Attack Detection Design and Distributed Resilient Control of Multi-agent Systems Under Cyber-attacks
-
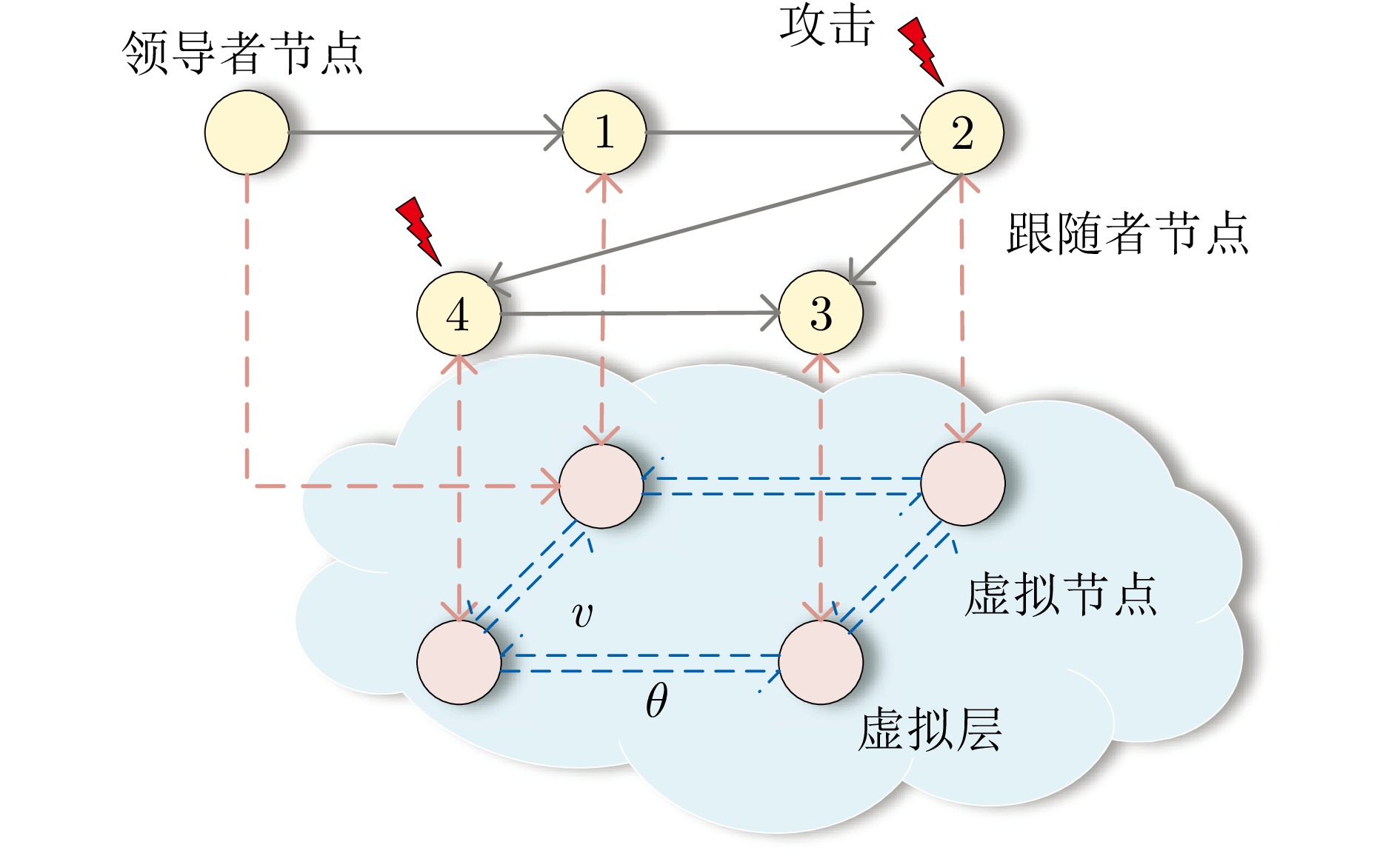
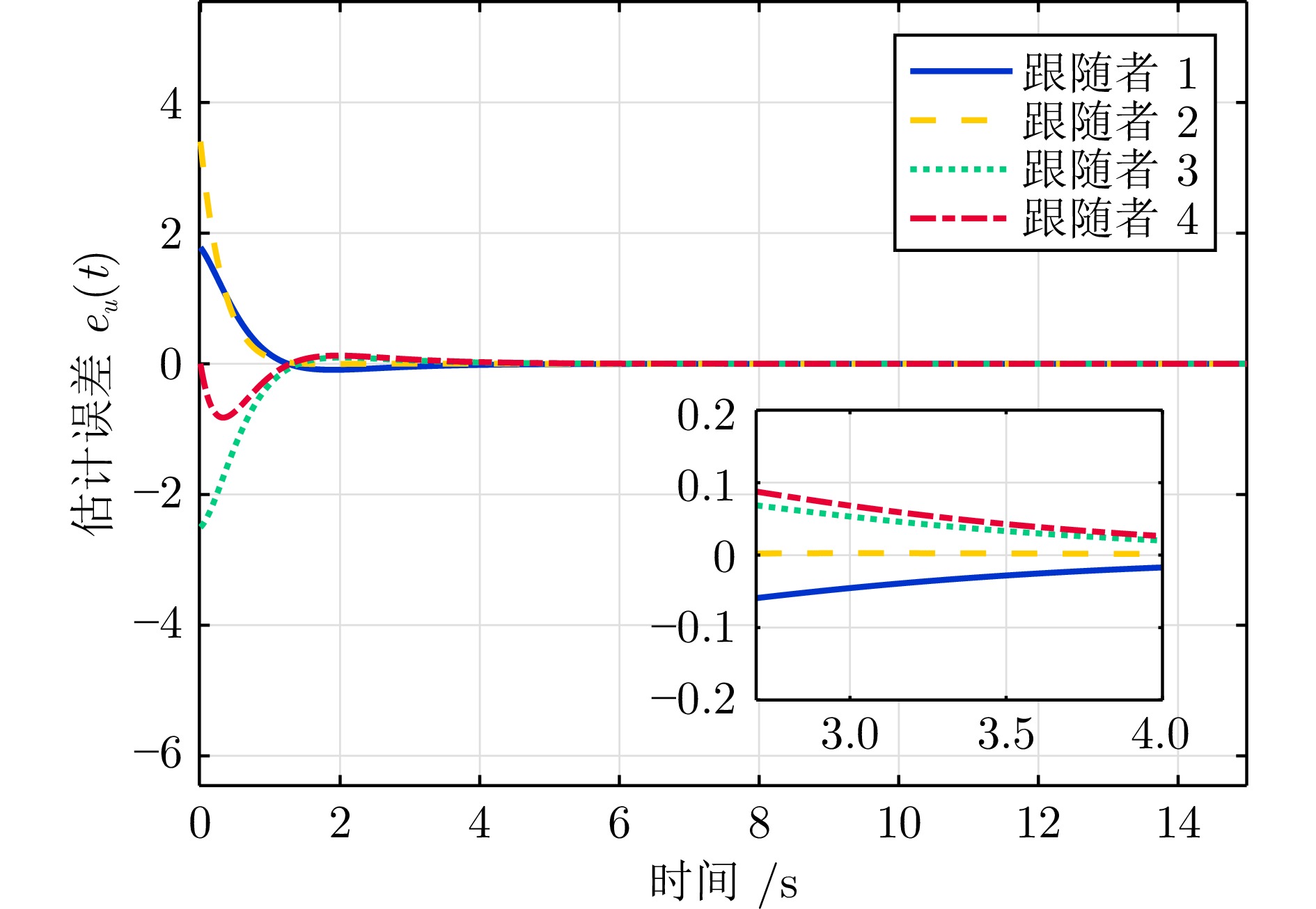
摘要: 提出一种集攻击检测与防御控制于一体的策略来研究执行器攻击下多智能体系统的弹性跟踪控制问题. 在攻击检测方面, 设计一种基于状态机的动态特征函数建模检测方案. 该方案提出采用线性函数观测器对执行器信号进行估计, 并依据实际信号与估计值之间的误差特性构建攻击检测准则, 以此实现对执行器攻击的有效检测. 在防御策略设计上, 为降低执行器攻击对系统跟踪共识性能的影响, 构建一种基于虚拟网络增强的协同控制系统. 该系统通过与领导者及各跟随者建立连接, 在执行器攻击信息未知的情况下, 确保系统能够实现弹性跟踪控制. 具体而言, 当检测到攻击发生时, 各跟随者的防御控制策略将切换至虚拟层提供的控制信号; 若未检测到攻击, 则维持各跟随者原有的实际控制信号. 与现有研究成果相比, 所设计的控制器无需预先获取恶意节点数量及攻击者位置等先验信息, 具有更强的实用性和适应性. 最后, 通过一个数值算例对所提出的理论算法进行验证, 结果表明该算法能够有效应对执行器攻击, 实现多智能体系统的弹性跟踪控制.Abstract: This paper proposes an integrated strategy that combines attack detection and defensive control to investigate the resilient tracking control problem of multi-agent systems under actuator attacks. In terms of attack detection, a dynamic feature function modeling detection scheme based on a state machine is designed. This scheme suggests employing a linear function observer to estimate the actuator signals and constructing an attack detection criterion based on the error characteristics between the actual signals and the estimated values, thereby enabling effective detection of actuator attacks. For the design of defensive strategies, to mitigate the impact of actuator attacks on the system's tracking consensus performance, this paper constructs a collaborative control system enhanced by a virtual network. By establishing connections with the leader and each follower, this system ensures resilient tracking control even when the information about actuator attacks is unknown. Specifically, when an attack is detected, the defensive control strategy of each follower switches to the control signal provided by the virtual layer; If no attack is detected, the original actual control signals of the followers are maintained. Compared with existing research findings, the controller designed in this paper does not require prior information such as the number of malicious nodes and the positions of attackers in advance, thus exhibiting stronger practicality and adaptability. Finally, a numerical example is presented to validate the proposed theoretical algorithm. The results demonstrate that the algorithm can effectively cope with actuator attacks and achieve resilient tracking control in multi-agent systems.
-
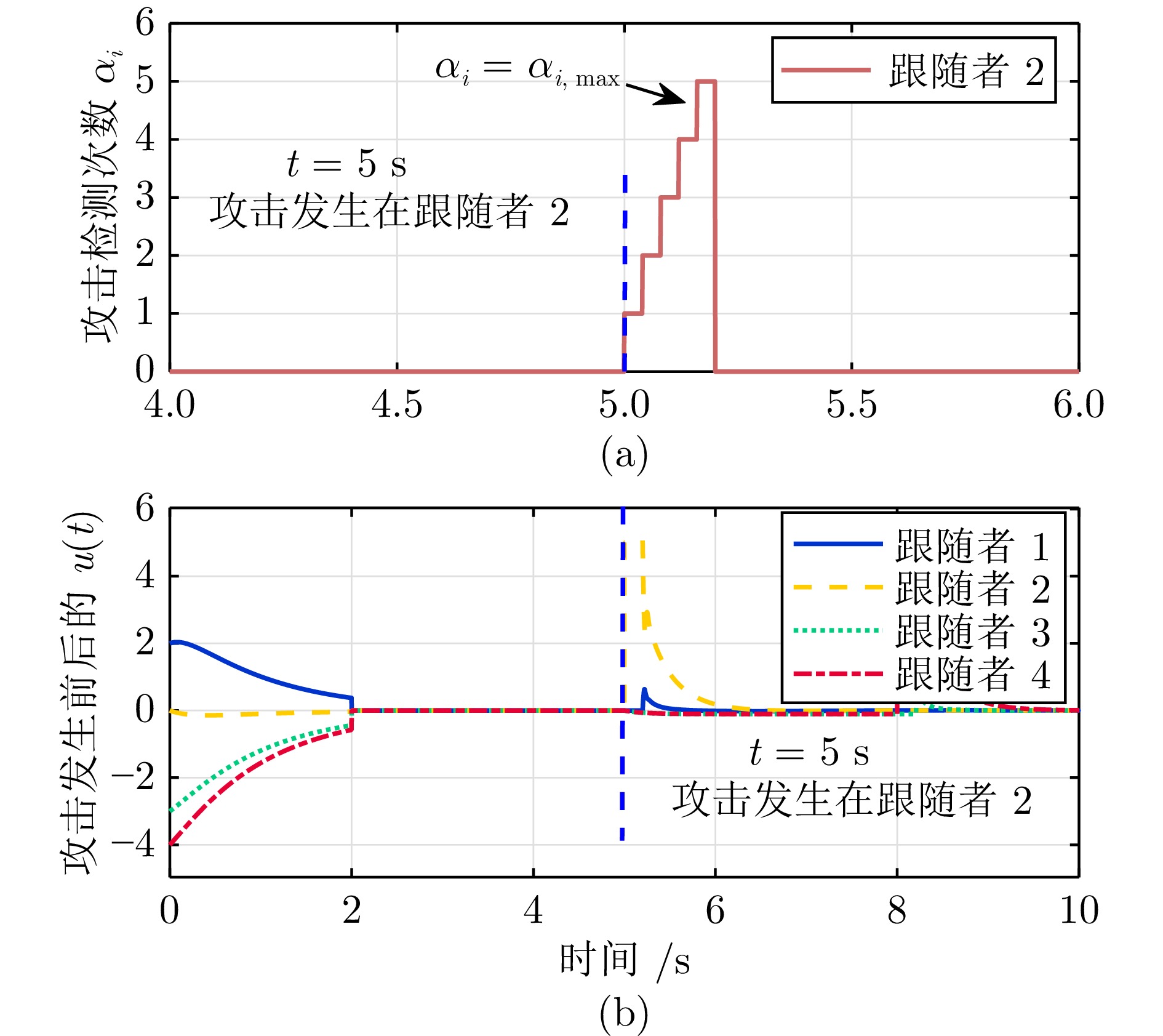
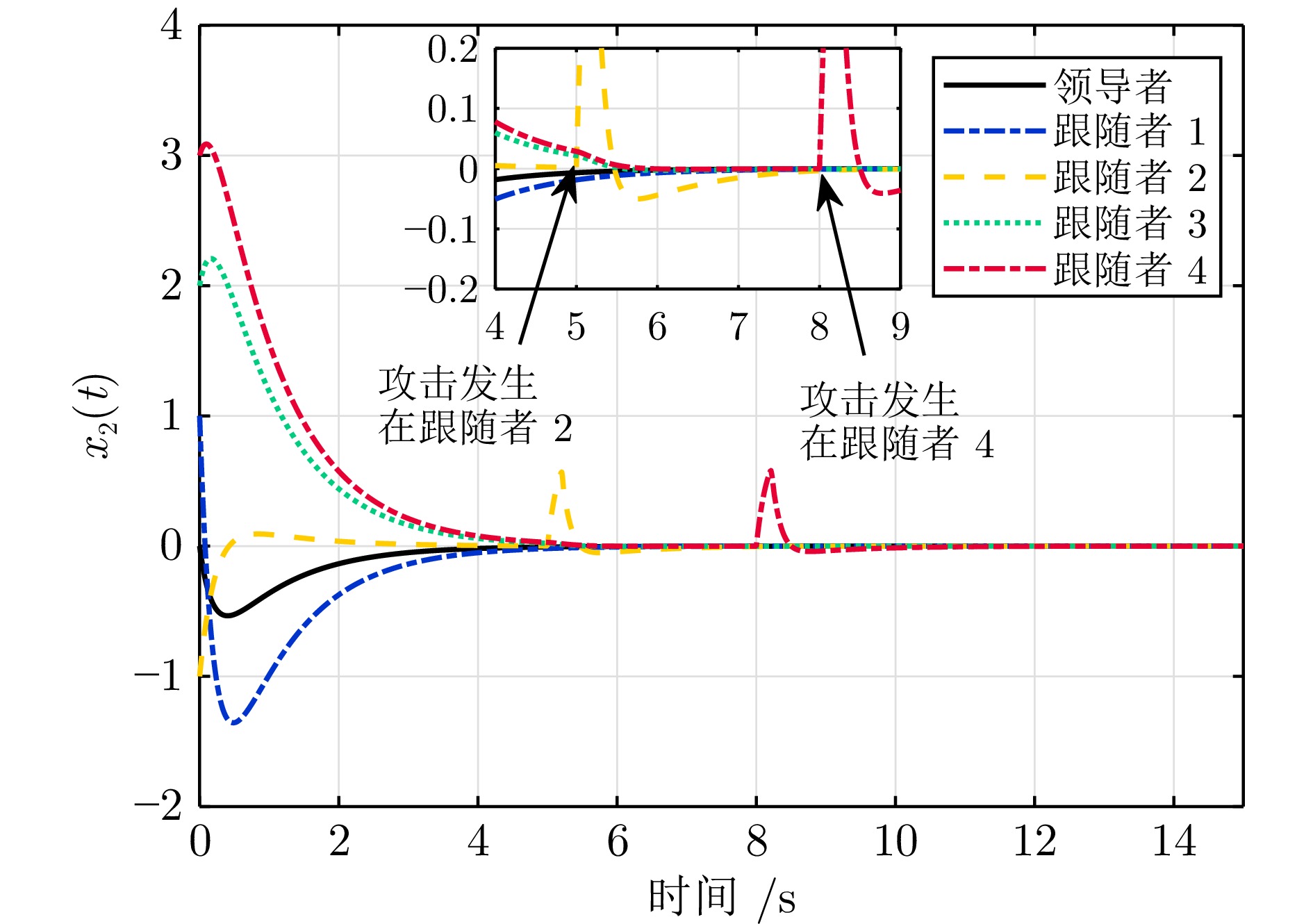
图 4 $t=5\; \mathrm{s}$时, 攻击发生在智能体2((a) 攻击检测计数$\alpha_{i}$即$\alpha_{2}$超过计数阈值$\alpha_{2,\;\mathrm{max}}$; (b) 控制器$u_{2}(t)$切换到$\bar{u}_{2}(t)$)
Fig. 4 Attack on agent 2 at $t = 5\; \mathrm{s}$ ((a) The attack detection count $\alpha_{i}$ namely $\alpha_{2}$ exceeds a count threshold $\alpha_{2,\;\mathrm{max}}$; (b) Controller $u_{2}(t)$ switched to $\bar{u}_{2}(t)$)
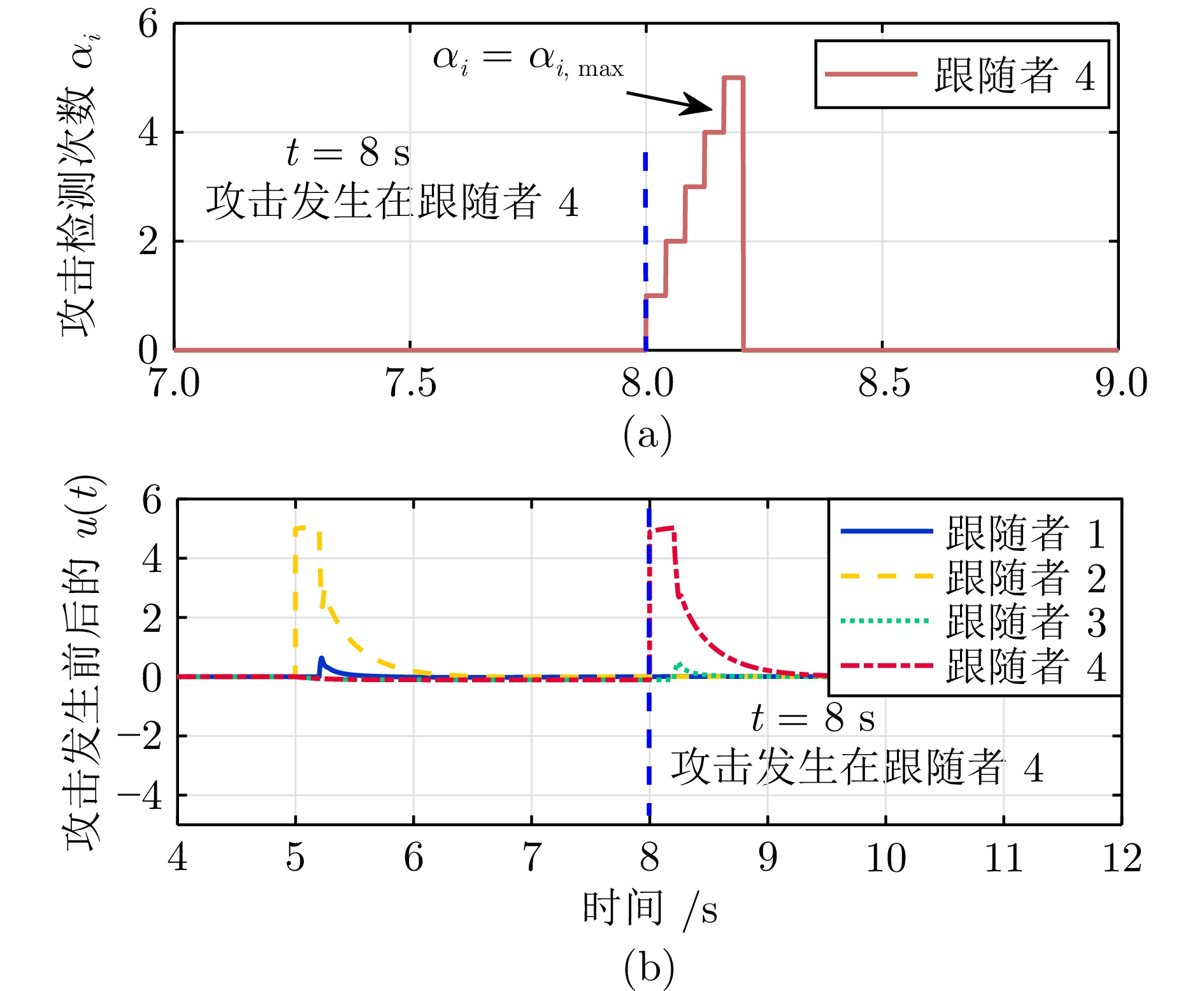
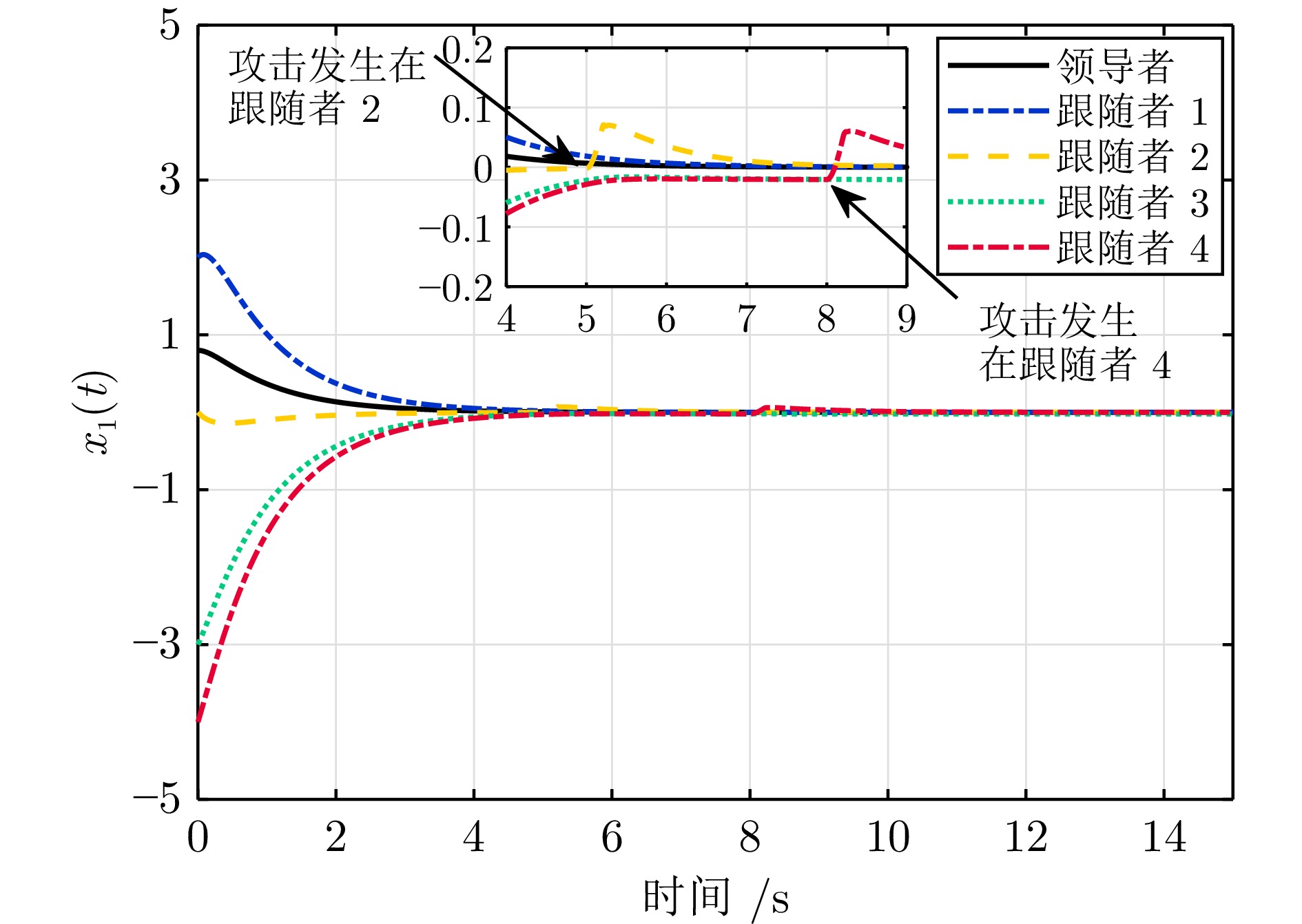
图 5 $t=8\; \mathrm{s}$时, 攻击发生在智能体4((a) 攻击检测计数$\alpha_{i}$即$\alpha_{4}$超过计数阈值$\alpha_{4,\;\mathrm{max}}$; (b) 控制器$u_{4}(t)$切换到$\bar{u}_{4}(t))$
Fig. 5 Attack on agent 4 at $t = 8\; \mathrm{s}$((a) The attack detection count $\alpha_{i}$ namely $\alpha_{4}$ exceeds a count threshold $\alpha_{4,\;\mathrm{max}}$; (b) Controller $u_{4}(t)$ switched to $\bar{u}_{4}(t)$)
表 1 攻击检测算法的相关参数
Table 1 Relevant parameters of attack detection algorithm
参数 符号 值 积分时间周期 $ T_{o} $ 0.2 避免误报时间周期 $ T_{c} $ 1 攻击检测准则阈值 $ \Psi_{i,\;\mathrm{max}} $ 1 攻击检测计数阈值 $ \alpha_{i,\;\mathrm{max}} $ 5 积分系数 $ \mu_{i} $ 1 虚拟网络层系数 $ T_{vi},\; T_{wi},\; T_{\theta i} $ 0.01, 0.1, 0.001 系统参数 $ k,\; \beta,\; \alpha_{i},\; \eta_{i} $ 10, 10, 10, 0.1 -
[1] Baheti R, Gill H. Cyber-physical systems. The impact of control technology, 2011, 12(1): 161−166 [2] Xu Y, Wu Z G, Pan Y J. Observer-based dynamic event-triggered adaptive control of distributed networked systems with application to ground vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(4): 4148−4157 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2022.3176242 [3] Xu Y, Sun J, Pan Y J, Wu Z G. Dynamic deadband event-triggered strategy for distributed adaptive consensus control with applications to circuit systems. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2022, 69(11): 4663−4673 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3197846 [4] Gorbachev S, Mani A, Li L, Li L, Zhang Y. Distributed energy resources based two-layer delay-independent voltage coordinated control in active distribution network. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(2): 1220−1230 doi: 10.1109/TII.2023.3270668 [5] X Y, Wu Z G, Pan Y J. Off-policy learning-based following control of cooperative autonomous vehicles under distributed attacks. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(5): 5120−5130 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3240731 [6] Wu S, Luo H, Yin S, Li K, Jiang Y C. A residual-driven secure transmission and detection approach against stealthy cyber-physical attacks for accident prevention. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2023, 18: 5762−5771 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2023.3314194 [7] Zhao X, Ma Z J, Shi X Y, Zou S L. Attack detection and mitigation scheme of load frequency control systems against false data injection attacks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(8): 9952−9962 doi: 10.1109/TII.2024.3390549 [8] Liu H, Li Y Z, Han Q L, Raïssi T, Chai T Y. Secure estimation, attack isolation, and reconstruction based on zonotopic unknown Input observer. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(12): 7312−7325 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3275965 [9] Qi X, Zhu L K, Li X, Gong R Q. Observer-based event-triggered sliding mode security control for nonlinear cyber-physical systems under DoS attacks. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2024, 21(4): 7480−7493 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2023.3343752 [10] Zhao D, Yang B, Li Y Y, Zhang H. Replay attack detection for cyber-physical control systems: A dynamical delay estimation method. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2025, 72(1): 867−875 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2024.3406859 [11] Zhao D, Shi Y, Ding S X, Li Y Y, Fu F Z. Replay attack detection based on parity space method for cyber-physical systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2025, 70(4): 2390−2405 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2024.3476309 [12] Siu J Y, Kumar N, Panda S K. Command authentication using multiagent system for attacks on the economic dispatch problem. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2022, 58(4): 4381−4393 doi: 10.1109/TIA.2022.3172240 [13] Zhu P, Jin S T, Bu X H, Hou Z S, Yin C K. Model-free adaptive control for a class of MIMO nonlinear cyber-physical systems under false data injection attacks. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2023, 10(1): 467−478 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2022.3203354 [14] Suprabhath K S, Prasad M V S, Madichetty S, Mishra S. A deep learning based cyber attack detection scheme in DC microgrid systems. CPSS Transactions on Power Electronics and Applications, 2023, 8(2): 119−127 [15] Abianeh A J, Wan Y, Ferdowsi F, Mijatovic N, Dragicevic T. Vulnerability identification and remediation of FDI attacks in islanded DC microgrids using multi-agent reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2022, 37(6): 6359−6370 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2021.3132028 [16] Gusrialdi A, Qu Z, Simaan M A. Competitive interaction design of cooperative systems against attacks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(9): 3159−3166 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2793164 [17] Ahmed A, Saeed M A, Jenabzadeh A, Xu X L, Zhang W D. Frequency domain resilient consensus of multiagent systems under IMP-based and non IMP-based attacks. Automatica, 2022, 146(110582): 0005−1098 [18] Wang Y C, Rajabinezhad M, Zuo S. Secondary defense strategies of AC microgrids under polynomially unbounded FDI attacks and communication link faults. IEEE Control Systems Letters, 2024, 8: 2223−2228 doi: 10.1109/LCSYS.2024.3415485 [19] Zuo S, Wang Y C, Rajabinezhad M, Zhang Y. Resilient containment control of heterogeneous multiagent systems against unbounded attacks on sensors and actuators. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2024, 11(3): 1537−1547 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2023.3338772 [20] Lan J, Wang H, Liu Y J, Tong S C. Adaptive intelligent resilient bipartite formation control for nonlinear multiagent systems with false data injection attacks on actuators and sensors. IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 5(10): 5194−5204 [21] Kachhwaha M, Modi H, Nehra M K, Fulwani D. Robust observer-based defense strategy against actuator and sensor cyber-attacks in DCMGs. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(10): 11687−11696 doi: 10.1109/TII.2024.3412211 [22] Yue W B, Yang Y, Sun W. Resilient consensus control for heterogeneous multiagent systems via multiround attack detection and isolation algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(3): 4735−4744 doi: 10.1109/TII.2023.3327175 [23] Tan S, Xie P, Guerrero J M, Vasquez J C, Han R K. Cyberattack detection for converter-based distributed DC microgrids: Observer-based approaches. IEEE Industrial Electronics Magazine, 2022, 16(3): 67−77 doi: 10.1109/MIE.2021.3059996 [24] Gusrialdi A, Qu Z H, Simaan M A. Competitive interaction design of cooperative systems against attacks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(9): 3159−3166 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2793164 [25] Kachhwaha M, Modi H, Nehra M K, Fulwani D. Resilient control of DC microgrids against cyber attacks: A functional observer based approach. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2023 [26] Sadabadi M S, Atman M W S, Aynala A, Gusrialdi A. Resilient design of leader–follower consensus against cyber-attacks. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2024, 11(2): 1080−1092 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2023.3332778 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 11
- HTML全文浏览量: 10
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: