-
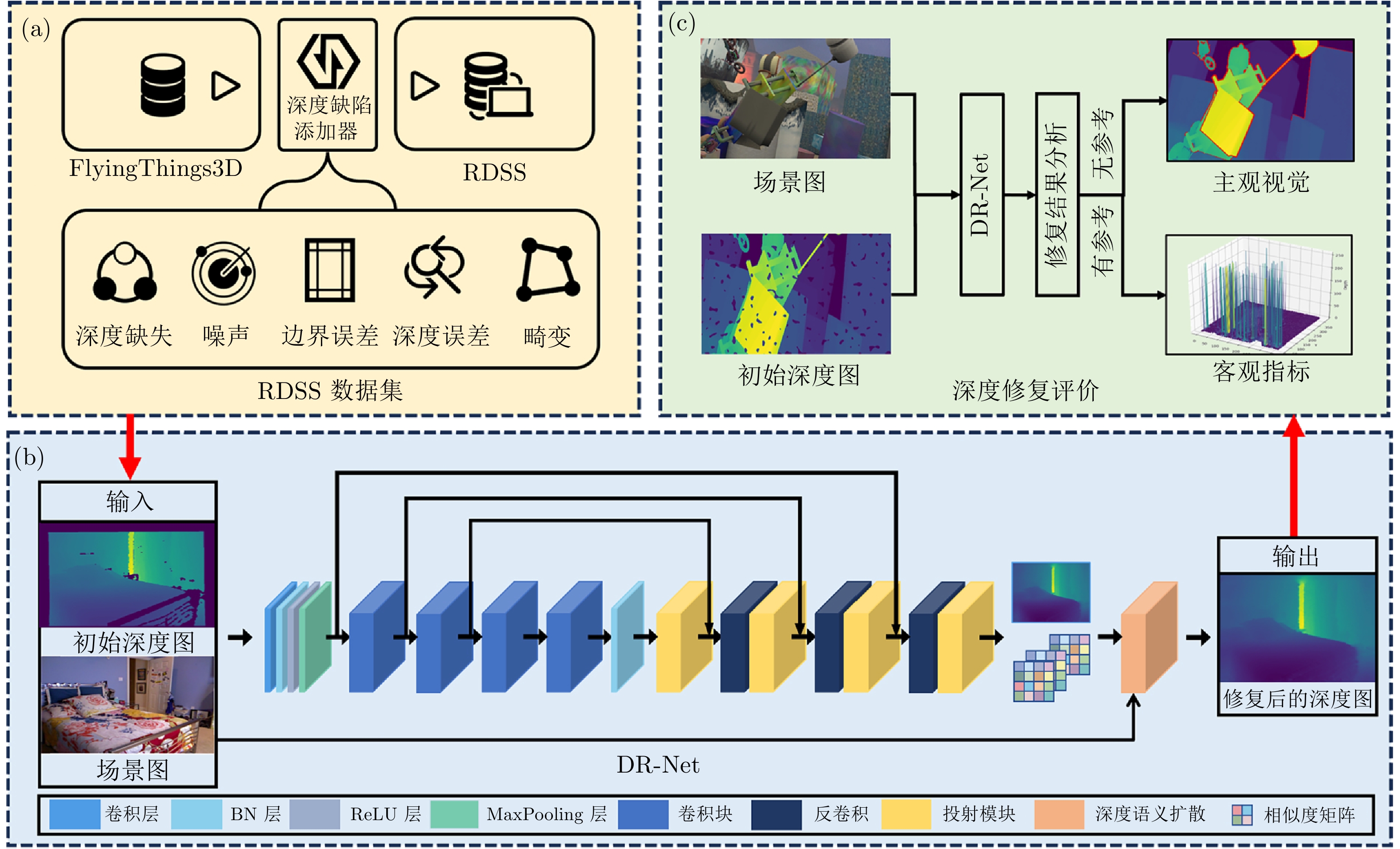
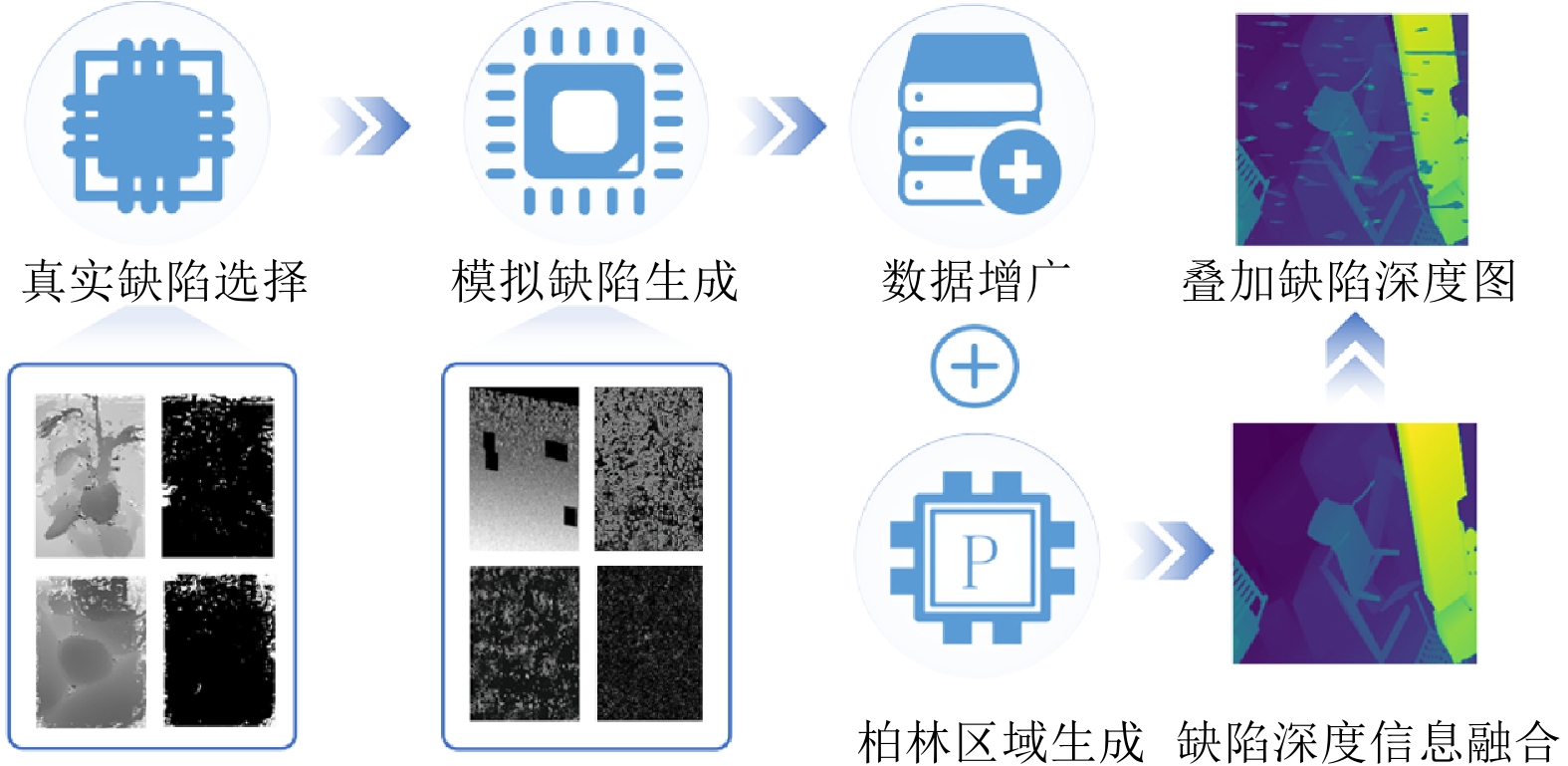
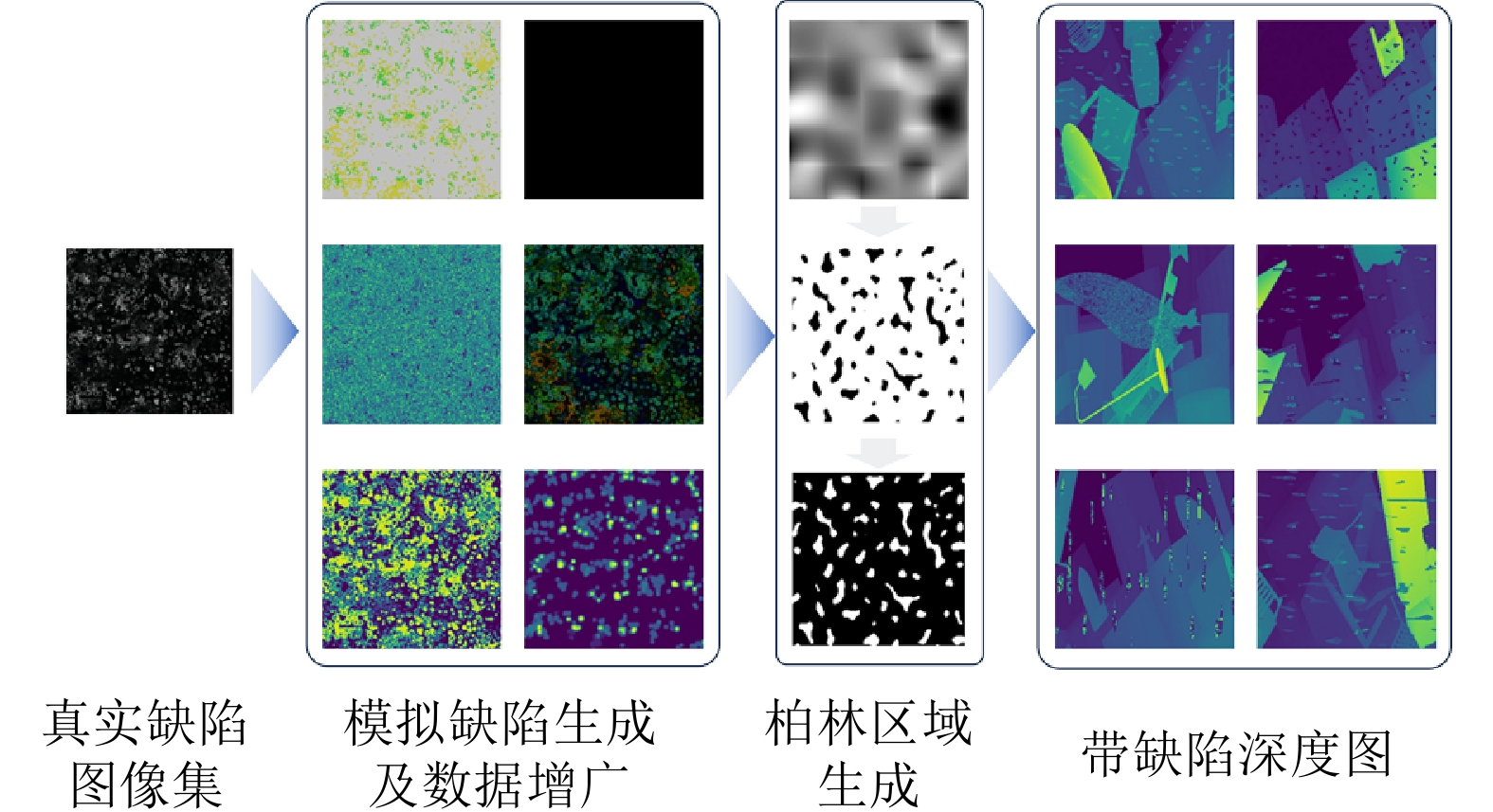
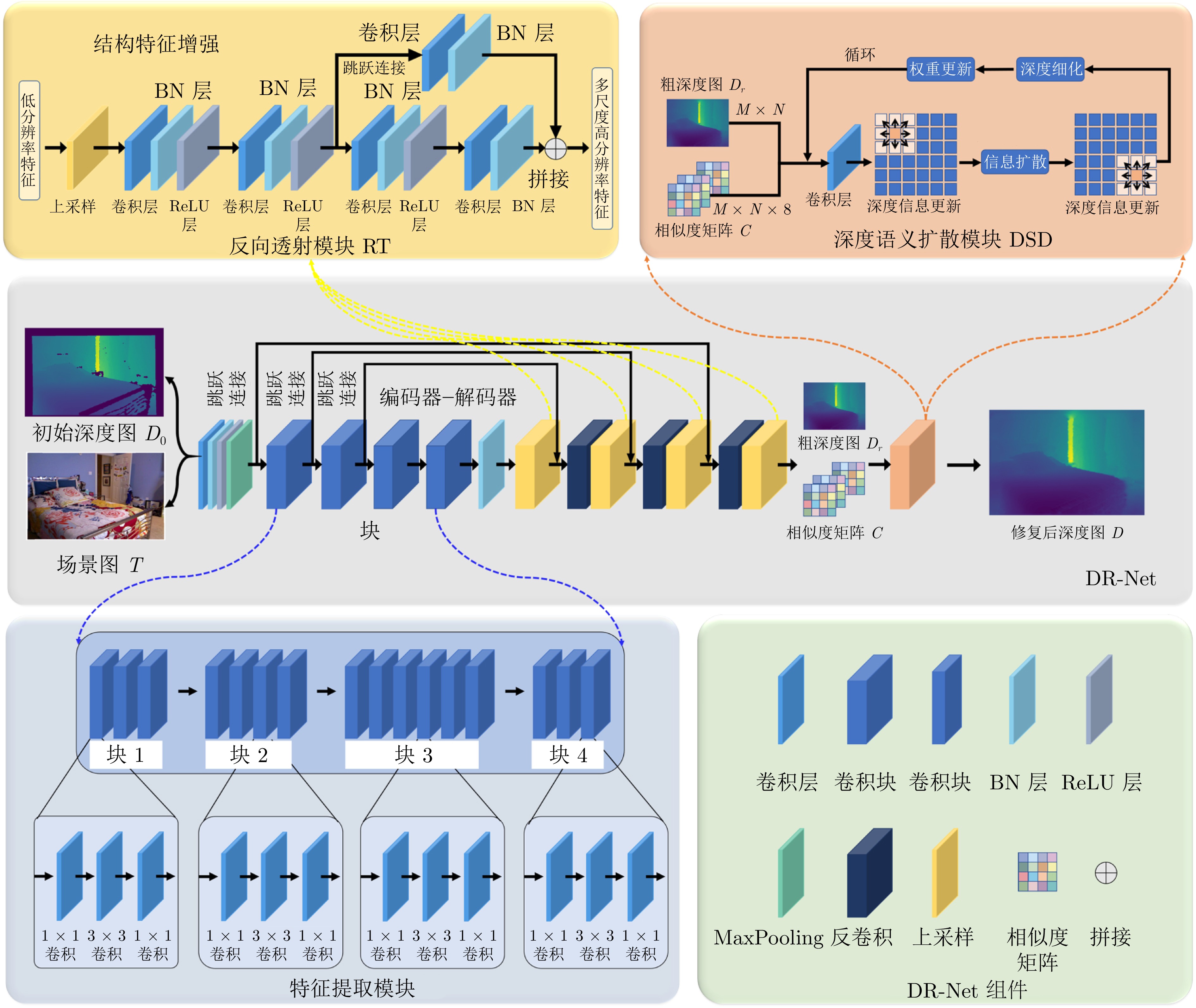
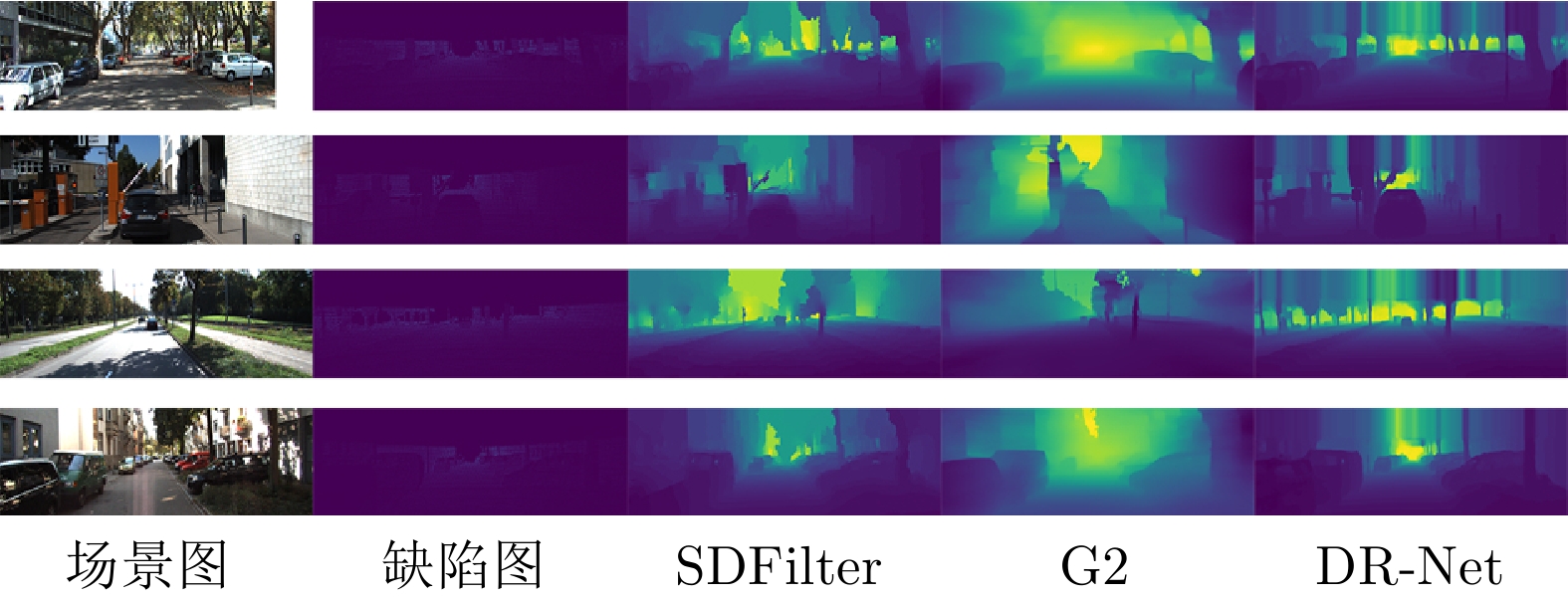
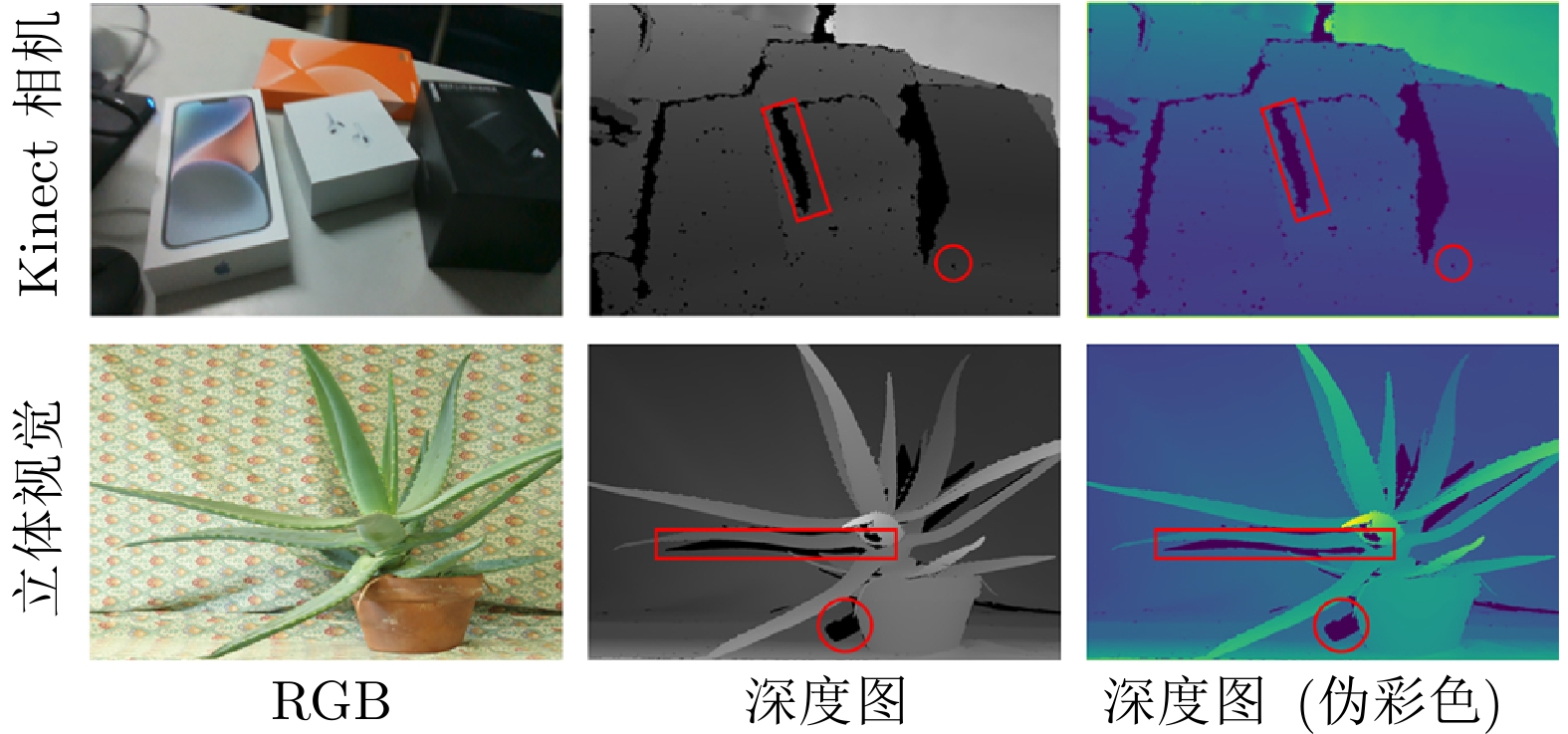
摘要: 深度修复旨在解决三维重建过程中深度图的缺失、噪声和遮挡问题. 然而, 由于深度图来源的多样性和异质性, 现有的深度修复方法难以对复杂场景结构及未知类型深度缺陷实现有效修复. 针对上述问题, 不同于现有方法单纯从提升算法鲁棒性的角度进行研究, 从深度缺陷数据集构建的逆向视角出发, 构建一种真实缺陷采样仿真RDSS数据集, 并在此基础上提出一种基于深度语义扩散的深度图修复模型DR-Net. RDSS数据集通过对真实缺陷的采集与建模, 结合同质化形变拓展和异质化交叉组合, 能够对多种复杂场景中的深度缺陷进行形式化仿真, 有效提升深度缺陷的多样性和场景的覆盖性. 设计的深度图修复模型DR-Net基于U型网络结构, 利用反向透射模块实现高分辨率细节保持的同时, 通过深度语义扩散模块传播图像中的深度语义信息, 进而有效提升修复性能. 实验结果表明: 以RDSS数据集为基准训练数据集, 可实现在其他数据集中深度图的有效修复. 此外, 与最先进的模型设计类修复方法SDFilter和数据驱动类修复方法G2相比, DR-Net模型在RDSS、NYU Depth V2和KITTI三类数据集上的均方根误差指标分别平均下降24.85%和29.54%, 验证了DR-Net模型的有效性和先进性.Abstract: Depth repair aims to address the issues of missing data, noise and occlusion in depth maps during 3D reconstruction. However, due to the diversity and heterogeneity of depth map sources, existing depth repair methods struggle to effectively repair complex scene structures and unknown types of depth defects. To address these issues, unlike current approaches that focus solely on enhancing algorithmic robustness, we propose a novel solution from the inverse perspective of depth defect dataset construction. We construct a real defect sampling simulation (RDSS) dataset. Based on this, we propose a DR-Net depth map repair model utilizing depth semantic diffusion. The RDSS dataset constructs formalized simulations of diverse depth defects in complex scenes by capturing and modeling real defects, combined with homogeneous deformation augmentation and heterogeneous cross-combination. This significantly enhances depth defect diversity and scene coverage. The designed DR-Net model builds upon a U-Net structure. It employs a reverse transmission module to preserve high-resolution details while propagating depth semantic information within the image through a depth semantic diffusion module, thereby effectively improving repair performance. Experimental results demonstrate that models trained on the RDSS benchmark dataset achieve effective depth map repair across other datasets. Furthermore, compared to state-of-the-art model design repair method (SDFilter) and data-driven repair method (G2), the DR-Net model reduces the root mean squared error metric by 24.85% and 29.54% on average across the RDSS, NYU Depth V2 and KITTI datasets, respectively. These results validate the effectiveness and advancement of the proposed DR-Net model.
-
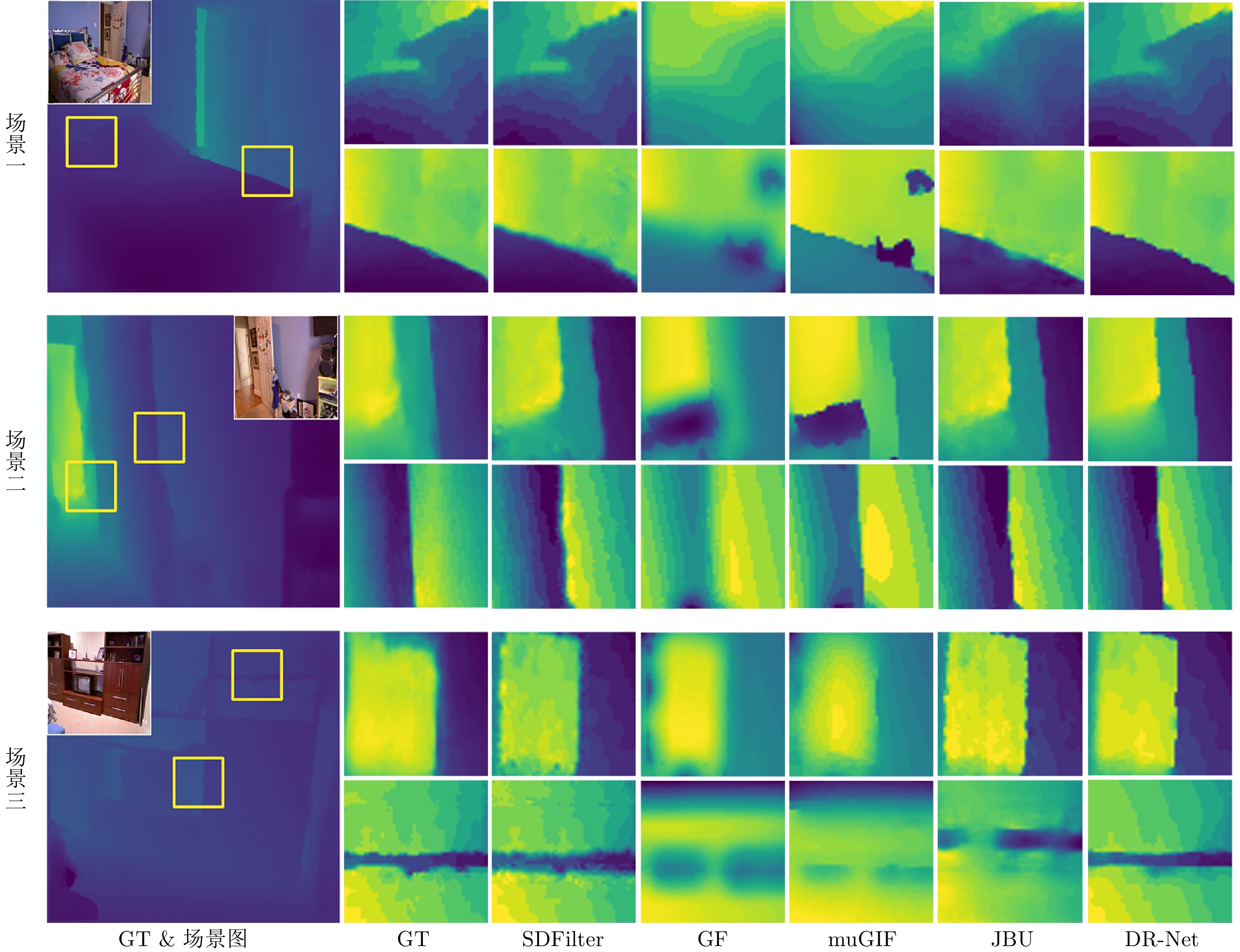
表 1 对比算法信息汇总
Table 1 Summary of comparison algorithm information
算法模型 期刊或会议 发表年份 参数选择/参数预设 模型设计类修复方法 SDFilter[23] TPAMI 2017 nei = 0, lambda = 10, step = 20, issparse = True GF[17] TPAMI 2012 radius = [2, 4, 8], eps = [$ 0.1^{2} $, $ 0.2^{2} $, $ 0.4^{2} $] muGIF[19] TPAMI 2018 alpha_t = [0.001, 0.050, 0.005], alpha_r = [0, 0.020] JBU[18] TOG 2007 radius = 2, sigma-spatial = 2.5 数据驱动类修复方法 SDformer[30] CVPR 2024 lr = $ 3.0\times10^{-4} $, epochs = 250, momentum = 0.9, epsilon = $ 10^{-8} $ G2[31] TPAMI 2023 lr = $ 2.0\times10^{-4} $, epochs = 250, amp = True, wd = 0.05 SICNN[24] 3DV 2017 lr = $ 10^{-4} $, epochs = 300, wd = $ 2.0\times10^{-4} $ SDC[32] ICMV 2019 lr = $ 10^{-3} $, epochs = 200, gamma = 0.5, wd = 0 表 2 模型设计类修复方法性能比较
Table 2 Performance comparison of model design repair methods
数据集 模型 MAE MSE RMSE PSNR SSIM Correlation Log RMSE Abs rel Sq rel Avg rank NYU Depth V2 SDFilter 0.0077 0.0010 0.0269 32.9778 0.9874 0.9656 0.0006 0.0297 0.0043 1.8889 GF 0.1952 0.0564 0.2308 12.9909 0.7843 0.2134 0.0294 0.8131 0.2366 4.7778 muGIF 0.0976 0.0317 0.1658 16.2343 0.7496 0.4426 0.0211 0.3090 0.0806 3.3333 JBU 0.1798 0.0567 0.2131 14.6377 0.8230 0.9748 0.0257 0.6534 0.1933 3.7778 DR-Net 0.0102 0.0007 0.0206 36.0192 0.9916 0.9816 0.0003 0.0347 0.0019 1.2222 RDSS SDFilter 0.1520 0.0441 0.2027 14.1857 0.8185 0.0536 0.0224 0.5041 0.1381 3.0000 GF 0.2339 0.0817 0.2795 11.2853 0.5652 0.1080 0.0480 0.6618 0.1904 3.7778 muGIF 0.1490 0.0424 0.1984 14.3945 0.8317 0.0583 0.0216 0.4926 0.1310 1.7778 JBU 0.2348 0.0822 0.2802 11.2608 0.5614 0.1100 0.0484 0.6640 0.1916 4.5556 DR-Net 0.1490 0.0405 0.1960 14.3759 0.8442 0.1346 0.0205 0.5233 0.1366 1.4444 KITTI SDFilter 0.0227 0.0018 0.0406 28.2303 0.8464 0.6726 0.0014 0.3856 0.0270 2.1111 GF 0.1463 0.0304 0.1726 15.3280 0.4240 0.3973 0.0224 0.3845 0.7825 4.4444 muGIF 0.0568 0.0054 0.0727 22.8580 0.3559 0.7248 0.0079 0.9355 0.0546 3.2222 JBU 0.0725 0.0095 0.0954 20.6184 0.3329 0.6967 0.0080 0.8013 0.0889 4.0000 DR-Net 0.0098 0.0005 0.0211 33.7587 0.7631 0.8372 0.0004 0.2972 0.0487 1.2222 表 3 数据驱动类修复方法性能比较
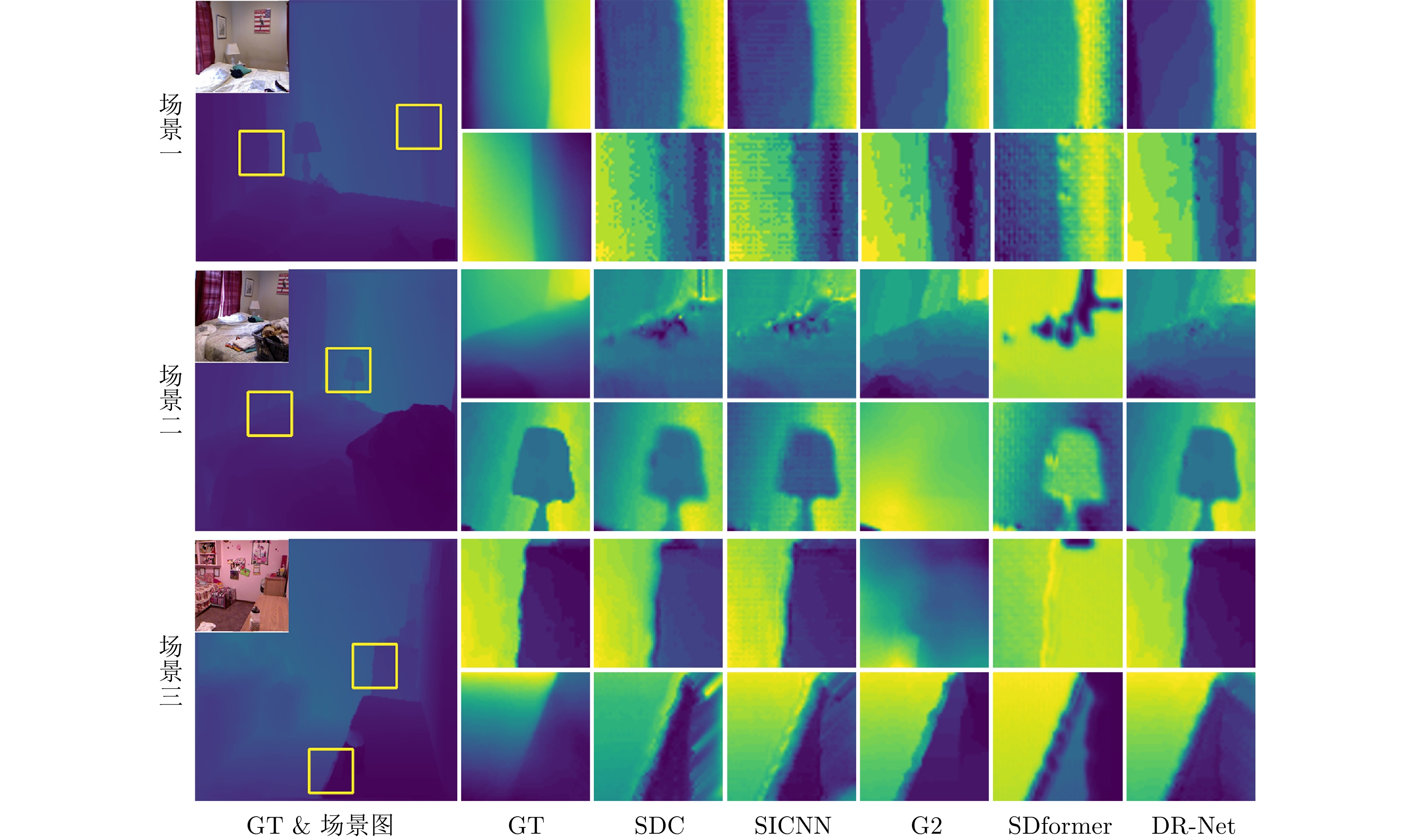
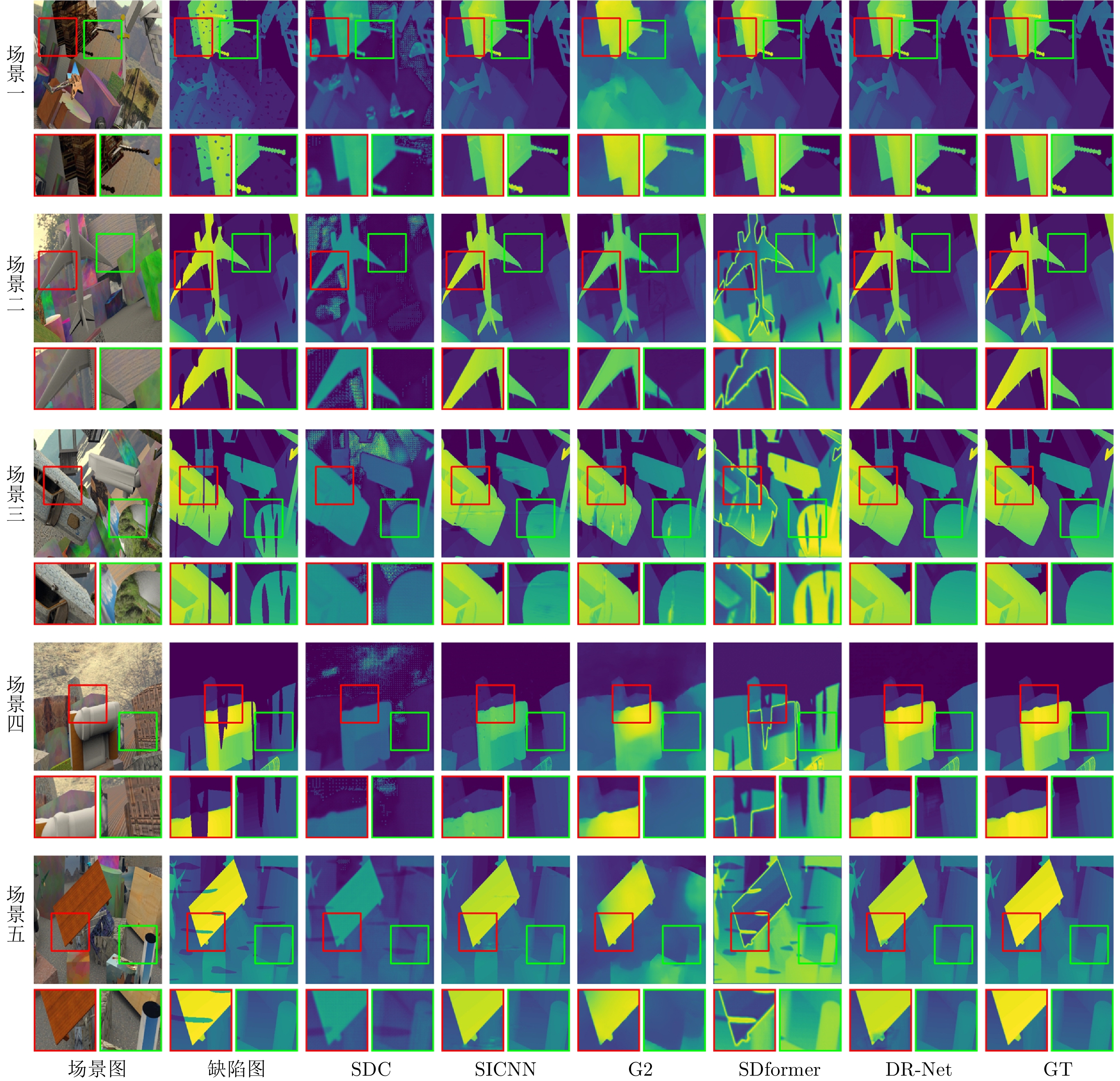
Table 3 Performance comparison of data-driven repair methods
数据集 模型 MAE MSE RMSE PSNR SSIM Correlation Log RMSE Abs rel Sq rel Avg rank NYU Depth V2 SDC 0.0836 0.0146 0.1102 20.0451 0.9152 0.3461 0.0079 0.3103 0.0478 4.3333 SICNN 0.0841 0.0143 0.1093 20.0730 0.9112 0.3527 0.0079 0.3178 0.0489 4.3333 G2 0.0248 0.0101 0.0311 30.3234 0.9605 0.8324 0.0045 0.0823 0.0041 1.2222 SDformer 0.0352 0.0162 0.0395 28.2451 0.9242 0.8058 0.0072 0.0602 0.0065 3.1111 DR-Net 0.0102 0.0007 0.0206 36.0192 0.9916 0.9816 0.0003 0.0347 0.0019 1.0000 RDSS SDC 0.2360 0.0834 0.2834 11.1192 0.5127 0.0253 0.0488 0.6835 0.2047 4.3333 SICNN 0.2339 0.0817 0.2795 11.2837 0.5655 0.1083 0.0480 0.6615 0.1906 3.3333 G2 0.2483 0.0971 0.3069 10.3930 0.7547 0.1085 0.0453 0.9300 0.3897 4.3333 SDformer 0.1565 0.0424 0.1997 14.2495 0.8020 0.1165 0.0229 0.5072 0.0035 1.7778 DR-Net 0.1490 0.0405 0.1960 14.3759 0.8442 0.1346 0.0205 0.5233 0.1366 1.2222 KITTI SDC 0.0439 0.0050 0.0698 23.2631 0.7535 0.7433 0.0039 0.8013 0.0889 4.4444 SICNN 0.0432 0.0051 0.0707 23.1433 0.7596 0.8935 0.0040 0.7768 0.0907 4.2222 G2 0.0102 0.0007 0.0260 31.8424 0.8092 0.8497 0.0006 0.0049 0.0595 1.7778 SDformer 0.0217 0.0037 0.0318 30.5623 0.7924 0.8138 0.0013 0.3547 0.0647 3.0000 DR-Net 0.0098 0.0005 0.0211 33.7587 0.7631 0.8372 0.0004 0.2972 0.0487 1.4444 表 4 数据驱动类修复方法计算代价和预测精度实验结果
Table 4 Experimental results on computational cost and prediction accuracy of data-driven repair methods
数据集 模型 MSE $ \downarrow $ Params. (M) FLOPs (G) Time (ms) NYU Depth V2 SDC 0.0146 1.8 3.5 18 SICNN 0.0143 3.2 6.8 32 G2 0.0101 12.5 24.3 85 SDformer 0.0162 38.7 68.2 210 DR-Net 0.0007 22.1 41.5 125 RDSS SDC 0.0884 1.8 3.5 19 SICNN 0.0817 3.2 6.8 33 G2 0.0971 12.5 24.3 87 SDformer 0.0424 38.7 68.2 215 DR-Net 0.0405 22.1 41.5 130 KITTI SDC 0.0050 1.8 3.5 21 SICNN 0.0051 3.2 6.8 35 G2 0.0007 12.5 24.3 90 SDformer 0.0037 38.7 68.2 230 DR-Net 0.0005 22.1 41.5 140 表 5 消融实验的量化及计算代价比较结果
Table 5 Quantitative and computational cost comparison results of ablation experiments
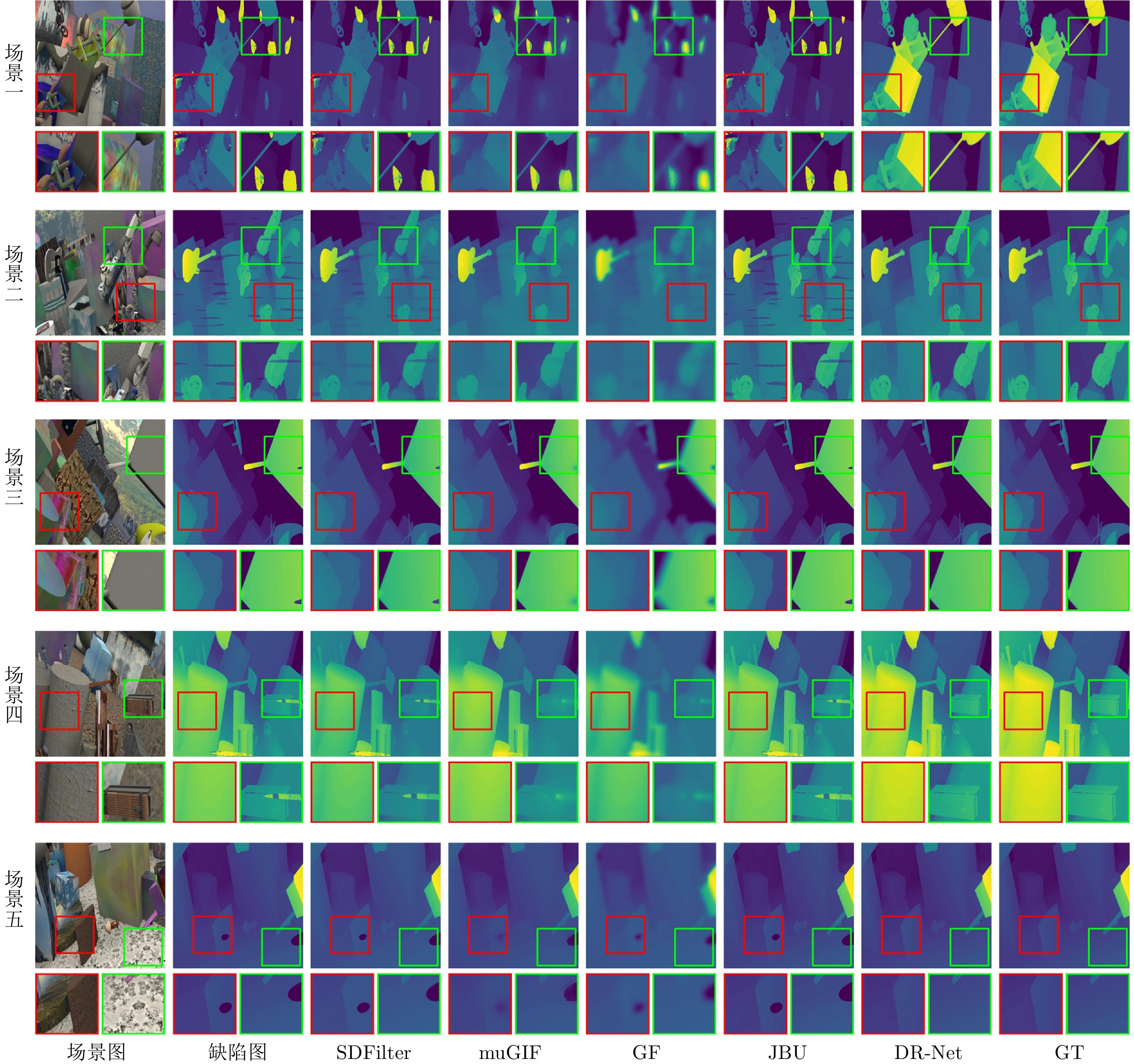
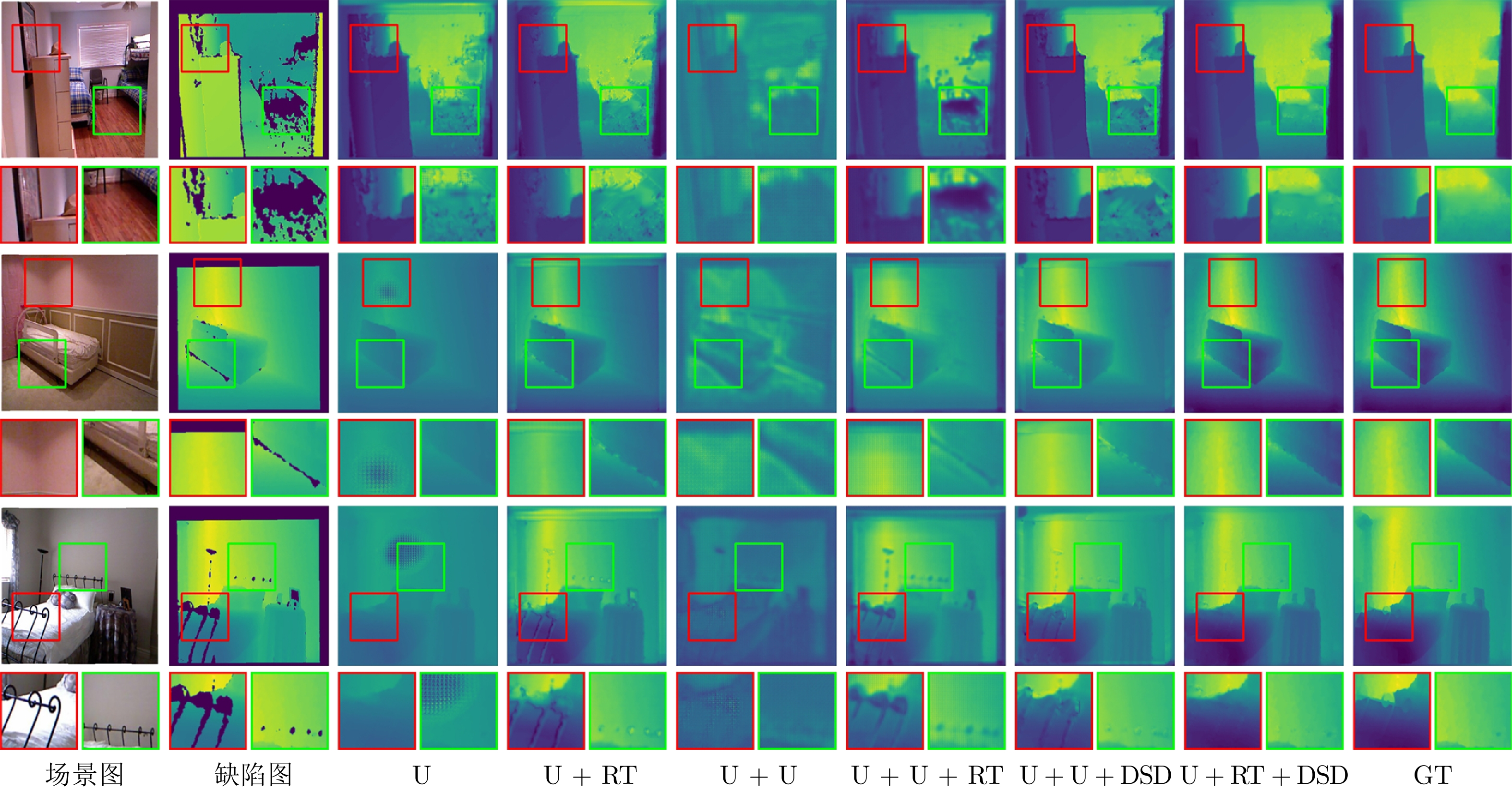
模型名称 结构组成 RMSE MSE MAE Params. (M) FLOPs (G) Time (ms) U-Net RT DSD U $ \surd $ 0.1519 0.0267 0.1193 15.2 28.5 90 U + RT $ \surd $ $ \surd $ 0.0882 0.0100 0.0617 15.2 34.2 117 U + RT + DSD $ \surd $ $ \surd $ $ \surd $ 0.0206 0.0007 0.0102 22.1 41.5 125 U + U $ \surd $ 0.1253 0.0200 0.0982 30.4 57.0 180 U + U + DSD $ \surd $ $ \surd $ 0.0437 0.0031 0.0213 32.5 62.5 201 U + U + RT $ \surd $ $ \surd $ 0.0498 0.0036 0.0316 30.4 68.4 234 表 6 RDSS数据集构建过程中各模块消融定量实验结果
Table 6 Quantitative ablation experimental results of each module in the RDSS dataset construction process
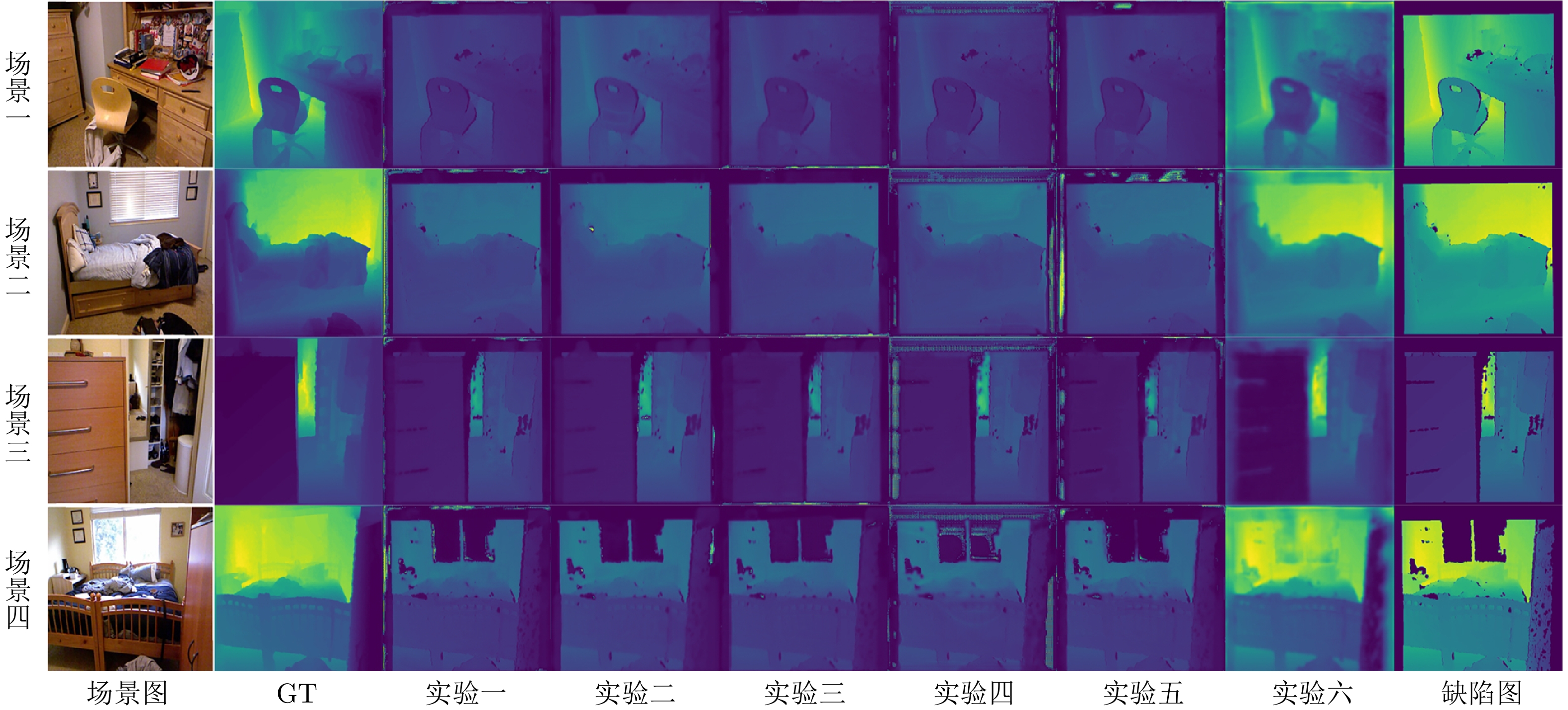
序号 结构 RMSE$ \downarrow $ MSE$ \downarrow $ MAE$ \downarrow $ Correlation$ \uparrow $ 真实缺陷选择 模拟缺陷生成 数据增广 实验一 × √ √ 0.1350 0.0189 0.0667 0.4351 实验二 √ × √ 0.1262 0.0167 0.0726 0.4884 实验三 √ √ × 0.1339 0.0188 0.0768 0.4275 实验四 × √ × 0.1212 0.0153 0.0640 0.5166 实验五 √ × × 0.1340 0.0188 0.0707 0.4459 实验六 √ √ √ 0.0882 0.0100 0.0617 0.7870 表 7 各模型在NYU Depth V2数据集中的泛化性能比较
Table 7 Generalization performance comparison of various models on the NYU Depth V2 dataset
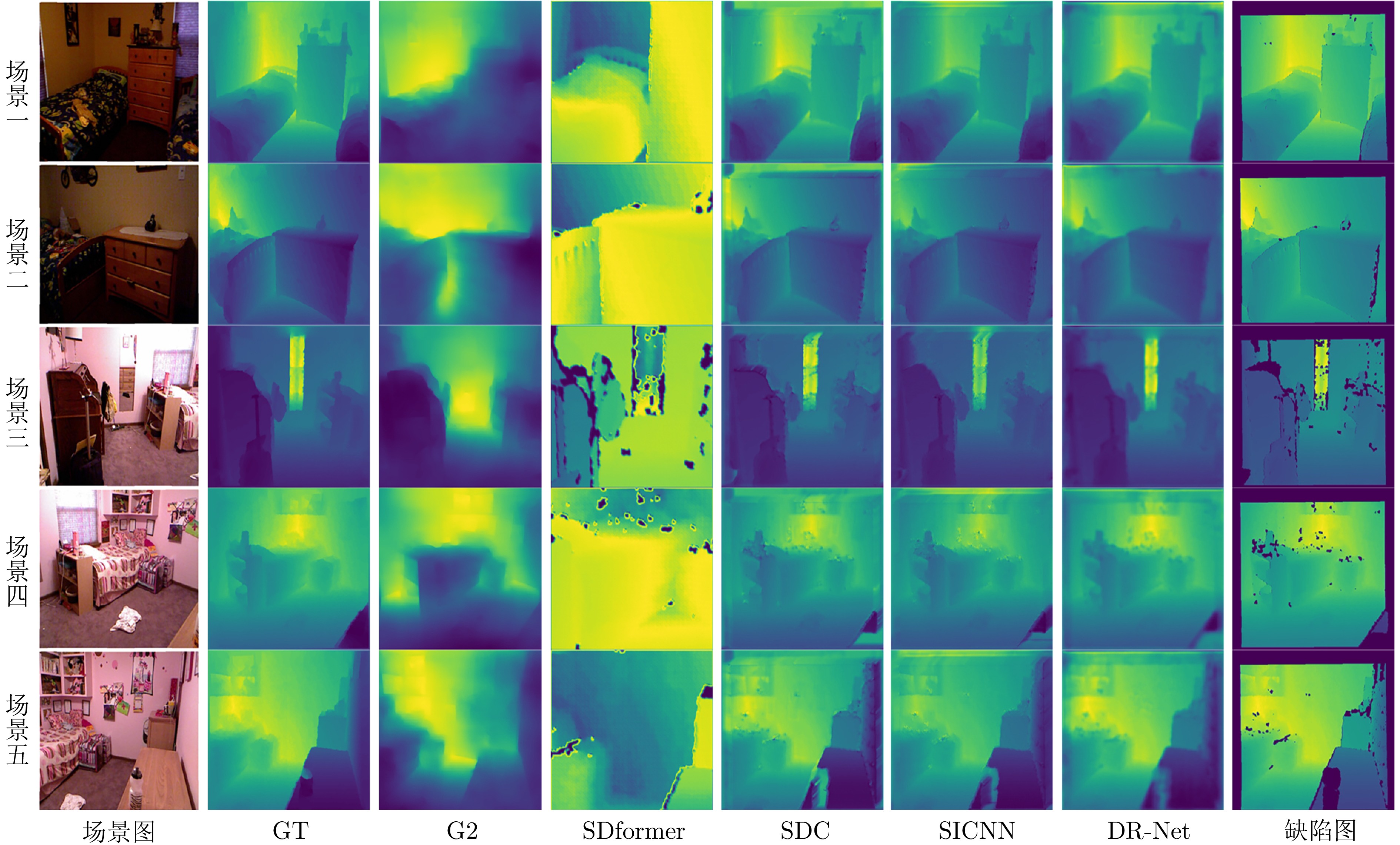
模型 MAE$ \downarrow $ MSE$ \downarrow $ RMSE$ \downarrow $ Correlation$ \uparrow $ SDC 0.1614 0.0986 0.2584 0.8209 SICNN 0.1687 0.1093 0.2531 0.8608 G2 0.2651 0.1189 0.3396 0.7662 SDformer 0.4234 0.2254 0.4659 0.3713 DR-Net 0.1069 0.0895 0.2098 0.8482 -
[1] Wang X H, Wang W G, Shao J Y, Yang Y. Learning to follow and generate instructions for language-capable navigation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 44(3): 3334−3350 [2] Chen L, Wu P H, Chitta K, Jaeger B, Geiger A, Li H Y. End-to-end autonomous driving: Challenges and frontiers. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(12): 10164−10183 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3435937 [3] Yan T, Hu Z G, Qian Y H, Qiao Z W, Zhang L Y. 3D shape reconstruction from multifocus image fusion using a multidirectional modified Laplacian operator. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 98: Article No. 107065 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.107065 [4] Yan T, Wu P, Qian Y H, Hu Z G, Liu F X. Multiscale fusion and aggregation PCNN for 3D shape recovery. Information Sciences, 2020, 536: 277−297 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.05.100 [5] 张江峰, 闫涛, 王克琪, 钱宇华, 吴鹏. 多景深图像聚焦信息的三维形貌重建: 数据集与模型. 计算机学报, 2023, 46(8): 1734−1752 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2023.01734Zhang Jiang-Feng, Yan Tao, Wang Ke-Qi, Qian Yu-Hua, Wu Peng. 3D shape reconstruction of multi depth image focusing information: Dataset and model. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2023, 46(8): 1734−1752 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2023.01734 [6] 闫涛, 钱宇华, 李飞江, 闫泓任, 王婕婷, 梁吉业, 等. 三维时频变换视角的智能微观三维形貌重建方法. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2023, 53(2): 282−308 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0386Yan Tao, Qian Yu-Hua, Li Fei-Jiang, Yan Hong-Ren, Wang Jie-Ting, Liang Ji-Ye, et al. Intelligent microscopic 3D shape reconstruction method with three dimensional time frequency transform perspective. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2023, 53(2): 282−308 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2021-0386 [7] 闫涛, 高浩轩, 张江峰, 钱宇华, 张临垣. 分组并行的轻量化实时微观三维形貌重建方法. 软件学报, 2024, 35(4): 1717−1731Yan Tao, Gao Hao-Xuan, Zhang Jiang-Feng, Qian Yu-Hua, Zhang Lin-Yuan. Group parallel lightweight real-time micro 3D morphology reconstruction method. Journal of Software, 2024, 35(4): 1717−1731 [8] Yan T, Qian Y H, Zhang J F, Wang J T, Liang J Y. SAS: A general framework induced by sequence association for shape from focus. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2025.3577595 [9] 张振宇, 杨健. 基于元学习的双目深度估计在线适应算法. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(7): 1446−1455Zhang Zhen-Yu, Yang Jian. Online adaptation through meta-learning for stereo depth estimation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(7): 1446−1455 [10] 闫涛, 尚起慧, 吴鹏, 张江峰, 钱宇华, 陈斌. 多尺度代价聚合的多聚焦图像3维形貌重建框架. 计算机研究与发展, 2025, 62(7): 1771−1785 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.202330984Yan Tao, Shang Qi-Hui, Wu Peng, Zhang Jiang-Feng, Qian Yu-Hua, Chen Bin. Multi-scale cost aggregation framework for 3D shape reconstruction from multi-focus images. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2025, 62(7): 1771−1785 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.202330984 [11] Wang C L, Chen N, Heidrich W. dO: A differentiable engine for deep lens design of computational imaging systems. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2022, 8: 905−916 doi: 10.1109/TCI.2022.3212837 [12] Ramirez P Z, Tosi F, Stefano L D, Timofte R, Costanzino A, Poggi M, et al. NTIRE 2024 challenge on HR depth from images of specular and transparent surfaces. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Milan, Italy: IEEE, 2024. 6499−6512 [13] Scharstein D, Szeliski R. A taxonomy and evaluation of dense two-frame stereo correspondence algorithms. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2002, 47: 7−42 doi: 10.1023/A:1014573219977 [14] Silberman N, Hoiem D, Kohli P, Fergus R. Indoor segmentation and support inference from RGBD images. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Florence, Italy: Springer, 2012. 746−760 [15] Geiger A, Lenz P, Urtasun R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? The KITTI vision benchmark suite. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Providence, USA: IEEE, 2012. 3354−3361 [16] Mayer N, Ilg E, Husser P, Fischer P, Cremers D, Dosovitskiy A, et al. A large dataset to train convolutional networks for disparity, optical flow, and scene flow estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 4040−4048 [17] He K M, Sun J, Tang X O. Guided image filtering. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 35(6): 1397−1409 [18] Kopf J, Cohen M F, Lischinski D, Uyttendaele M. Joint bilateral upsampling. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2007, 26(3): 96−102 doi: 10.1145/1276377.1276497 [19] Guo X J, Li Y, Ma J Y. Mutually guided image filtering. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 42(3): 694−707 [20] Liu X M, Zhai D M, Chen R, Ji X Y, Zhao D B, Gao W. Depth restoration from RGBD data via joint adaptive regularization and thresholding on manifolds. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 28(3): 1068−1079 [21] Lo K H, Hua K L, Wang Y C F. Depth map super-resolution via Markov random fields without texture-copying artifacts. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2013. 1414−1418 [22] Zhao E Z, Dong L L, Li C X, Ji Y J. Infrared maritime target detection based on temporal weight and total variation regularization under strong wave interferences. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5005819−5005838 [23] Ham B, Cho M, Ponce J. Robust guided image filtering using nonconvex potentials. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 40(1): 192−207 [24] Uhrig J, Schneider N, Schneider L, Franke U, Brox T, Geiger A. Sparsity invariant CNNs. In: Proceedings of International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV). Qingdao, China: IEEE, 2017. 11−20 [25] Huang Z X, Fan J M, Cheng S G, Yi S, Wang X G, Li H S. HMS-Net: Hierarchical multi-scale sparsity-invariant network for sparse depth completion. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29: 3429−3441 [26] Eldesokey A, Felsberg M, Khan F S. Propagating confidences through CNNs for sparse data regression. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC). Northumbria, Britain: BMVA, 2018. 1−11 [27] Kim B, Ponce J, Ham B. Deformable kernel networks for joint image filtering. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(2): 579−600 doi: 10.1007/s11263-020-01386-z [28] Hui T W, Loy C C, Tang X O. Depth map super-resolution by deep multi-scale guidance. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Amsterdam, Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 353−369 [29] Guo C L, Li C Y, Guo J C, Cong R M, Fu H Z, Han P. Hierarchical features driven residual learning for depth map super-resolution. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 28(5): 2545−2557 [30] Qian J, Sun M, Lee A, Li J, Zhuo S L, Chiang P Y. SDformer: Efficient end-to-end transformer for depth completion. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2409.08159, 2024. [31] Wang H, Yang M, Zheng N. G2-MonoDepth: A general framework of generalized depth inference from monocular RGB+X data. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 46(5): 3753−3771 [32] Gansbeke V W, Neven D, Brabandere D B, Gool L V. Sparse and noisy LiDAR completion with RGB guidance and uncertainty. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA). Tokyo, Japan: IEEE, 2019. 1−6 [33] Wang Y Q, Cheng K, He J W, Wang Q T, Dai H C, Chen Y T, et al. Drivingdojo dataset: Advancing interactive and knowledge-enriched driving world model. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2410.10738, 2024. [34] Luisier F, Blu T, Unser M. Image denoising in mixed Poisson-Gaussian noise. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 20(3): 696−708 [35] Azzeh J, Zahran B, Alqadi Z. Salt and pepper noise: Effects and removal. JOIV: International Journal on Informatics Visualization, 2018, 2(4): 252−256 doi: 10.30630/joiv.2.4.151 [36] Le T, Chartrand R, Asaki T J. A variational approach to reconstructing images corrupted by Poisson noise. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 2007, 27(3): 257−263 doi: 10.1007/s10851-007-0652-y [37] Ramdas A, Poczos B, Singh A, Wasserman L. An analysis of active learning with uniform feature noise. In: Proceedings of Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS). Reykjavik, Iceland: PMLR, 2014. 805−813 [38] Cubuk E D, Zoph B, Shlens J, Le Q V. Randaugment: Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Washington, USA: IEEE, 2020. 702−703 [39] Perlin K. An image synthesizer. ACM Special Interest Group for Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques Computer Grap-hics, 1985, 19(3): 287−296 doi: 10.1145/325165.325247 -




 下载:
下载: