-
摘要: 提出一种航天器编队的深度强化学习控制方法. 该方法通过引入动力学奖励, 考虑轨迹的动力学可行性并优化燃料消耗量. 在训练环境中, 引入$J_{2}$摄动相对动力学模型, 基于近端策略优化算法, 将航天器的局部观测信息作为策略网络和评价网络的输入. 策略网络输出航天器的期望位置和速度, 结合动力学模型限制策略任意动作之间的转换控制, 使输出轨迹考虑动力学可行性. 评价网络基于局部观测信息估计由动力学模型限制的优势函数, 从而辅助策略网络更新参数. 进一步地, 以燃料消耗量的负数作为动力学奖励, 结合避撞和任务相关奖励后, 训练得到的策略网络在完成航天器编队任务的同时优化了燃料消耗.Abstract: This paper presents a deep reinforcement learning control method for spacecraft formation. The method deals with the dynamical feasibility of the trajectory and optimizes the fuel consumption by introducing dynamical reward. Based on proximal policy optimization algorithm, a dynamic model of relative motion with $J_{2}$ perturbation is introduced in the training environment, and the inputs of Actor and Critic networks are the local observed information of the spacecraft. The outputs of the Actor network are the desired position and velocity of the spacecraft. Combining the dynamic model that restricts the control of transitions between two arbitrary actions of the strategy, the Actor network outputs the desired position and velocity, which makes the output trajectory account for the dynamical feasibility. The Critic network estimates the advantage function constrained by the dynamic model based on local observed information, therefore, the Actor network updates the parameters based on the advantage function. Further, the dynamical reward is defined as the negative value of the fuel consumption. As a result, combining collision avoidance and task-related rewards, the obtained Actor network achieves the distributed spacecraft formation task while optimizing the fuel consumption.
-
Key words:
- Deep reinforcement learning /
- spacecraft formation /
- distributed control /
- dynamics
-
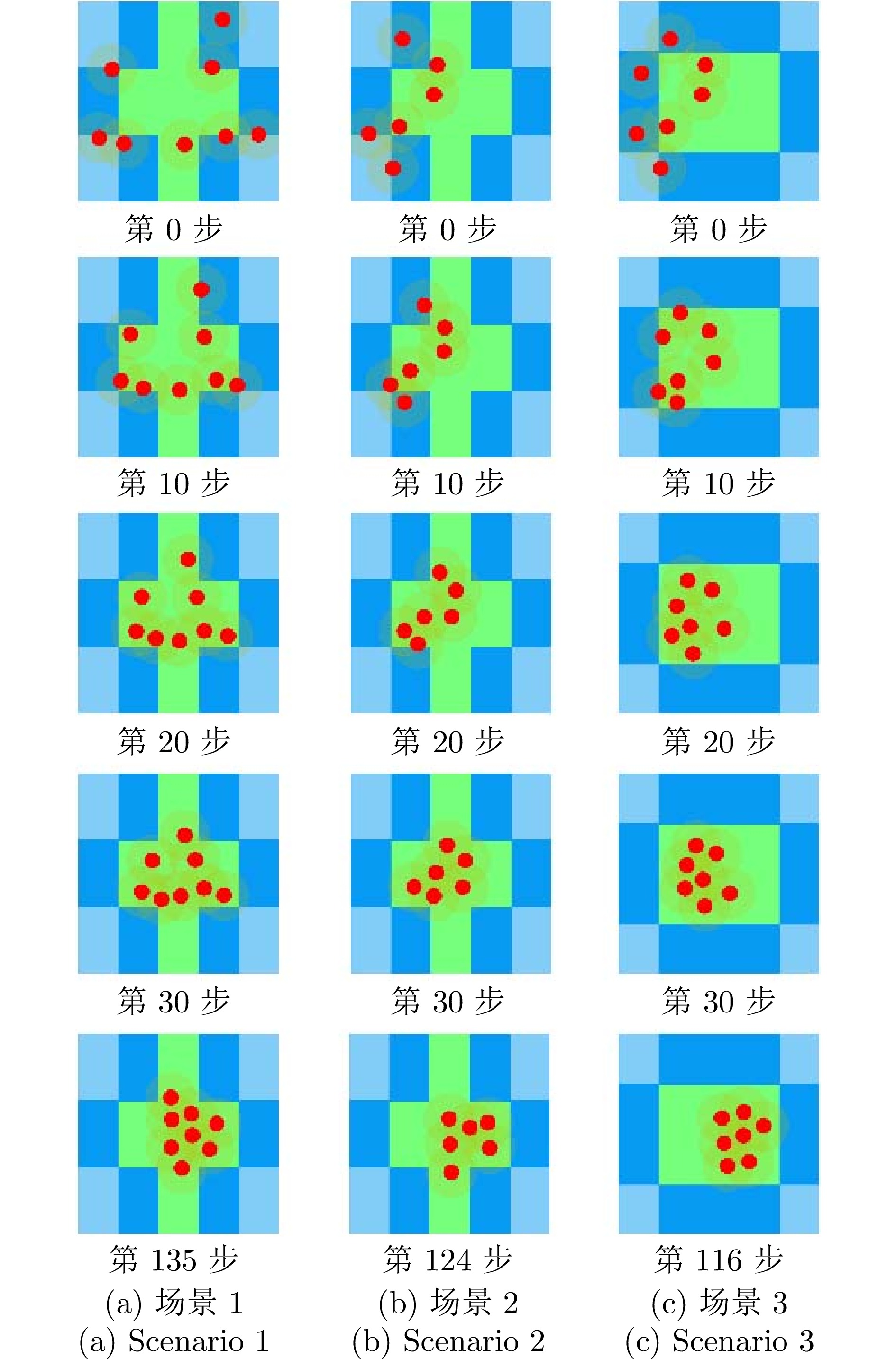
表 1 部分超参数取值
Table 1 The values of some hyperparameters
参数符号 含义 取值 $p$ 并行训练环境数 128 $\sigma $ 策略信息熵加权系数 $\{3\times10^{-3},\;3\times10^{-5}\}$ $\varepsilon,\; \delta $ 裁剪超参数 0.2 $\gamma $ 折扣因子 0.99 ${{u}_{\min }}$ 控制加速度下限 $-$0.001 m/s2 ${{u}_{\max }}$ 控制加速度上限 0.001 m/s2 $\dim({\boldsymbol{l}})$ 低功耗雷达检测数据数 90 ${{r}_{\text{b}}}$ 与边界碰撞的奖励 $-$500 ${{r}_{\text{inter}}}$ 相互碰撞的奖励 $-$10 ${{r}_{\text{base}}},\; {{r}_{\text{inc}}}$ 期望奖励相关超参数 1, 35 ${{\alpha }_{1}}$ 期望奖励加权系数 0.6 ${{l}_{r}}$ 学习率 $\{2\times10^{-4},\; 0\}$ $a$ 半长轴 7 100 km $\omega $ 近地点幅角 $-{{20}^{\circ }}$ $f$ 真近点角 ${{20}^{\circ }}$ $\Omega $ 升交点经度 $0^{\circ }$ $e$ 离心率 0.05 $i_{o}$ 轨道倾角 ${{15}^{\circ }}$ $k_{p},\; k_{i},\; k_{d}$ PID跟踪器参数 1.0, 0.01, 2.0 表 2 500轮后不同动力学奖励占比的结果
Table 2 Results under different percentages of dynamical reward after 500 epochs
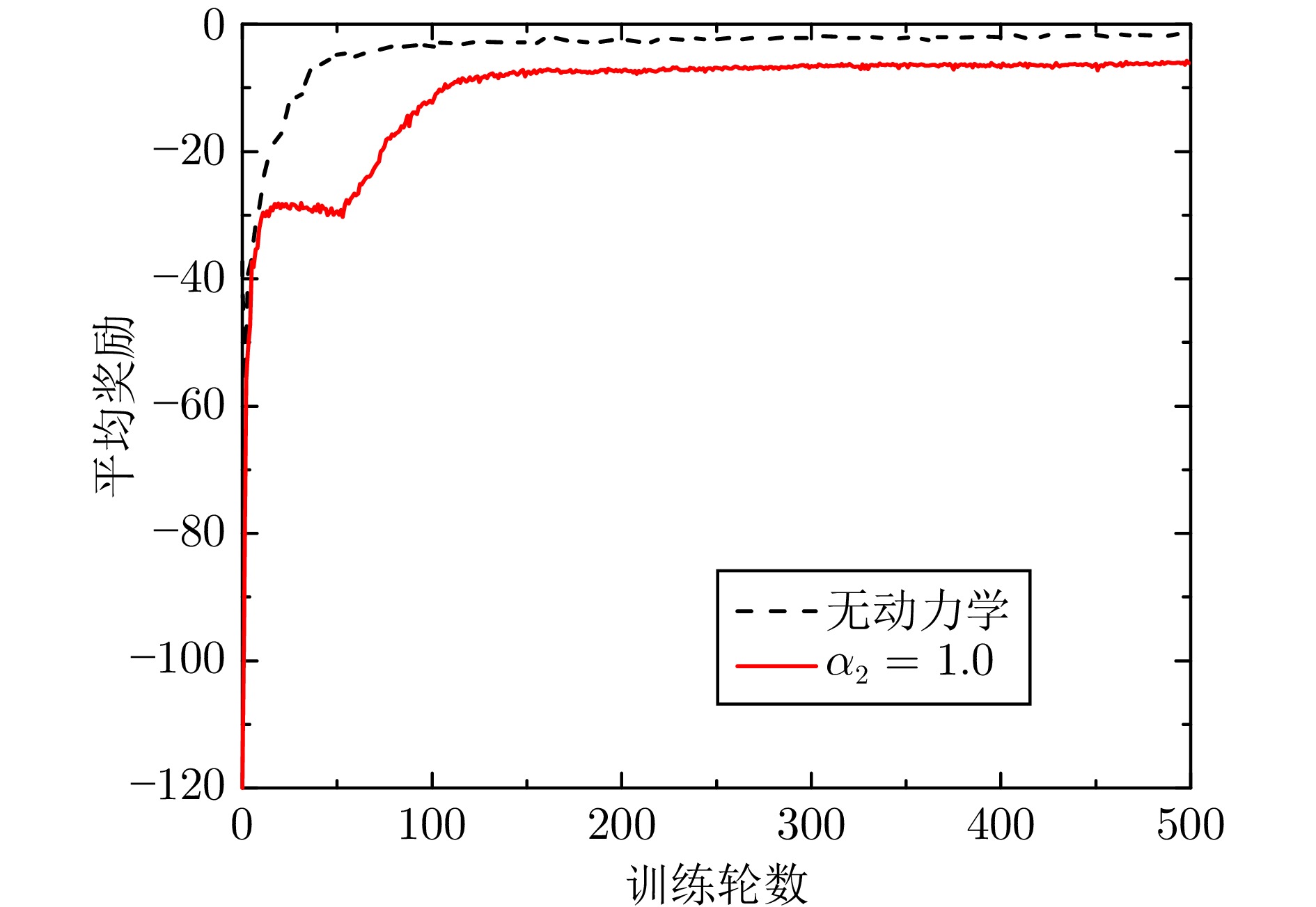
$\alpha_{2} $ 完成率(%) 平均完成步数 燃料消耗率(%) 燃料消耗绝对值 - 91.5 142.95 0 84.5 123.95 61.21 75.88 0.5 69.5 125.42 58.17 72.96 1.0 64.0 127.79 46.83 59.84 1.5 0 -
[1] Xue Z H, Liu J G, Wu C C, Tong Y C. Review of in-space assembly technologies. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2021, 34(11): 21−47 doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2020.09.043 [2] 马亚杰, 姜斌, 任好. 航天器位姿运动一体化直接自适应容错控制研究. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 678−686Ma Ya-Jie, Jiang Bin, Ren Hao. Adaptive direct fault-tolerant control design for spacecraft integrated attitude and orbit system. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 678−686 [3] Lymer J, Hanson M, Tadros A, Boccio J, Hollenstein B, Emerick K, et al. Commercial application of in-space assembly. In: Proceedings of the AIAA SPACE. Long Beach, USA: AIAA, 2016. 5236−5253 [4] Bartlett R O. NASA standard multimission modular spacecraft for future space exploration. In: Proceedings of the 16th Goddard Memorial Symposium. Washington, USA: American Astronautical Society and Deutsche Gesellschaft für Luft- und Raumfahrt, 1978. [5] 韦正涛. 模块化航天器自主组装控制及地面实验研究 [博士学位论文], 南京航空航天大学, 中国, 2023.Wei Zheng-Tao. Autonomous Assembly Control and Ground Experiment of Modular Spacecraft [Ph.D. dissertation], Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China, 2023. [6] Dennison K, Stacey N, D'Amico S. Autonomous asteroid characterization through nanosatellite swarming. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 4604−4624 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3245997 [7] Zheng S K, Li T J, Zhao J, Ma X F, Zhu J L, Huang Z R, et al. Deployment impact experiment and dynamic analysis of modular truss antenna. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2022: Article No. 2038932 [8] Burns R, McLaughlin C A, Leitner J, Martin M. TechSat 21: Formation design, control, and simulation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Aerospace Conference. Proceedings (Cat. No.00TH8484). Big Sky, USA: IEEE, 2000. 19−25 [9] Bonin G, Roth N, Armitage S, Newman J, Risi B, Zee R E. CanX-4 and CanX-5 precision formation flight: Mission accomplished! In: Proceedings of the 29th Annual AIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites. 2015. [10] 郑重, 李鹏, 钱默抒. 具有角速度和输入约束的航天器姿态协同控制. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(6): 1444−1452Zheng Zhong, Li Peng, Qian Mo-Shu. Spacecraft attitude coordination control with angular velocity and input constraints. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(6): 1444−1452 [11] Foust R C, Lupu E S, Nakka Y K, Chung S J, Hadaegh F Y. Autonomous in-orbit satellite assembly from a modular heterogeneous swarm. Acta Astronautica, 2020, 169: 191−205 doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.01.006 [12] Camacho E F, Bordons C. Model Predictive Control. London: Springer, 2007. [13] Ortolano N, Geller D K, Avery A. Autonomous optimal trajectory planning for orbital rendezvous, satellite inspection, and final approach based on convex optimization. The Journal of the Astronautical Sciences, 2021, 68(2): 444−479 doi: 10.1007/s40295-021-00260-5 [14] Basu H, Pedari Y, Almassalkhi M, Ossareh H R. Computationally efficient collision-free trajectory planning of satellite swarms under unmodeled orbital perturbations. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2023, 46(8): 1548−1563 [15] 于杰. 基于深度强化学习的多智能体协同包围算法研究 [硕士学位论文], 哈尔滨理工大学, 中国, 2024.Yu Jie. Research on Multi-agent Cooperative Encirclement Algorithm Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning [Master thesis], Harbin University of Science and Technology, China, 2024. [16] 王龙, 黄锋. 多智能体博弈、学习与控制. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 580−613Wang Long, Huang Feng. An interdisciplinary survey of multi-agent games, learning, and control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 580−613 [17] 赵春宇, 赖俊. 元强化学习综述. 计算机应用研究, 2023, 40(1): 1−10Zhao Chun-Yu, Lai Jun. Survey on meta reinforcement learning. Application Research of Computers, 2023, 40(1): 1−10 [18] Luo B, Wu H N, Huang T W. Off-policy reinforcement learning for ${H_{\infty}}$ control design. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2015, 45(1): 65−76 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2319577 [19] Vamvoudakis K G, Lewis F L. Online solution of nonlinear two-player zero-sum games using synchronous policy iteration. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2012, 22(13): 1460−1483 doi: 10.1002/rnc.1760 [20] Yan C, Xiang X J, Wang C. Fixed-wing UAVs flocking in continuous spaces: A deep reinforcement learning approach. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2020, 131: Article No. 103594 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2020.103594 [21] Xu D, Guo Y X, Yu Z Y, Wang Z F, Lan R Z, Zhao R H, et al. PPO-exp: Keeping fixed-wing UAV formation with deep reinforcement learning. Drones, 2023, 7(1): Article No. 28 [22] Chen Y F, Liu M, Everett M, How J P. Decentralized non-communicating multiagent collision avoidance with deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Singapore: IEEE, 2017. 285−292 [23] 胡成. 基于深度强化学习的多智能体协作关键技术研究 [博士学位论文], 北京邮电大学, 中国, 2025.Hu Cheng. Research on Key Technologies of Multi-agent Collaboration Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning [Ph.D. dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China, 2025. [24] Wang D W, Wu B L, Poh E K. Satellite Formation Flying. Singapore: Springer, 2017. [25] Hansen E A, Bernstein D S, Zilberstein S. Dynamic programming for partially observable stochastic games. In: Proceedings of the 19th National Conference on Artifical Intelligence. San Jose, USA: AAAI, 2004. 709−715 [26] 温广辉, 杨涛, 周佳玲, 付俊杰, 徐磊. 强化学习与自适应动态规划: 从基础理论到多智能体系统中的应用进展综述. 控制与决策, 2023, 38(5): 1200−1230Wen Guang-Hui, Yang Tao, Zhou Jia-Ling, Fu Jun-Jie, Xu Lei. Reinforcement learning and adaptive/approximate dynamic programming: A survey from theory to applications in multi-agent systems. Control and Decision, 2023, 38(5): 1200−1230 [27] Schulman J, Wolski F, Dhariwal P, Radford A, Klimov O. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1707.06347, 2017. [28] Yu C, Velu A, Vinitsky E, Gao J X, Wang Y, Bayen A, et al. The surprising effectiveness of PPO in cooperative multi-agent games. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. Article No. 1787 [29] Zhao S Y. Mathematical Foundations of Reinforcement Learning. Singapore: Springer, 2025. -




 下载:
下载: