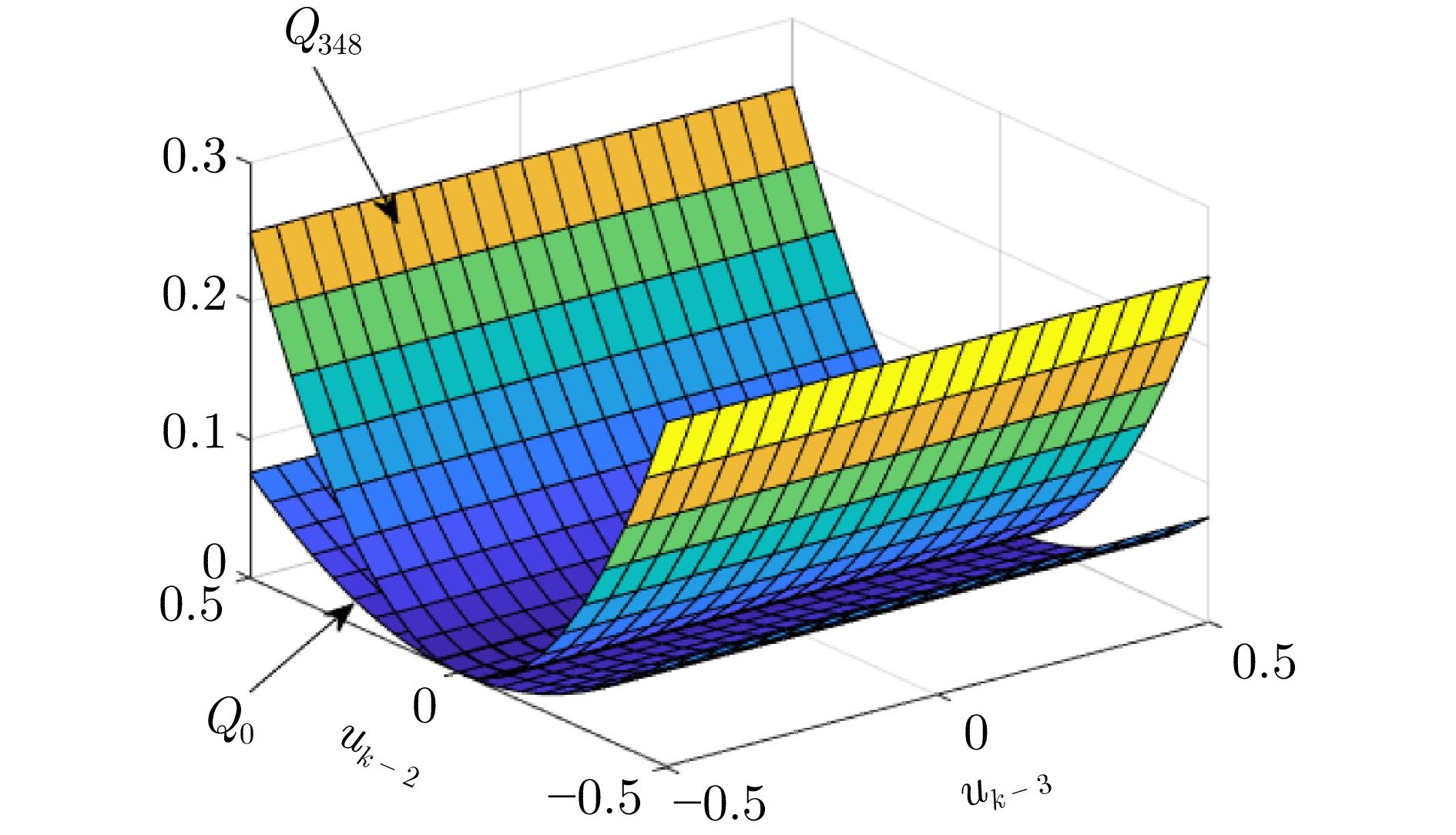
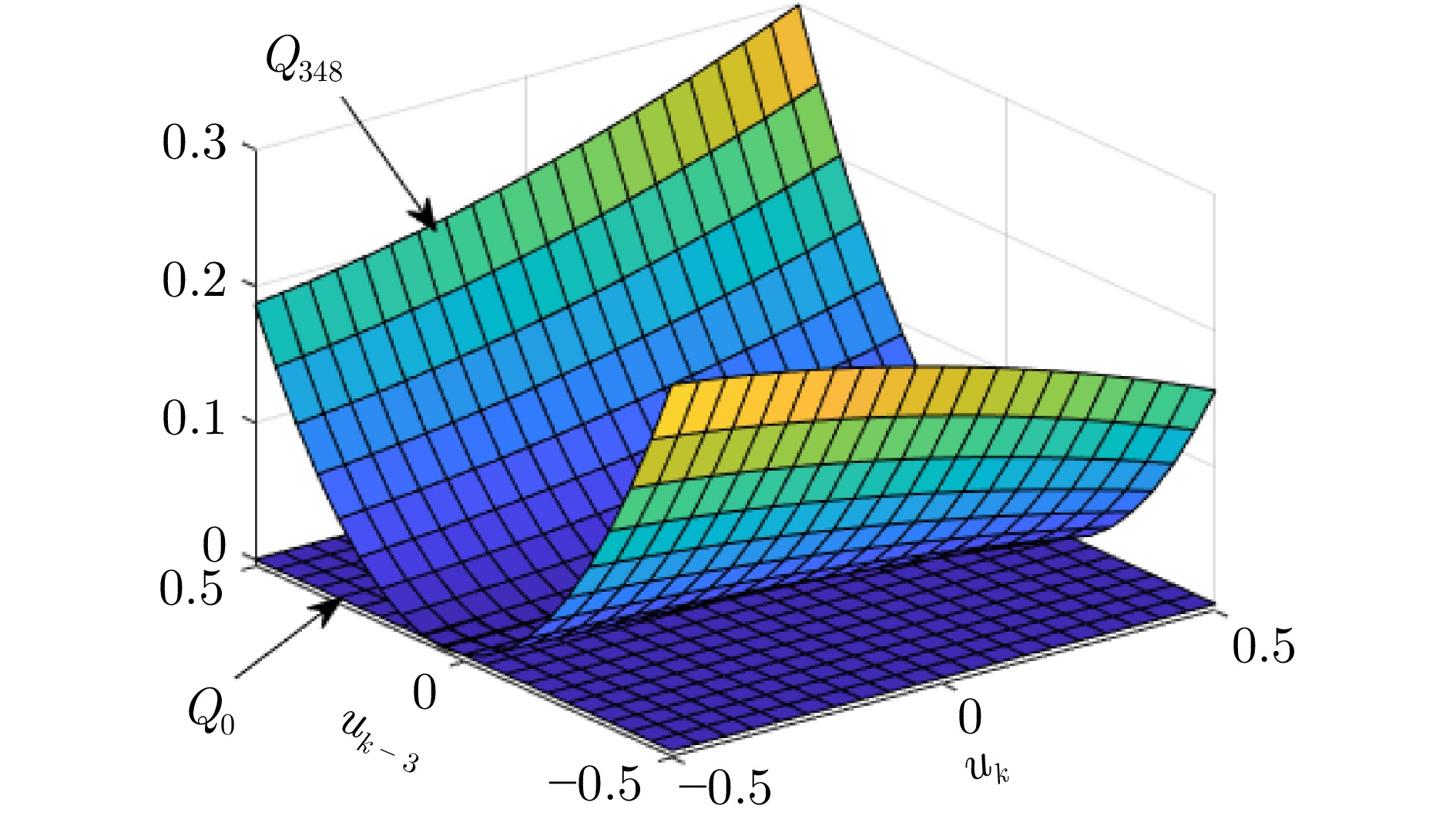
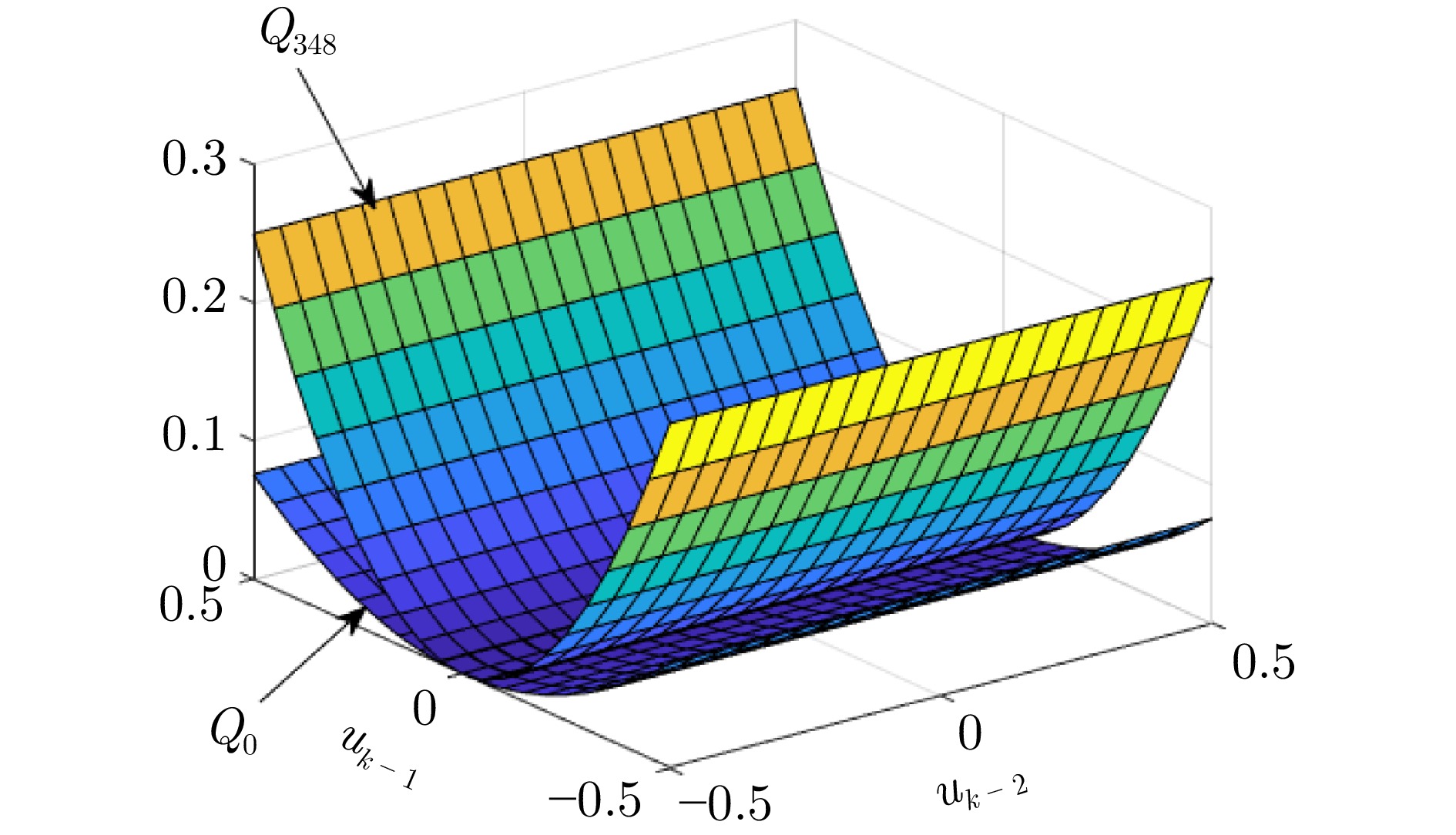
|
[1]
|
Lewis F L, Vrabie D L, Syrmos V L. Optimal Control. Hoboken: Wiley, 2012.
|
|
[2]
|
Gao W N, Jiang Z P, Chai T Y. Bridging the gap between reinforcement learning and nonlinear output-feedback control. In: Proceedings of the 43rd Chinese Control Conference (CCC). Kunming, China: IEEE, 2024. 2425−2431
|
|
[3]
|
Gao W N, Jiang Z P. Data-driven cooperative output regulation of multi-agent systems under distributed denial of service attacks. Science China Information Sciences, 2023, 66(9): Article No. 190201 doi: 10.1007/s11432-022-3702-4
|
|
[4]
|
Hou Z S, Wang Z. From model-based control to data-driven control: Survey, classification and perspective. Information Sciences, 2013, 235: 3−35 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2012.07.014
|
|
[5]
|
Bu X H, Yu Q X, Hou Z S, Qian W. Model free adaptive iterative learning consensus tracking control for a class of nonlinear multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 49(4): 677−686 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2734799
|
|
[6]
|
Hou Z S, Xiong S S. On model-free adaptive control and its stability analysis. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(11): 4555−4569 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2894586
|
|
[7]
|
Liu S D, Lin G, Ji H H, Jin S T, Hou Z S. A novel enhanced data-driven model-free adaptive control scheme for path tracking of autonomous vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2025, 26(1): 579−590 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2024.3487299
|
|
[8]
|
Xiong S S, Hou Z S. Model-free adaptive control for unknown MIMO nonaffine nonlinear discrete-time systems with experimental validation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(4): 1727−1739 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3043711
|
|
[9]
|
董昱辰, 高伟男, 姜钟平. 基于分布式自适应内模的多智能体系统协同最优输出调节. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(3): 678−691Dong Yu-Chen, Gao Wei-Nan, Jiang Zhong-Ping. Cooperative optimal output regulation for multi-agent systems based on distributed adaptive internal model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(3): 678−691
|
|
[10]
|
Lewis F L, Liu D R. Reinforcement Learning and Approximate Dynamic Programming for Feedback Control. Hoboken: Wiley, 2013.
|
|
[11]
|
Vrabie D, Vamvoudakis K G, Lewis F L. Optimal Adaptive Control and Differential Games by Reinforcement Learning Principles. London: Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2013.
|
|
[12]
|
Jiang Y, Jiang Z P. Global adaptive dynamic programming for continuous-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 60(11): 2917−2929 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2414811
|
|
[13]
|
Wei Q L, Liu D R, Liu Y, Song R Z. Optimal constrained self-learning battery sequential management in microgrid via adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2017, 4(2): 168−176 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2016.7510262
|
|
[14]
|
Zhang H G, Liu D R, Luo Y H, Wang D. Adaptive Dynamic Programming for Control: Algorithms and Stability. London: Springer, 2013.
|
|
[15]
|
Lewis F L, Vrabie D, Vamvoudakis K G. Reinforcement learning and feedback control: Using natural decision methods to design optimal adaptive controllers. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2012, 32(6): 76−105 doi: 10.1109/MCS.2012.2214134
|
|
[16]
|
Liu D R, Wei Q L, Wang D, Yang X, Li H L. Adaptive Dynamic Programming With Applications in Optimal Control. Cham: Springer, 2017.
|
|
[17]
|
Yang Y L, Modares H, Vamvoudakis K G, He W, Xu C Z, Wunsch D C. Hamiltonian-driven adaptive dynamic programming with approximation errors. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(12): 13762−13773 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3108034
|
|
[18]
|
Gao W N, Jiang Z P. Learning-based adaptive optimal output regulation of linear and nonlinear systems: An overview. Control Theory and Technology, 2022, 20(1): 1−19 doi: 10.1007/s11768-022-00081-3
|
|
[19]
|
Liu D R, Wei Q L. Policy iteration adaptive dynamic programming algorithm for discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(3): 621−634 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2281663
|
|
[20]
|
Li C, Liu D R, Wang D. Data-based optimal control for weakly coupled nonlinear systems using policy iteration. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2018, 48(4): 511−521 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2016.2606479
|
|
[21]
|
Zhao B, Wang D, Shi G, Liu D R, Li Y C. Decentralized control for large-scale nonlinear systems with unknown mismatched interconnections via policy iteration. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2018, 48(10): 1725−1735 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2690665
|
|
[22]
|
Gao W N, Jiang Z P, Chai T Y. Resilient control under denial-of-service and uncertainty: An adaptive dynamic programming approach. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2025, 70(6): 4085−4092 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2025.3527305
|
|
[23]
|
Jiang Y, Jiang Z P. Computational adaptive optimal control for continuous-time linear systems with completely unknown dynamics. Automatica, 2012, 48(10): 2699−2704 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2012.06.096
|
|
[24]
|
Kleinman D. On an iterative technique for Riccati equation computations. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1968, 13(1): 114−115 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1968.1098829
|
|
[25]
|
Wei Q L, Liu D R, Lin H Q. Value iteration adaptive dynamic programming for optimal control of discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(3): 840−853 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2492242
|
|
[26]
|
Gao W N, Mynuddin M, Wunsch D C, Jiang Z P. Reinforcement learning-based cooperative optimal output regulation via distributed adaptive internal model. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(10): 5229−5240 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3069728
|
|
[27]
|
Gao W N, Huang M Z, Jiang Z P, Chai T Y. Sampled-data-based adaptive optimal output-feedback control of a 2-degree-of-freedom helicopter. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2016, 10(12): 1440−1447
|
|
[28]
|
Liu D R, Wei Q L. Adaptive dynamic programming for a class of discrete-time non-affine nonlinear systems with time-delays. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2010. 1−6
|
|
[29]
|
Xiao F, Shi Y, Ren W. Robustness analysis of asynchronous sampled-data multiagent networks with time-varying delays. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(7): 2145−2152 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2017.2756860
|
|
[30]
|
Liu Y, Zhang H G, Yu R, Xing Z X. H∞ tracking control of discrete-time system with delays via data-based adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 50(11): 4078−4085 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2946397
|
|
[31]
|
Gao W N, Jiang Z P. Adaptive optimal output regulation of time-delay systems via measurement feedback. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(3): 938−945 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2850520
|
|
[32]
|
Gao W N, Jiang Y, Jiang Z P, Chai T Y. Output-feedback adaptive optimal control of interconnected systems based on robust adaptive dynamic programming. Automatica, 2016, 72: 37−45 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.05.008
|
|
[33]
|
Lewis F L, Vamvoudakis K G. Reinforcement learning for partially observable dynamic processes: Adaptive dynamic programming using measured output data. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 2011, 41(1): 14−25 doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2010.2043839
|
|
[34]
|
Moraal P E, Grizzle J W. Observer design for nonlinear systems with discrete-time measurements. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1995, 40(3): 395−404 doi: 10.1109/9.376051
|
|
[35]
|
Heydari A. Analyzing policy iteration in optimal control. In: Proceedings of the American Control Conference (ACC). Boston, USA: IEEE, 2016. 5728−5733
|




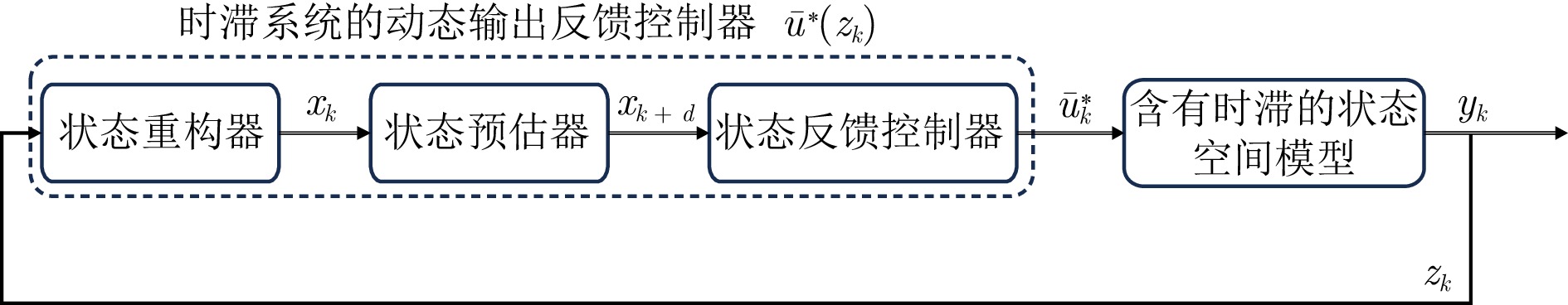
 下载:
下载: