金领域, 构建首个有色冶金具身智控大模型, 实验验证了该范式的有效性, 为大模型从实验室走向工业现场, 架起从技术到落地的桥梁.Abstract: The industrial domain-specific adaptation of large models is an inevitable trend in the evolution of general intelligence towards specialized applications. It is also the core engine driving the intelligent transformation of industries. However, the application of large models in the industrial field encounters several challenges, such as difficulties in understanding the implications of industrial time-series data, embedding industrial physical and chemical laws, ensuring the reliability of model outputs, and solving complex industrial problems. To overcome these bottlenecks, a paradigm for developing industrial domain-specific embodied intelligent control large models is proposed. This paradigm innovatively introduces a time-series data meta-modeling approach that converts industrial time-series data into code semantics, thereby improving the large model's ability to interpret and reason with time-series data. Additionally, an industrial law knowledge graph is constructed based on meta-models and integrated into the large model generation process, utilizing deterministic scientific principles to mitigate randomness of generation. A dual-track verification platform combining digital twins and physical entities has been established. The platform employs a virtual-physical embodied feedback mechanism and real-time reinforcement learning to optimize the credibility of the model outputs. A hybrid reward function is designed, combining knowledge graph rule-based scoring with expert evaluations from both virtual and physical validations. By integrating adaptive learning with length regularization strategies, the model overcomes the tendency to “prioritize simplicity over complexity” in solving complex industrial problems. Ultimately, this approach forms a four-layer closed-loop architecture that incorporates domain-specific adaptation, embodied control, credible verification, and embodied feedback. When applied to the non-ferrous metallurgy sector, the first embodied intelligent control large model for non-ferrous metallurgy was constructed, and experimental validation demonstrated the effectiveness of this paradigm. This establishes a bridge for transitioning large models from laboratory settings to industrial applications, connecting technology with practical implementation.
-
表 1 控制方法指标比较
Table 1 Comparison of control method metrics
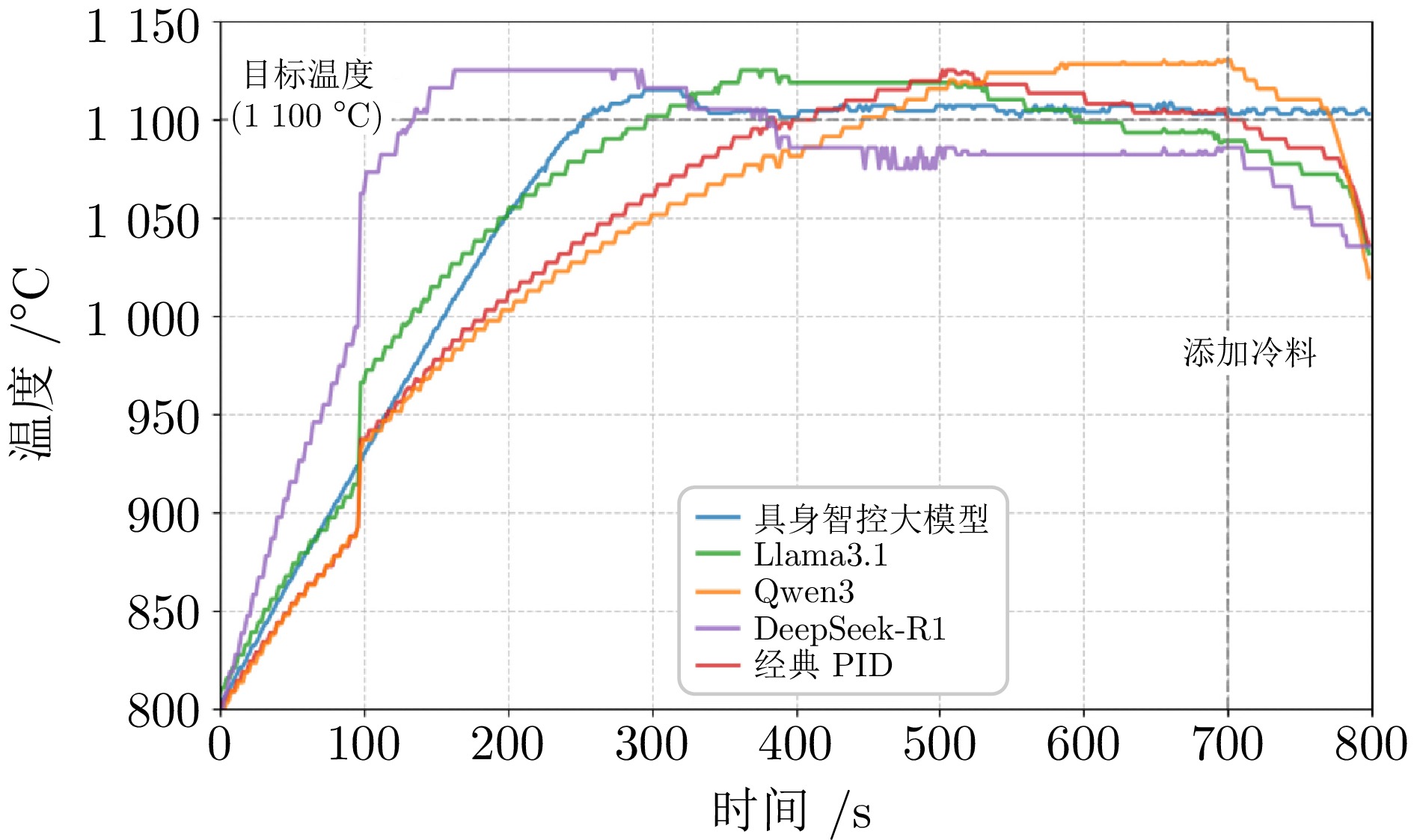
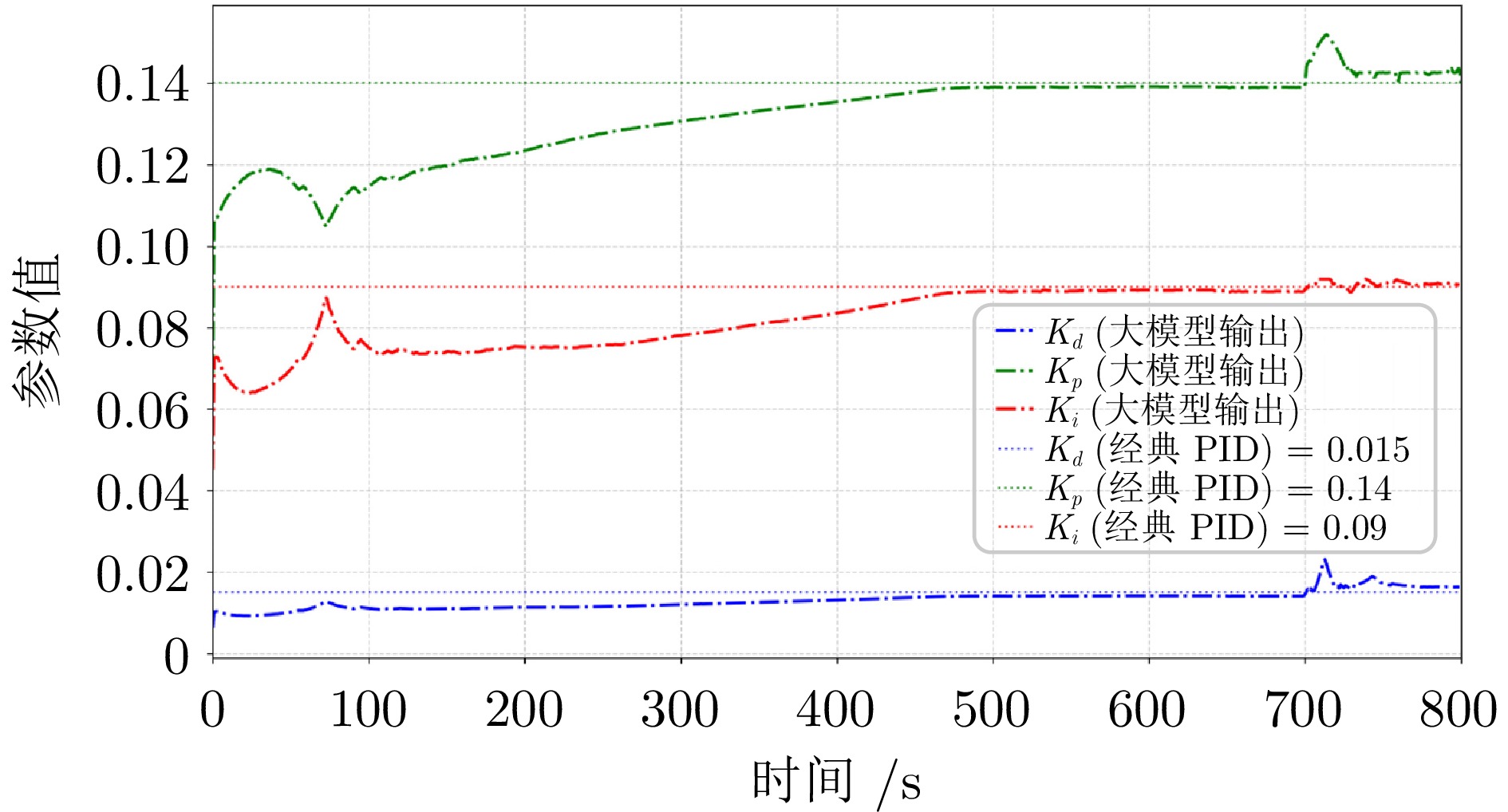
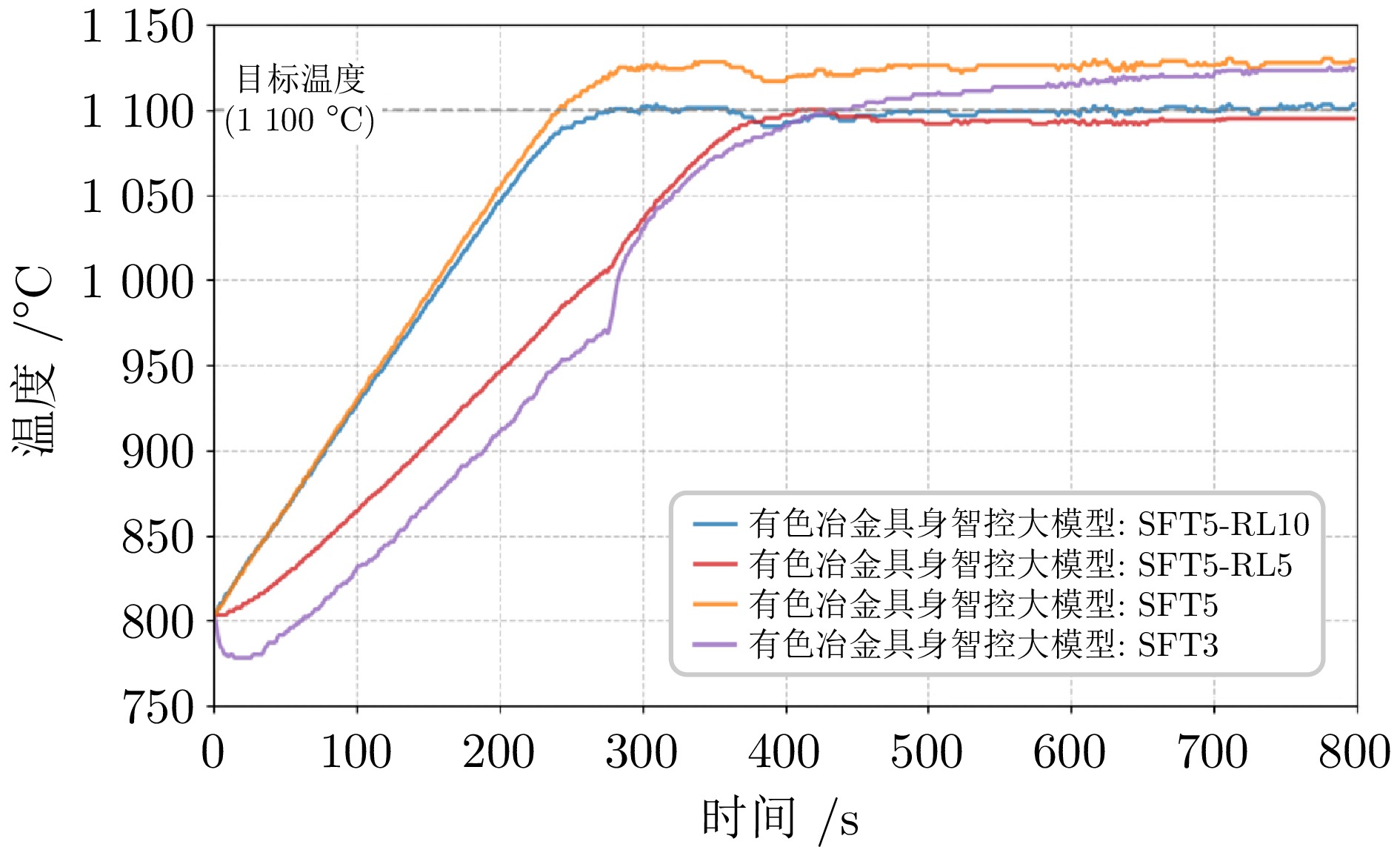
指标 PID 垂域大模型 最大调节时间 (min) 11.3 6.7 平均调节时间 (min) 10.9 4.8 最大超调量 (%) 3.73 2.37 平均超调量 (%) 3.24 2.26 最大稳态误差 (℃) 9.1 8.4 平均稳态误差 (℃) 8.0 7.8 最大偏差 (℃) 42.4 31.3 平均偏差 (℃) 35.1 24.2 表 2 平台运行指标比较 (%)
Table 2 Comparison of platform operation metrics (%)
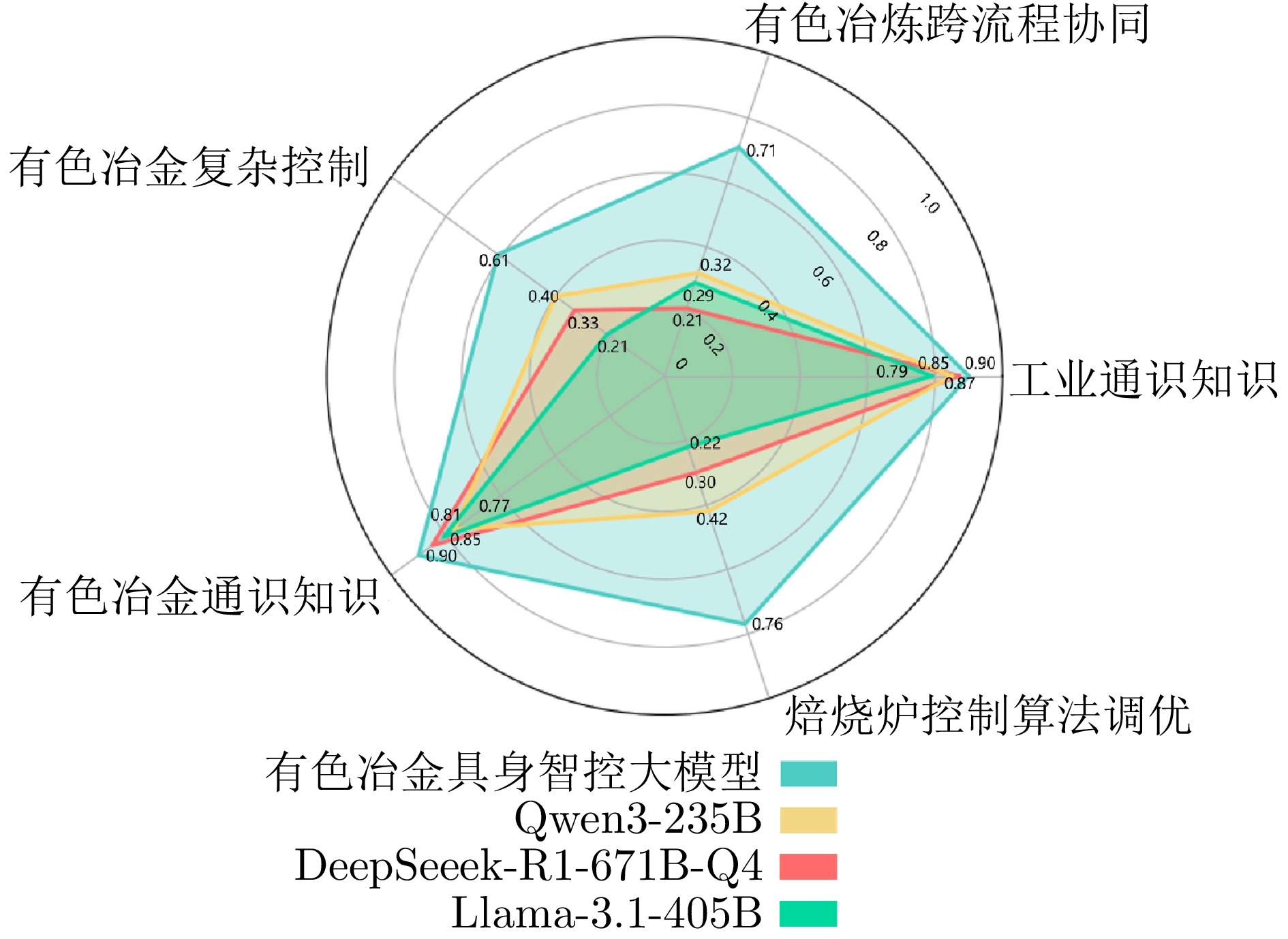
指标 垂域模型部署前 垂域模型部署后 平均故障率 14.0 6.5 平均控制精度误差 5.0 3.7 大模型覆盖工序率 − 95.0 运行参数达标率 87.2 93.5 -
[1] Brown T B, Mann B, Ryder N, Subbiah M, Kaplan J, Dhariwal P, et al. Language models are few-shot learners. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 159 [2] Xiong L L, Wang H F, Chen X, Sheng L, Xiong Y, Liu J P, et al. DeepSeek: Paradigm shifts and technical evolution in large AI models. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2025, 12(5): 841−858 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2025.125495 [3] 缪青海, 王兴霞, 杨静, 赵勇, 王雨桐, 陈圆圆, 等. 从基础智能到通用智能: 基于大模型的GenAI和AGI之现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(4): 674−687Miao Qing-Hai, Wang Xing-Xia, Yang Jing, Zhao Yong, Wang Yu-Tong, Chen Yuan-Yuan, et al. From foundation intelligence to general intelligence: The state-of-art and perspectives of GenAI and AGI based on foundation models. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(4): 674−687 [4] Liu A X, Feng B, Xue B, Wang B X, Wu B C, Lu C D, et al. DeepSeek-v3 technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2412.19437, 2024. [5] Shao Z H, Wang P Y, Zhu Q H, Xu R X, Song J X, Bi X, et al. DeepSeekMath: Pushing the limits of mathematical reasoning in open language models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2402.03300, 2024. [6] 车万翔, 窦志成, 冯岩松, 桂韬, 韩先培, 户保田, 等. 大模型时代的自然语言处理: 挑战、机遇与发展. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2023, 53(9): 1645−1687 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0113Che Wan-Xiang, Dou Zhi-Cheng, Feng Yan-Song, Gui Tao, Han Xian-Pei, Hu Bao-Tian, et al. Towards a comprehensive understanding of the impact of large language models on natural language processing: Challenges, opportunities and future directions. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2023, 53(9): 1645−1687 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2023-0113 [7] 任磊, 王海腾, 董家宝, 贾子翟, 李世祥, 王宇清, 等. 工业大模型: 体系架构、关键技术与典型应用. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2024, 54(11): 2606−2622 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2024-0185Ren Lei, Wang Hai-Teng, Dong Jia-Bao, Jia Zi-Di, Li Shi-Xiang, Wang Yu-Qing, et al. Industrial foundation model: Architecture, key technologies, and typical applications. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2024, 54(11): 2606−2622 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2024-0185 [8] Wei J, Tay Y, Bommasani R, Raffel C, Zoph B, Borgeaud S, et al. Emergent abilities of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2206.07682, 2022. [9] Wen X M, Zhang H, Zheng S, Xu W, Bian J. From supervised to generative: A novel paradigm for tabular deep learning with large language models. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Barcelona, Spain: ACM, 2024. 3323−3333 [10] Norheim J J, Rebentisch E, Xiao D K, Draeger L, Kerbrat A, de Weck O L. Challenges in applying large language models to requirements engineering tasks. Design Science, 2024, 10: Article No. e16 doi: 10.1017/dsj.2024.8 [11] Raza M, Jahangir Z, Riaz M B, Saeed M J, Sattar M A. Industrial applications of large language models. Scientific Reports, 2025, 15(1): Article No. 13755 doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98483-1 [12] Wang R, Wu Z X, Weng Z J, Chen J J, Qi G J, Jiang Y G. Cross-domain contrastive learning for unsupervised domain adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2023, 25: 1665−1673 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2022.3146744 [13] Wu J D, Wang Z Y, Hong M X, Ji W, Fu H Z, Xu Y W, et al. Medical SAM adapter: Adapting segment anything model for medical image segmentation. Medical Image Analysis, 2025, 102: Article No. 103547 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2025.103547 [14] Diao S Z, Wang P C, Lin Y, Pan R, Liu X, Zhang T. Active prompting with chain-of-thought for large language models. In: Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). Bangkok, Thailand: ACL, 2024. 1330−1350 [15] Zhang Z Y, Han X, Liu Z Y, Jiang X, Sun M S, Liu Q. ERNIE: Enhanced language representation with informative entities. In: Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Florence, Italy: ACL, 2019. 1441−1451 [16] He B, Zhou D, Xiao J H, Jiang X, Liu Q, Yuan N J, et al. Integrating graph contextualized knowledge into pre-trained language models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1912.00147, 2019. [17] Callewaert B, Vandevelde S, Vennekens J. VERUS-LM: A versatile framework for combining LLMs with symbolic reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2501.14540, 2025. [18] Tassa Y, Doron Y, Muldal A, Erez T, Li Y Z, de Las Casas D, et al. DeepMind control suite. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1801.00690, 2018. [19] Lewis P, Perez E, Piktus A, Petroni F, Karpukhin V, Goyal N, et al. Retrieval-augmented generation for knowledge-intensive NLP tasks. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 793 [20] Gao Y F, Xiong Y, Gao X Y, Jia K X, Pan J L, Bi Y X, et al. Retrieval-augmented generation for large language models: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2312.10997, 2023. [21] Jiang Z B, Xu F, Gao L Y, Sun Z Q, Liu Q, Dwivedi-Yu J, et al. Active retrieval augmented generation. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Singapore: ACL, 2023. 7969−7992 [22] Guo Y, Cheng Z Y, Zhang J D, Sun B, Wang Y K. A review on adversarial-based deep transfer learning mechanical fault diagnosis. Journal of Big Data, 2024, 11(1): Article No. 151 doi: 10.1186/s40537-024-01006-4 [23] Sun D X, Fan Y S, Wang G F. Enhancing fault diagnosis in industrial processes through adversarial task augmented sequential meta-learning. Applied Sciences, 2024, 14(11): Article No. 4433 doi: 10.3390/app14114433 [24] Zhang Z S, Zhang A, Li M, Smola A. Automatic chain of thought prompting in large language models. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Learning Representations. Kigali, Rwanda: OpenReview.net, 2023. [25] Moor M, Huang Q, Wu S, Yasunaga M, Dalmia Y, Leskovec J, et al. Med-Flamingo: A multimodal medical few-shot learner. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Machine Learning for Health. New Orleans, USA: PMLR, 2023. 353−367 [26] Wang H, Li C X, Li Y F, Tsung F. An intelligent industrial visual monitoring and maintenance framework empowered by large-scale visual and language models. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems, 2024, 2: 166−175 doi: 10.1109/TICPS.2024.3414292 [27] Yang T T, Feng P, Guo Q X, Zhang J D, Zhang X F, Ning J H, et al. AutoHMA-LLM: Efficient task coordination and execution in heterogeneous multi-agent systems using hybrid large language models. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2025, 11(2): 987−998 doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2025.3528892 [28] Hong W Y, Wang W H, Lv Q S, Xu J Z, Yu W M, Ji J H, et al. CogAgent: A visual language model for GUI agents. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. 14281−14290 [29] Chen L L, Lei Y T, Jin S Y, Zhang Y, Zhang L J. RLingua: Improving reinforcement learning sample efficiency in robotic manipulations with large language models. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2024, 9(7): 6075−6082 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2024.3400189 [30] Tan M T, Merrill M A, Gupta V, Althoff T, Hartvigsen T. Are language models actually useful for time series forecasting? In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2024. Article No. 1922 [31] Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez A N, et al. Attention is all you need. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 6000−6010 [32] Huang L, Yu W J, Ma W T, Zhong W H, Feng Z Y, Wang H T, et al. A survey on hallucination in large language models: Principles, taxonomy, challenges, and open questions. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 2025, 43(2): Article No. 42 [33] Zhou D Y, Xue X, Ma Q, Guo C, Cui L Z, Tian Y L, et al. Federated experiments: Generative causal inference powered by LLM-based agents simulation and RAG-based domain docking. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2025, 12(7): 1301−1304 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2024.124671 [34] Liu Z C, Chen C Y, Li W J, Qi P H, Pang T Y, Du C, et al. Understanding R1-zero-like training: A critical perspective. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2503.20783, 2025. [35] 阳春华, 刘一顺, 黄科科, 孙备, 李勇刚, 陈晓方, 等. 有色金属工业智能模型库构建方法及应用. 中国工程科学, 2022, 24(4): 188−201 doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2022.04.013Yang Chun-Hua, Liu Yi-Shun, Huang Ke-Ke, Sun Bei, Li Yong-Gang, Chen Xiao-Fang, et al. Intelligent model library for nonferrous metal industry: Construction method and application. Strategic Study of CAE, 2022, 24(4): 188−201 doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2022.04.013 [36] Hu E J, Shen Y L, Wallis P, Allen-Zhu Z, Li Y Z, Wang S A, et al. LoRA: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). OpenReview.net, 2022.Hu E J, Shen Y L, Wallis P, Allen-Zhu Z, Li Y Z, Wang S A, et al. LoRA: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). OpenReview.net, 2022. [37] Hu Z Q, Wang L, Lan Y H, Xu W Y, Lim E P, Bing L D, et al. LLM-adapters: An adapter family for parameter-efficient fine-tuning of large language models. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Singapore: ACL, 2023. 5254−5276 [38] Luo W C, Yang C H, Liang X J, Zhang C B, Huang K K, Gui W H. Digital twin driven soft sensing for key variables in zinc rotary kiln. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(4): 6673−6683 doi: 10.1109/TII.2023.3342443 [39] Liu J S, Jiang Z H, Gui W H, Chen Z W, Luo W C, Zhang C B. Digital twin modeling and transformer prediction-based overall particle size distribution online estimation. In: Proceedings of the China Automation Congress (CAC). Chongqing, China: IEEE, 2023. 757−762 [40] Luo W C, Huang K K, Liang X J, Ren H, Zhou N, Zhang C B, et al. Process manufacturing intelligence empowered by industrial metaverse: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(11): 6679−6692 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2024.3420958 [41] Wei J, Wang X Z, Schuurmans D, Bosma M, Ichter B, Xia F, et al. Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. Article No. 1800 [42] Yasunaga M, Bosselut A, Ren H Y, Zhang X K, Manning C D, Liang P, et al. Deep bidirectional language-knowledge graph pretraining. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. Article No. 2704 [43] Zhang Q G, Dong J N, Chen H, Zha D C, Yu Z L, Huang X. KnowGPT: Knowledge graph based prompting for large language models. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2024. Article No. 196 -




 下载:
下载: