Intelligent Particle Filter for Real-time Measurement of Rotary Steerable Drilling Tool System
-
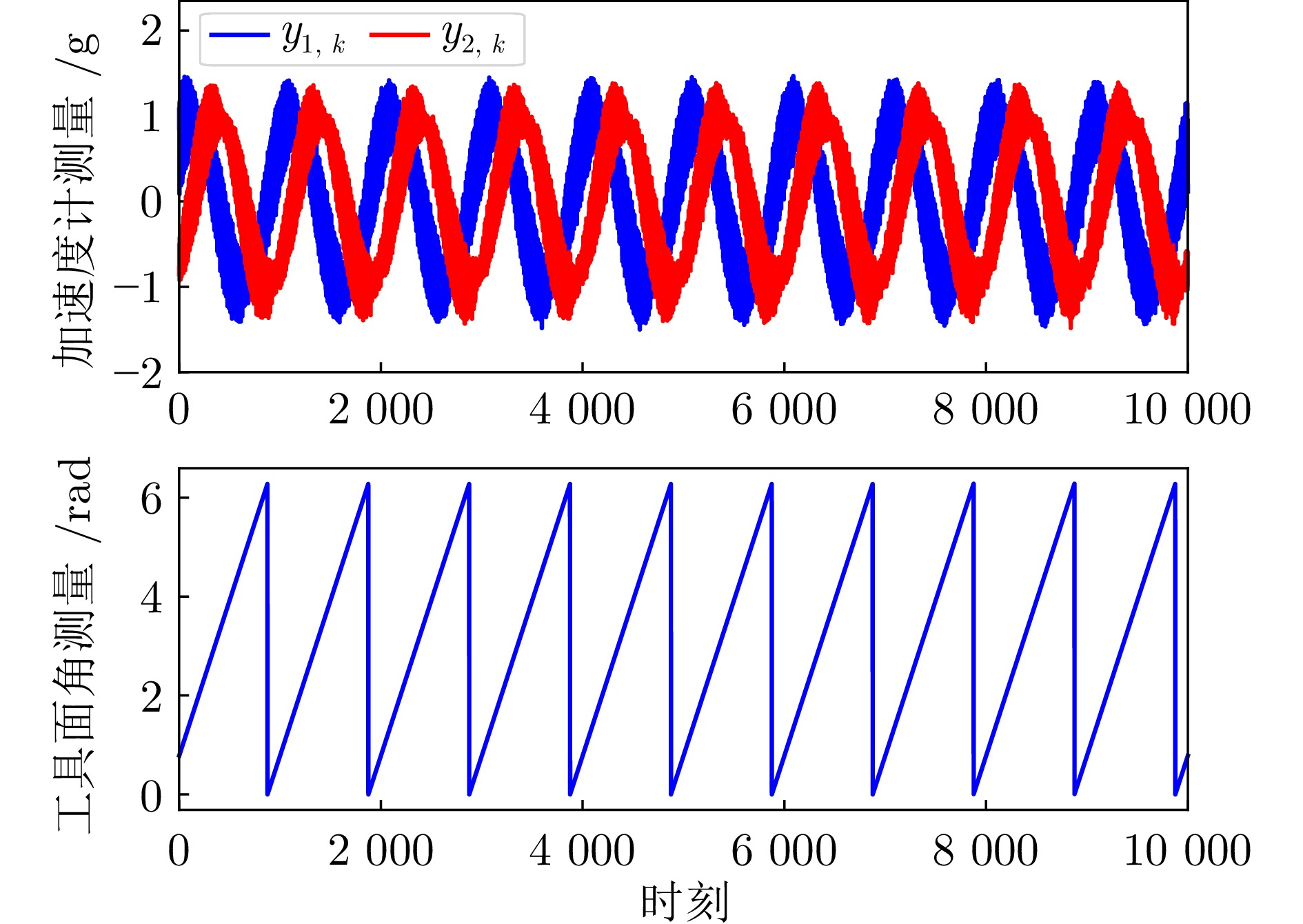
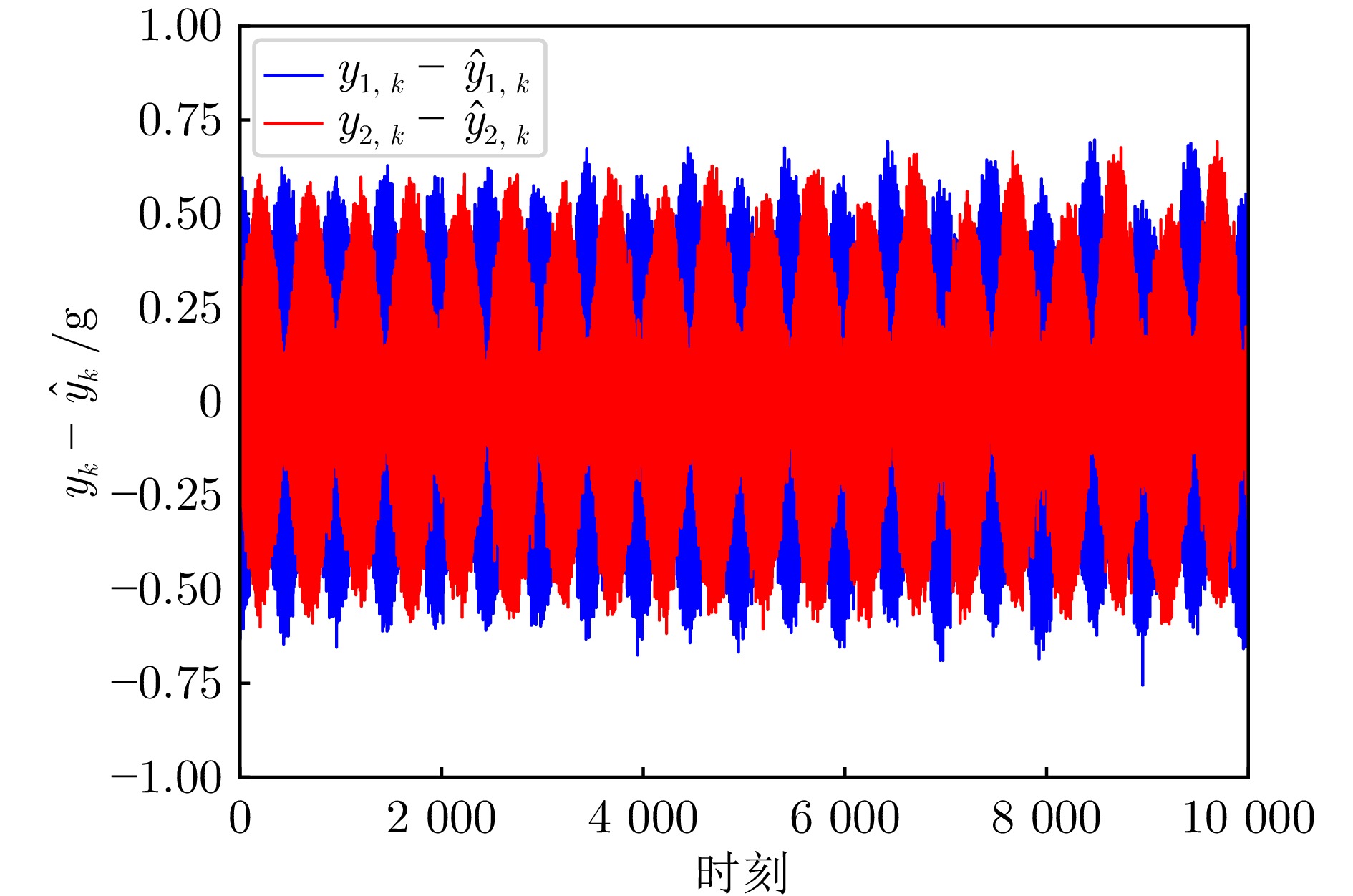
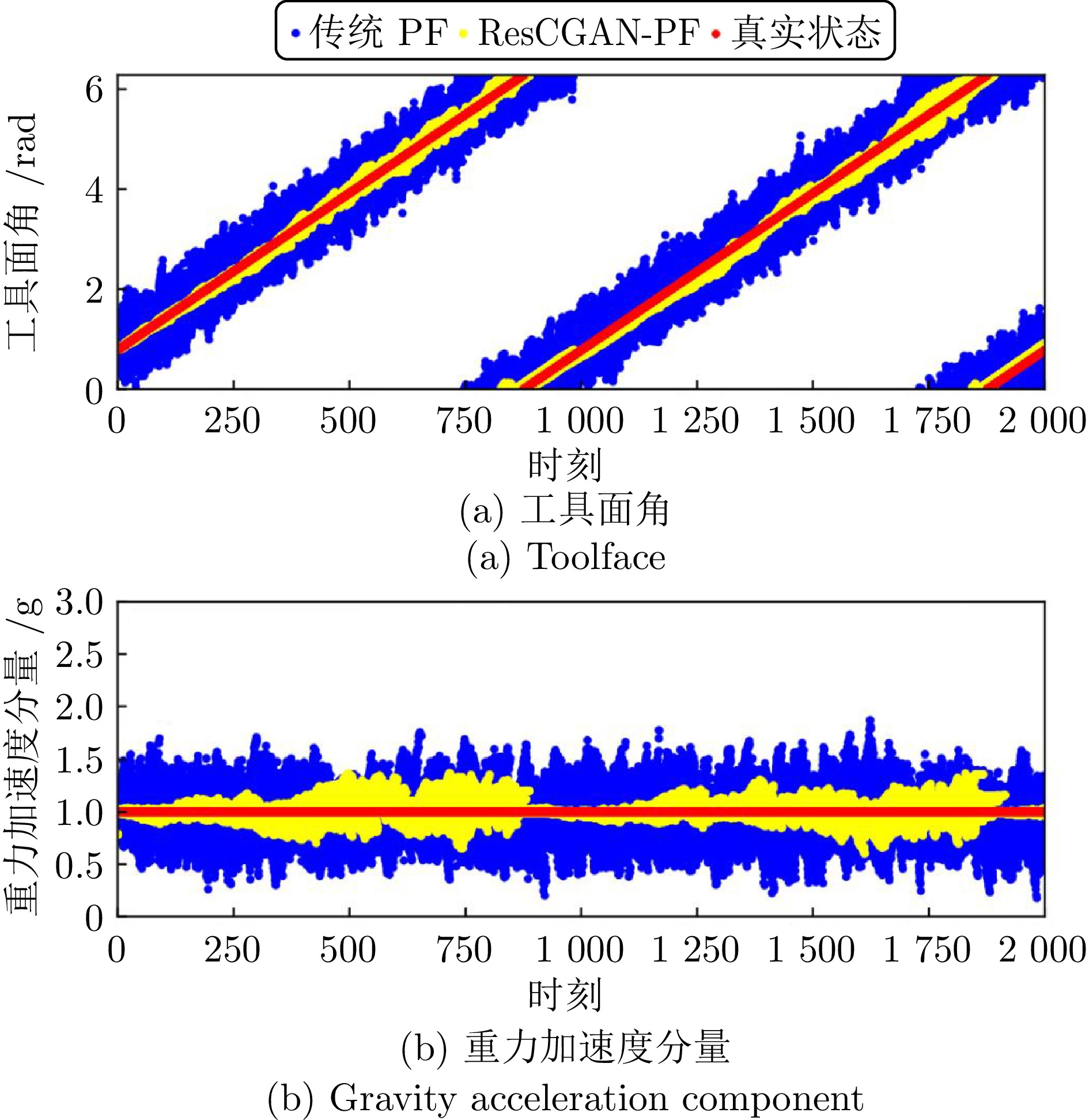
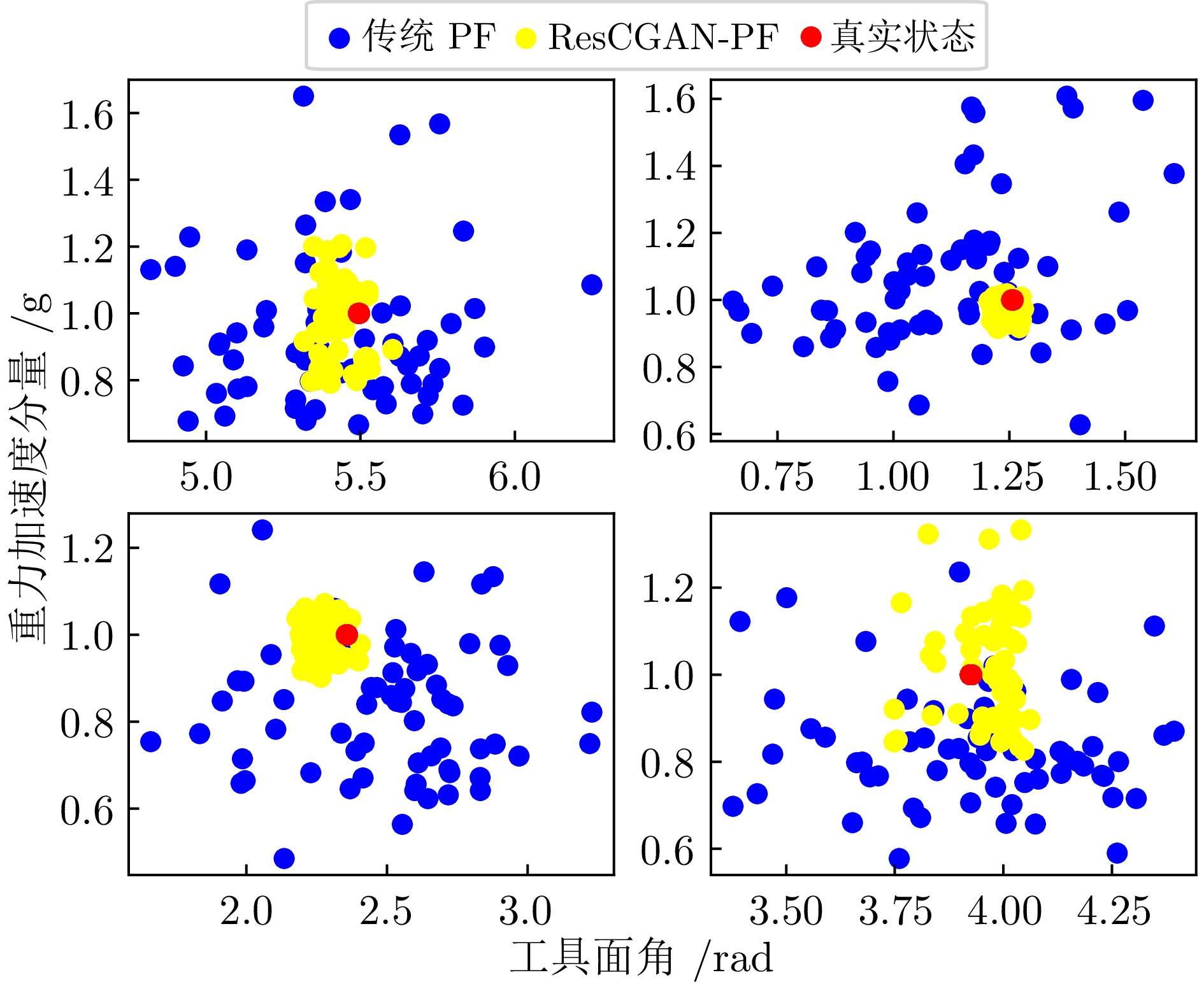
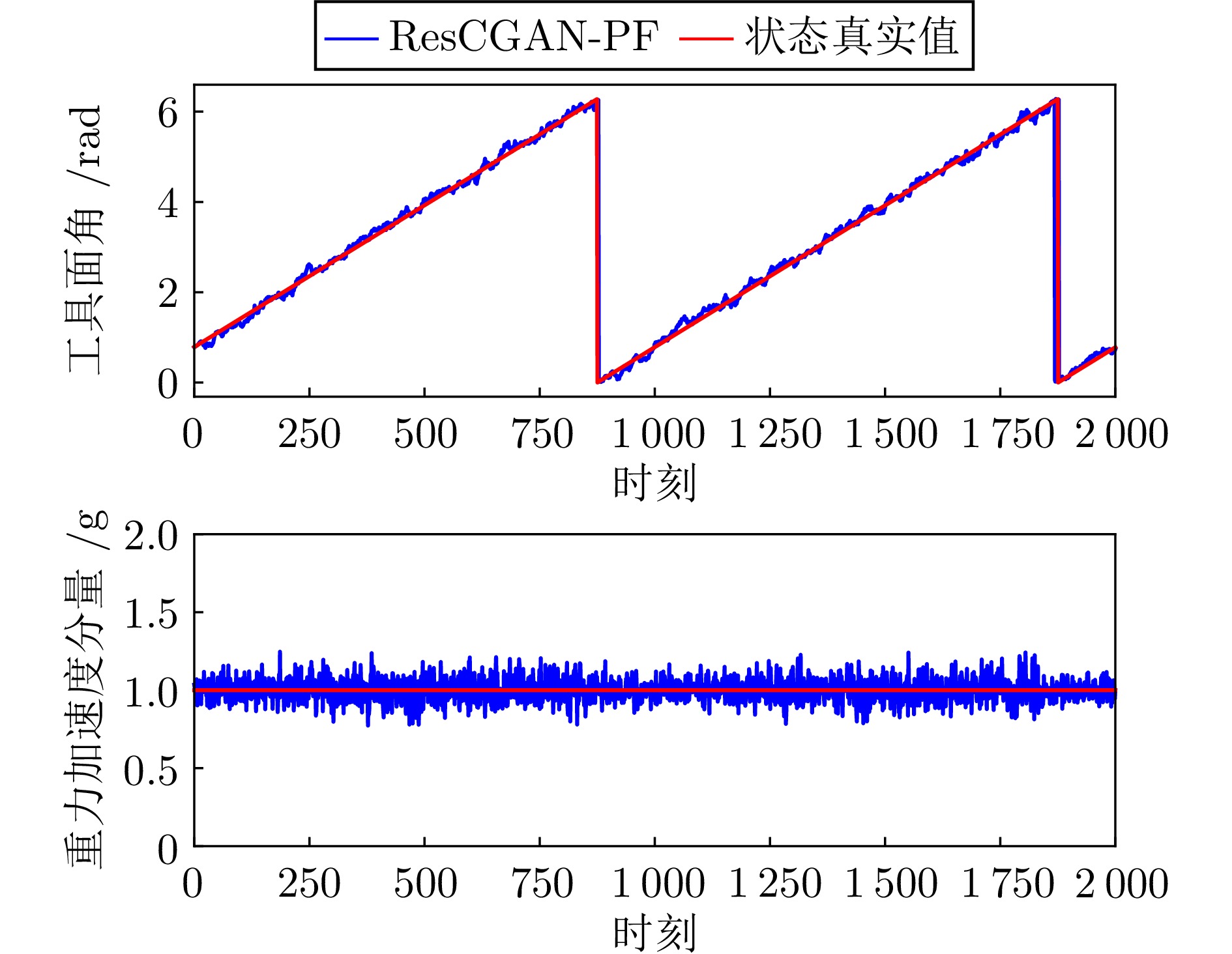
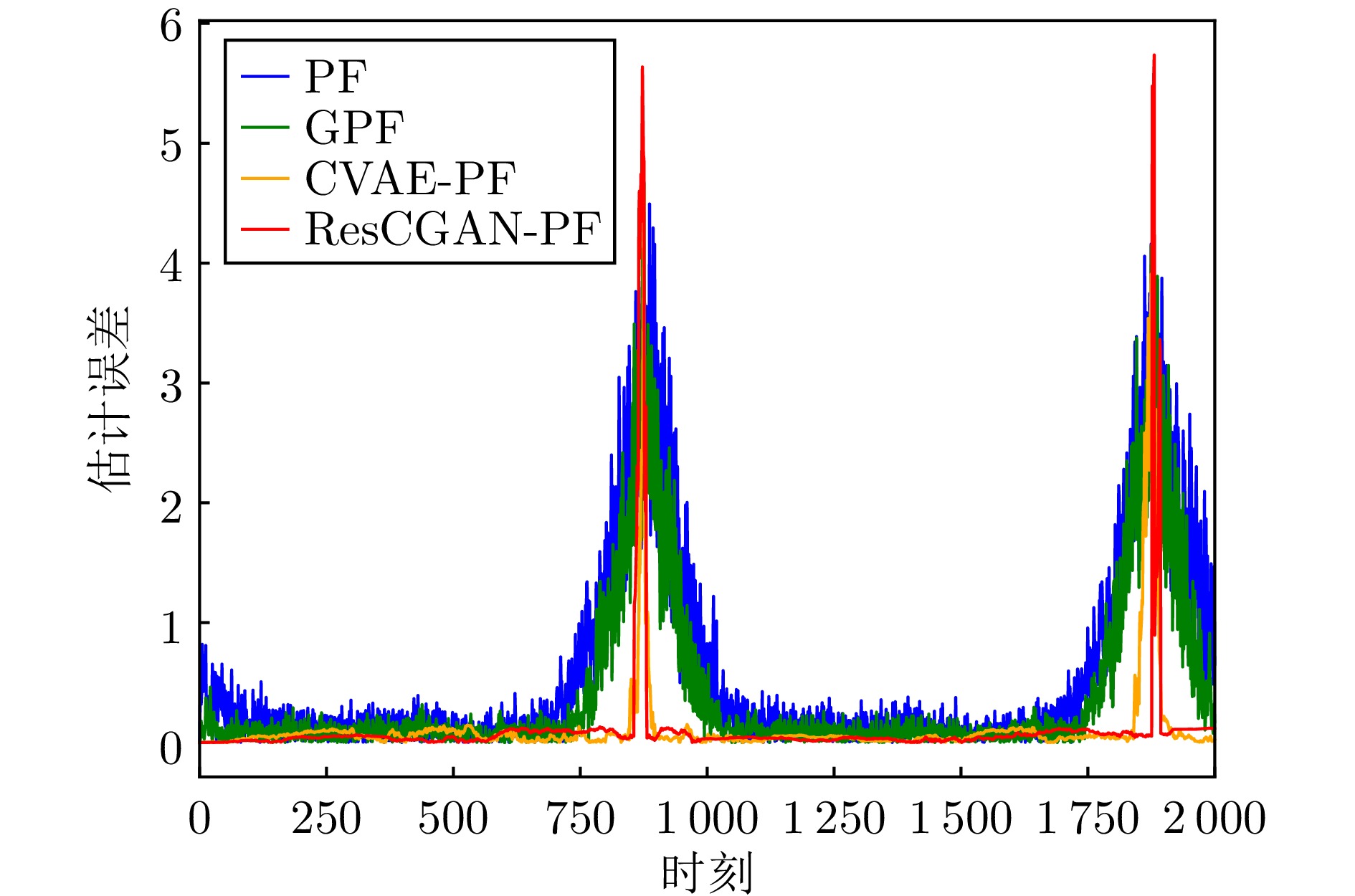
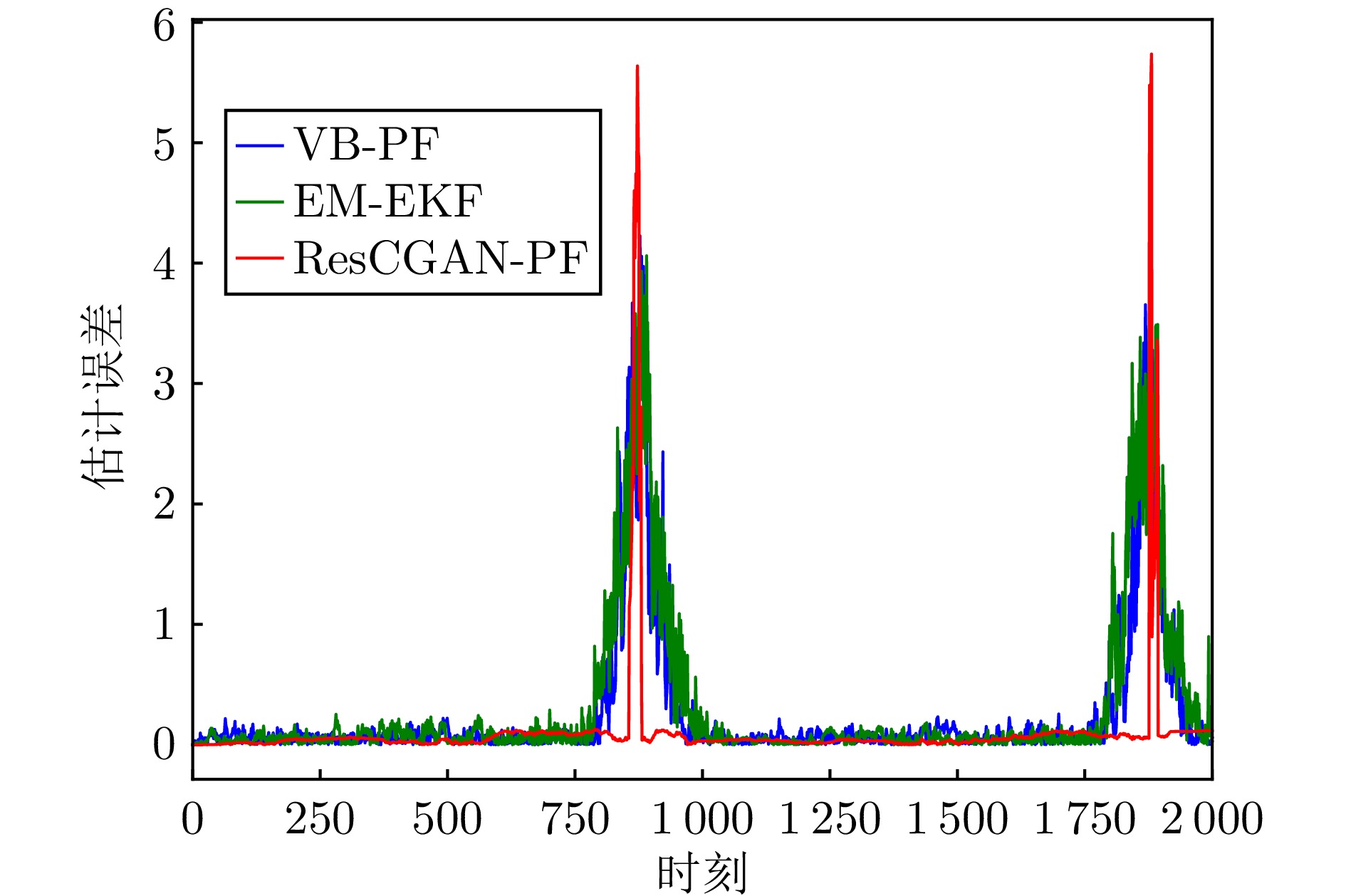
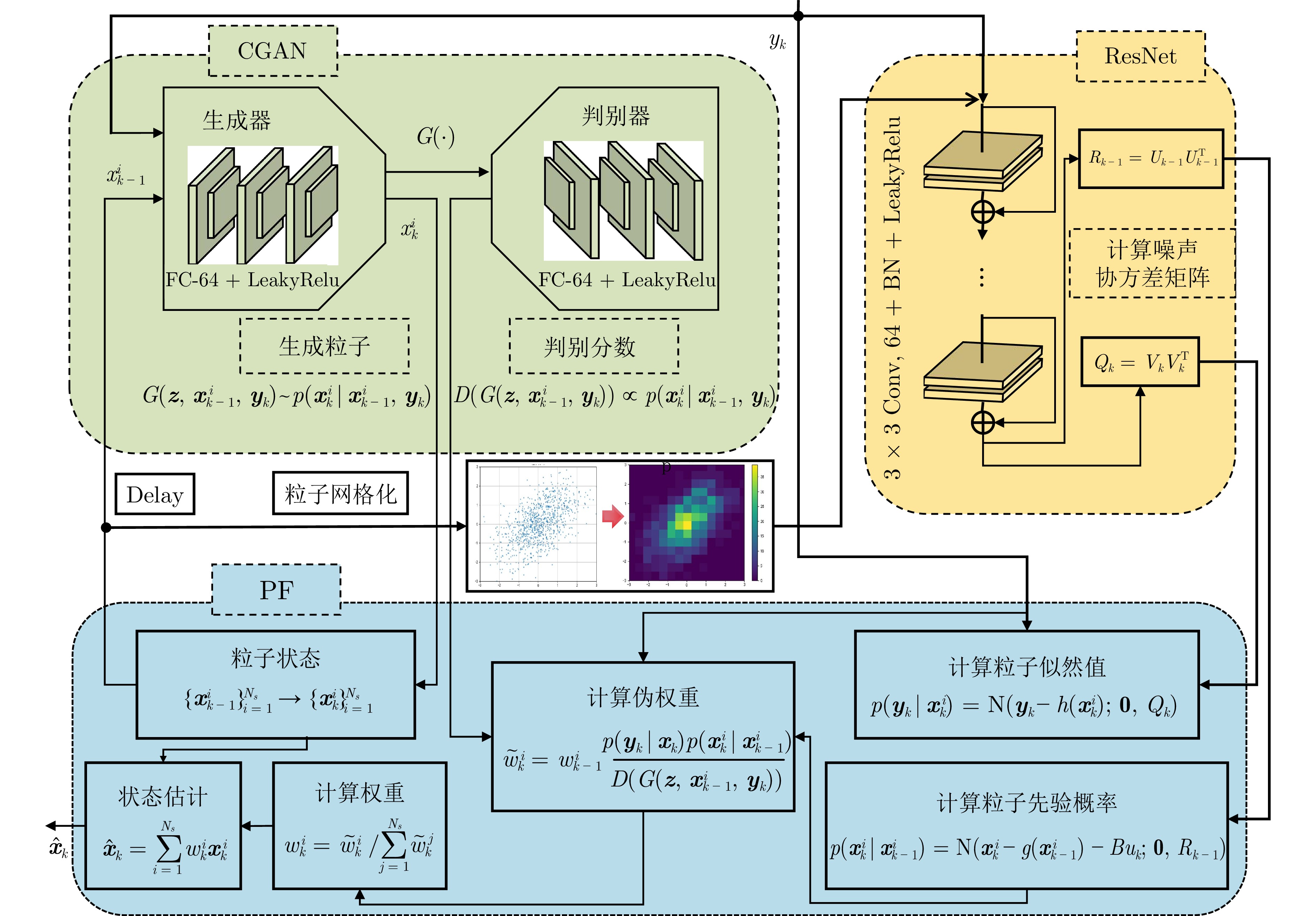
摘要: 针对旋转导向钻井工具系统中工具面角的实时测量问题, 提出一种基于深度学习的智能粒子滤波算法. 首先, 针对粒子滤波中的粒子短缺与退化问题, 建立条件生成对抗网络(CGAN)引导的粒子选择机制. 在该机制中, 生成器网络通过对抗训练优化采样分布, 生成高质量粒子集; 判别器则评估生成粒子在真实后验分布中的概率值, 指导粒子权重计算. 其次, 针对井下复杂工况中存在的噪声协方差矩阵未知且时变问题, 设计基于深度残差网络(ResNet)的协方差矩阵估计器. 该模块与CGAN引导的粒子滤波以端到端的方式集成, 形成闭环优化系统. ResNet模块得益于粒子滤波算法中的模型信息, 并为粒子滤波提供协方差矩阵的估计. 最后, 在旋转导向钻井工具平台上进行实验. 结果表明所提算法能够有效解决工具面角的实时测量问题, 与已有算法相比具有更高的精度.
-
关键词:
- 智能粒子滤波 /
- 旋转导向钻井工具系统 /
- 实时测量 /
- 深度学习算法 /
- 未知噪声协方差矩阵
Abstract: To address the real-time measurement challenge of Toolface in rotary steerable drilling tool system, this paper proposes an intelligent particle filtering algorithm based on deep learning. Initially, the particle selection mechanism guided by conditional generative adversarial network (CGAN) is established to tackle the issues of particle impoverishment and degeneracy in particle filtering. In this mechanism, the generator network optimizes the sampling distribution through adversarial training, producing a high-quality set of particles; The discriminator evaluates the probability of the generated particles within the true posterior distribution, guiding the particle weight calculation. Subsequently, the covariance matrix estimator is designed based on a deep residual network (ResNet) to address the unknown but time-varying noise covariance matrices in complex downhole conditions. This module is integrated with the CGAN-guided particle filter in an end-to-end manner, forming a closed-loop optimization system. The ResNet module benefits from the model information in the particle filtering algorithm and provides the particle filter with estimates of the covariance matrices. Finally, experiments are conducted on the rotary steerable drilling tool platform. The results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm effectively addresses the real-time measurement issue of Toolface and exhibits higher accuracy compared with existing algorithms. -
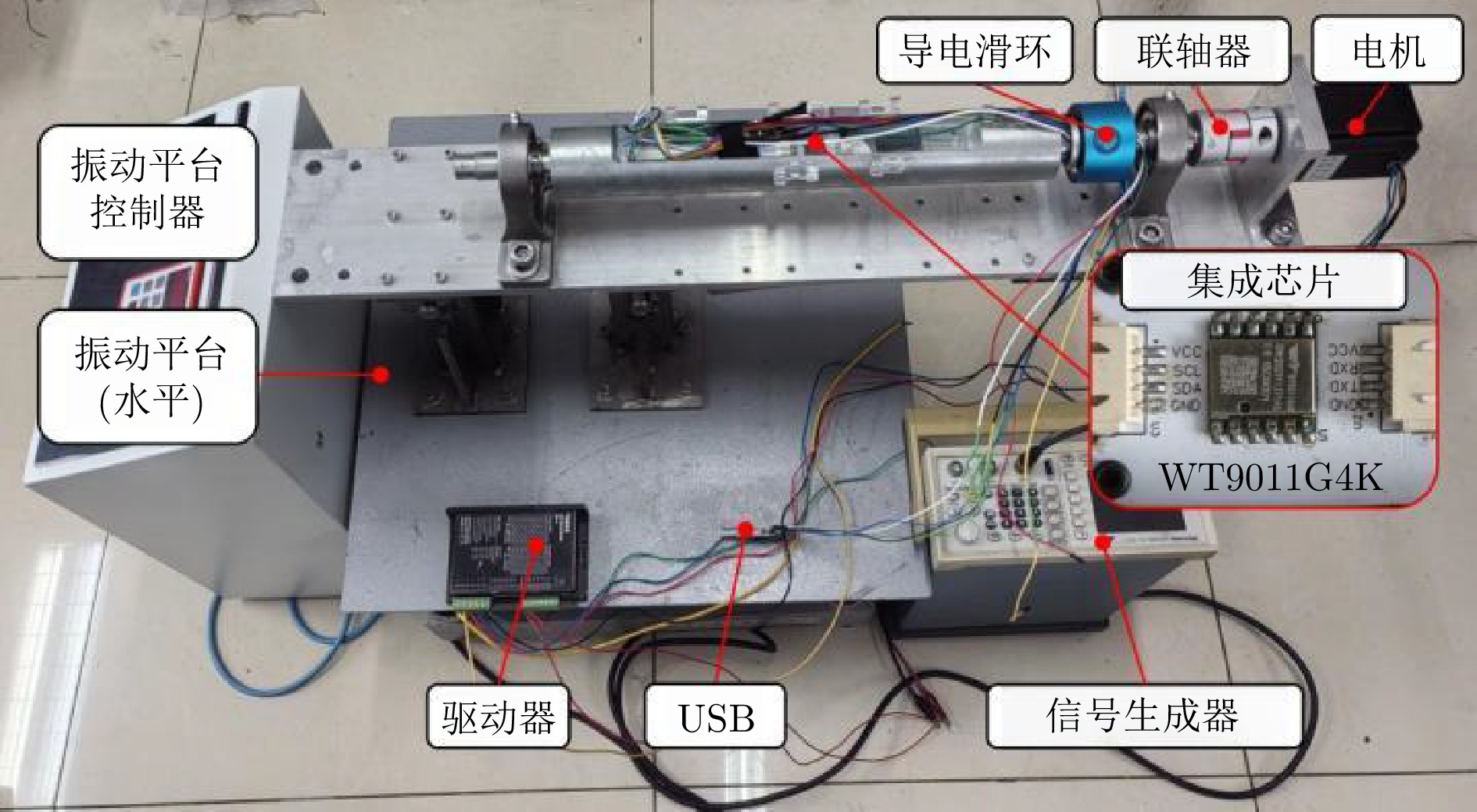
表 1 WT9011G4K芯片参数
Table 1 Parameters of chip WT9011G4K
参数 加速度计 陀螺仪 测量范围 16 g ± 4 000°/s 误差 0.0005 g0.061°/s 温漂 + 0.00015 g/℃0.005(°/s)/℃ 采样频率 5 ~ 256 Hz 5 ~ 256 Hz -
[1] 盛立, 牛艺春, 刘诗洋, 王伟亮, 高明, 周东华. 旋转导向钻井工具装备的微小故障检测. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2022, 52(11): 2106−2120Sheng Li, Niu Yi-Chun, Liu Shi-Yang, Wang Wei-Liang, Gao Ming, Zhou Dong-Hua. Incipient fault detection of rotary steerable drilling tool equipment. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2022, 52(11): 2106−2120 [2] Xue Q L, Wang R H, Sun F, Huang L L, Han L J. Continuous measurement-while-drilling utilizing strap-down multi-model surveying system. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2014, 63(3): 650−657 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2013.2282412 [3] Sheng L, Niu Y, Wang W L, Gao M, Geng Y F, Zhou D H. Estimation of Toolface for dynamic point-the-bit rotary steerable systems via nonlinear polynomial filtering. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(7): 7192−7201 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3097601 [4] Niu Y, Sheng L, Gao M, Wang Y C, Zhou D H. Variational Bayesian-based moving horizon estimation of Toolface for rotary steerable drilling tool systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(1): 813−823 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3153829 [5] Sheng L, Niu Y C, Gao M, Geng Y F, Zhou D H. Particle filter-based fault detection for Toolface measurement of rotary steerable systems. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: Article No. 3519511 [6] Arulampala M S, Maskell S, Gordon N, Clapp T. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(2): 174−188 doi: 10.1109/78.978374 [7] Liu J S, Chen R. Sequential Monte Carlo methods for dynamic systems. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1998, 93(443): 1032−1044 doi: 10.1080/01621459.1998.10473765 [8] Yin S, Zhu X P. Intelligent particle filter and its application to fault detection of nonlinear system. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(6): 3852−3861 [9] 田梦楚, 薄煜明, 陈志敏, 吴盘龙, 赵高鹏. 萤火虫算法智能优化粒子滤波. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(1): 89−97Tian Meng-Chu, Bo Yu-Ming, Chen Zhi-Min, Wu Pan-Long, Zhao Gao-Peng. Firefly algorithm intelligence optimized particle filter. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(1): 89−97 [10] Li T C, Sun S D, Sattar T P, Corchado J M. Fight sample degeneracy and impoverishment in particle filters: A review of intelligent approaches. Expert Systems With Applications, 2014, 41(8): 3944−3954 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2013.12.031 [11] 张文安, 林安迪, 杨旭升, 俞立, 杨小牛. 融合深度学习的贝叶斯滤波综述. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(8): 1502−1516Zhang Wen-An, Lin An-Di, Yang Xu-Sheng, Yu Li, Yang Xiao-Niu. A survey on Bayesian filtering with deep learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(8): 1502−1516 [12] Ma M, Fu L, Zhai Z, Sun R B. Transformer based Kalman filter with EM algorithm for time series prediction and anomaly detection of complex systems. Measurement, 2024, 229: Article No. 114378 doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2024.114378 [13] Qian Y N, Yan R Q. Remaining useful life prediction of rolling bearings using an enhanced particle filter. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2015, 64(10): 2696−2707 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2015.2427891 [14] Jiao R H, Peng K X, Dong J. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ton batteries based on conditional variational autoencoders-particle filter. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(11): 8831−8843 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.2996004 [15] Huang Y, Zhang Y, Xu B, Wu Z, Chambers A. A new adaptive extended Kalman filter for cooperative localization. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(1): 353−368 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2756763 [16] Niu Y, Sheng L, Gao M, Zhou D H. Moving horizon estimation for stochastic descriptor systems with inaccurate noise covariance matrices. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(8): 9530−9540 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3325555 [17] Li K, Zhao S Y, Liu F. Joint state estimation for nonlinear state-space model with unknown time-variant noise statistics. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 2021, 35(4): 498−512 doi: 10.1002/acs.3208 [18] Bertipaglia A, Alirezaei M, Happee R, Shyrokau B. An unscented Kalman filter-informed neural network for vehicle sideslip angle estimation. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(9): 12731−12746 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3389493 [19] Zhang Y P, Huang Y F, Deng K, Shi B F, Wang X Y, Li L, et al. Vehicle dynamics estimator utilizing LSTM-ensembled adaptive Kalman filter. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2025, 72(5): 5429−5439 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2024.3482011 [20] Zeng G X, Wu H, Chen S X, Yang M B. Modified Swin Transformer-based continuous-discrete extended Kalman filtering for bearings-only tracking with unknown noise statistics. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2025, 25(3): 9842−9852 [21] Ahwiadi M, Wang W. An adaptive particle filter technique for system state estimation and prognosis. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(9): 6756−6765 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.2973850 [22] 王坤峰, 苟超, 段艳杰, 林懿伦, 郑心湖, 王飞跃. 生成式对抗网络GAN的研究进展与展望. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(3): 321−332Wang Kun-Feng, Gou Chao, Duan Yan-Jie, Lin Yi-Lun, Zheng Xin-Hu, Wang Fei-Yue. Generative adversarial networks: The state of the art and beyond. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(3): 321−332 [23] 刘建伟, 谢浩杰, 罗雄麟. 生成对抗网络在各领域应用研究进展. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(12): 2500−2536Liu Jian-Wei, Xie Hao-Jie, Luo Xiong-Lin. Research progress on application of generative adversarial networks in various fields. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(12): 2500−2536 [24] 胡铭菲, 左信, 刘建伟. 深度生成模型综述. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 40−74Hu Ming-Fei, Zuo Xin, Liu Jian-Wei. Survey on deep generative model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 40−74 -




 下载:
下载: