-
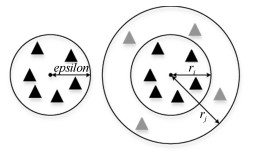
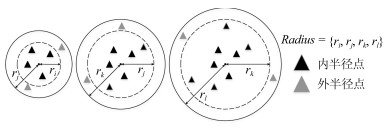
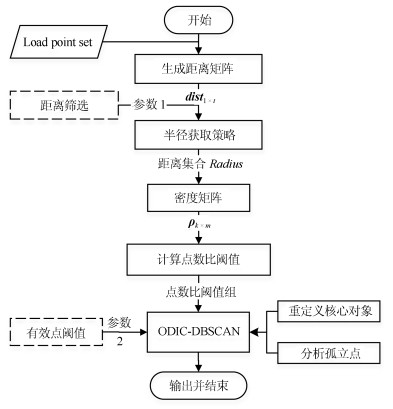
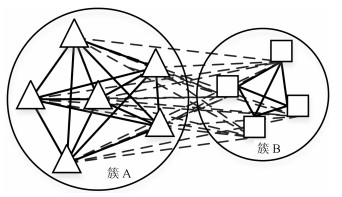
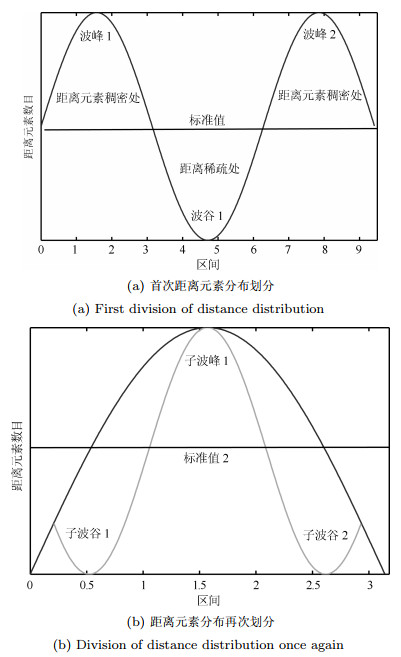
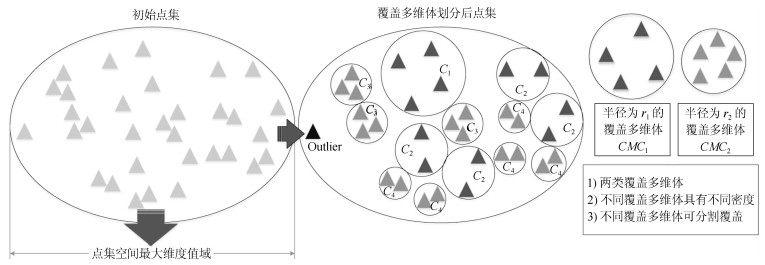
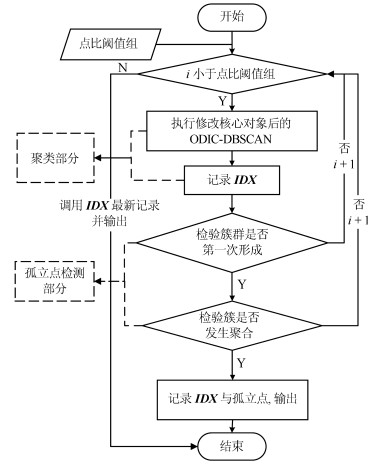
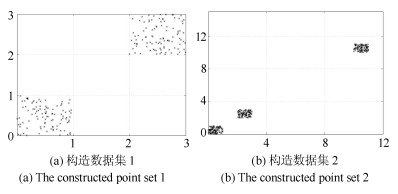
摘要: 长期以来,孤立点的检测一直聚焦于簇边缘的离散点,当聚类后簇的数目低于实际数目,或孤立点被伪装在簇内的情况下,簇内孤立点的判定则会更加困难.为判定簇内孤立点,提出一种基于密度聚类DBSCAN(Density based spatial clustering of application with noise)的簇内孤立点检测方法ODIC-DBSCAN(Outlier detection of inner-cluster based on DBSCAN).首先在建立距离矩阵的基础上,通过半径获取策略得到针对该点集的k个有效半径Radius集合,并据此构造密度矩阵;然后建立点集覆盖模型,提出了相邻有效半径构造的覆盖多维体能够覆盖点集的思想,并通过拉格朗日乘子法求取最优的覆盖多维体数目之比,输出点比阈值组;最后重建ODIC-DBSCAN的孤立点检测方法,以簇发生融合现象作为算法终止的判定条件.实验通过模拟数据集,公开benchmark与UCI数据集共同验证了ODIC-DBSCAN算法,展示了聚类过程;分析了算法性能;并通过与其他聚类、孤立点判定方法的对比,验证了算法对簇内孤立点的判定效果.Abstract: Outlier detection has been focused on the discrete points of cluster edges for a long time. When the number of clusters is less than the actual number, or the outliers are disguised within the cluster, the detection of inliers becomes more difficult. Therefore, a new analytical algorithm for inliers ODIC-DBSCAN (Outlier detection of inner-cluster based on DBSCAN), which is based on DBSCAN (Density based spatial clustering of application with noise), is proposed. First, on the basis of establishing the distance matrix, the set of k effective radii for the set of points is obtained through the proposed Radius Obtaining Strategy, and the density matrix is constructed accordingly. Then, the point-set covering model is established and the idea that the covering multidimensional cube with adjacent effective radius can cover the point sets is proposed. The Lagrange multiplier method is used to obtain the optimal ratio of the number of covering multidimensional cubes, and the group of point ratio thresholds is obtained. Finally, the method of outlier detection based on ODIC-DBSCAN is reconstructed, and the fusion phenomenon of the clusters is taken as the terminating condition of the algorithm. The experiment verifies the ODIC-DBSCAN algorithm through three kinds of point sets:the synthetic point sets, the public clustering benchmarks and the UCI real-world datasets; the clustering process is demonstrated and the performances are analyzed. Besides, experimental results show that comparing to other clustering and outlier detection methods, the ODIC-DBSCAN algorithm is able to determine the inliers more effectively.
-
Key words:
- Clustering /
- DBSCAN /
- inliers /
- density correlation /
- outlier detection
1) 本文责任编委 陈德旺 -
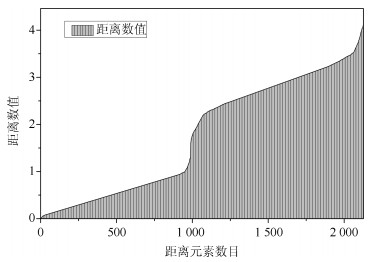
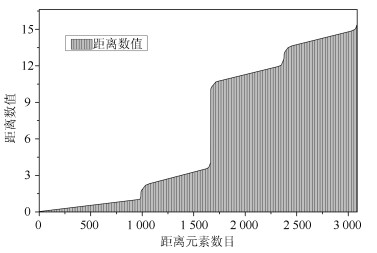
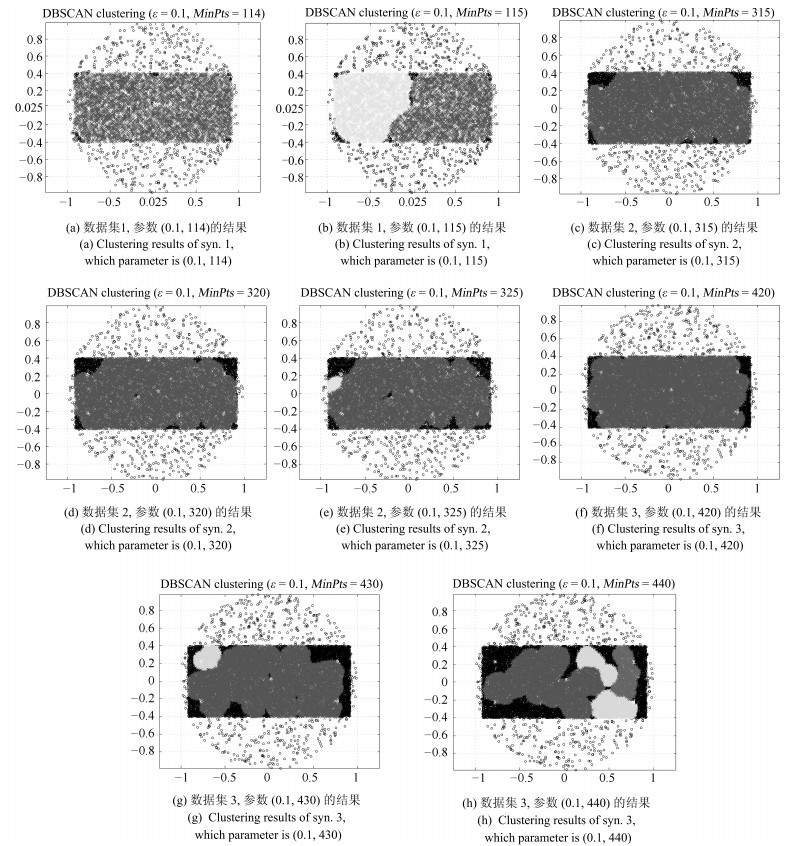
表 1 梯度含义
Table 1 The meaning of gradient
位置 意义 第一梯度左部 以三个簇各自内部点的距离为对象 第一梯度右部 以簇1、簇2间的距离为对象 第二梯度右部 以簇2、簇3间的距离为对象 第三梯度右部 以簇1、簇3间的距离为对象 表 2 距离筛选与有效点阈值的敏感性测试
Table 2 The sensitivity of distance filter and effective points threshold
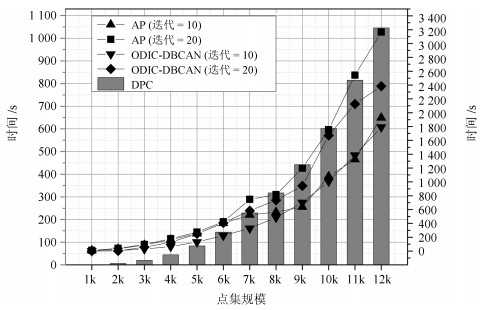
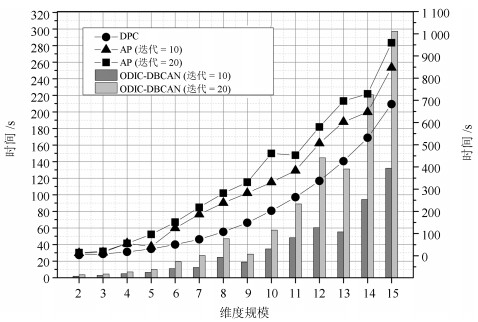
距离筛选 BA Chess WDBC 有效点阈值 孤立点数目 有效点阈值 孤立点数目 有效点阈值 孤立点数目 2 0.2 552 0.2~0.6 645 0.2~0.9 6 0.3~0.9 8 0.7~0.9 136 3 0.2 545 0.2~0.6 645 0.2~0.9 6 0.3~0.9 27 0.7~0.9 136 0.2~0.3 497 0.2~0.6 645 0.2~0.9 6 0.4~0.8 86 0.7~0.9 136 0.9 21 0.2~0.3 497 - - 0.2~0.9 6 0.4~0.8 86 0.9 9 6 0.2~0.3 497 - - 0.2~0.9 6 0.4~0.8 143 0.9 9 表 3 ODIC-DBSCAN在相同规模不同分布的数据集下时间运行细节
Table 3 Time details of ODIC-DBSCAN on the point sets that have same scale but different distributions
数据集 总时间(秒) 预处理(秒)} ODIC-DBSCAN (秒)
ExpandCluster (运行次数/时间/所占该函数百分比)其他 查询邻居 计算比值 合并邻居 建立簇等 95个簇 14.719 4.339 4 999/0.399/4.3 % 4 999/0.715/7.6 % 4 999/6.511/69.6 % 0.04 5个簇 3.718 1.631 2 980/0.182/28.4 % 2 980/0.378/59.1 % 2 980/0.010/1.6 % 0.43 表 4 特殊符号与其意义
Table 4 Symbols and its meanning
符号 意义 $k$ 近邻参数数目 Top-$n$ 查准率, 前$n$个检测结果中包含几个预设孤立点 $per$ DPC算法的截断距离$percentage$表示所有点的相互距离中由小到大排列占总数的百分比 $pre$ AP算法参数, 表示数据偏好$preference$, 用来确定簇数目 $cn$ 簇数目$cluster$ $number$ $para$ ODIC-DBSCAN参数$parameter$:(距离筛选, 有效点阈值) $ToDR$ ReCon-DBSCAN, ReCon-OPTICS两类算法参数: Threshold on density ratio表示密度比阈值 $DO$, $nDO$ 检测出的孤立点集合与其对应数目 $DI$, $nDI$ 检测出的簇内孤立点集合与其对应数目 表 5 DPC与AP在模拟数据集1~3的检测结果
Table 5 Detection results of DPC and AP on synthetic point sets 1~3
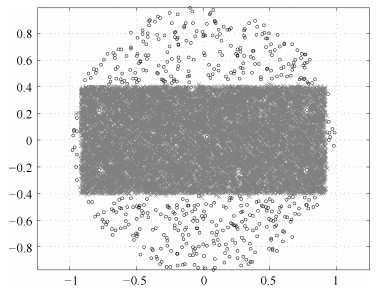
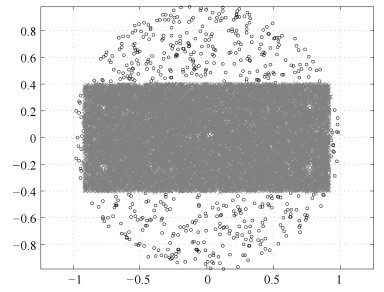
Point sets DPC AP $cn$ $per$ CORE HALO $position$ $pre$ $cn$ $n_{DI}$ Synthetic 1 2 1 % 1 585:1 411 1 278:1 805 78 $-200$ 3 - 2 2 % 1295:1 664 1 358:1 672 162 $-300 $ 2 - Synthetic 2 2 1 % 1 009:1 105 7 197:5 955 92 82 68 75 65 $-100$ 6 - 2 2 % 1 668:1 228 6 425:5 945 89 62 60 110 64 $-150$ 5 - Synthetic 3 2 1 % 2 688:1 631 7 770:7 989 48 40 58 32 37 $-100$ 8 - 2 2 % 5 082:688 10 028:4 280 58 39 37 34 47 $ -200/-300$ 4 - 表 6 Re-ConDBSCAN算法在模拟数据集1~3的检验结果
Table 6 Detection results of Re-Con DBSCAN on synthetic point sets 1~3
$Parameter$ Synthetic 1 Synthetic 2 Synthetic 3 $\langle eps, eta\rangle$ $ToDR$ $n_{DO}$ $HR$ $n_{DI}$ $n_{DO}$ $HR$ $n_{DI}$ $n_{DO}$ $HR$ $n_{DI}$ $\langle 0.08, 0.011\rangle$ 0.7 75 0.1412 - 79 0.1612 - 69 0.1324 - 0.8 175 0.3296 1 163 0.3327 3 176 0.3378 2 0.9 329 0.6196 1 256 0.5224 3 269 0.5163 - 1 280 0.5273 - 226 0.4612 - 234 0.4491 - 表 7 Re-ConOPTICS算法在模拟数据集1~3的检验结果
Table 7 Detection results of Re-Con OPTICS on synthetic point sets 1~3
$Parameter$ Synthetic 1 Synthetic 2 Synthetic 3 $\langle eps, MinPts\rangle$ $ToDR$ $n_{DO}$ $HR$ $n_{DI}$ $n_{DO}$ $HR$ $n_{DI}$ $n_{DO}$ $HR$ $n_{DI}$ $\langle 0.08, 8\rangle$ 10 345 0.6497 - 365 0.7449 - 345 0.6622 - 30 450 0.8457 - 457 0.9327 - 460 0.8829 - 50 475 0.8945 - 467 0.9531 - 481 0.9232 - 70 476 0.8964 - 471 0.9612 - 490 0.9405 - 表 8 六种不同检测方法在三类公开数据集上的对比
Table 8 Detection results of six OD methods on three public higher dimensional datasets
数据集 非二值检测结果: TOP-$n$ 二值检测结果 $k$ LOF LDOF F-ABOD OPTICS DPC ODIC-DBSCAN Top 10 $SRoPO$ Top 10 $SRoPO$ Top 10 $SRoPO$ Top 10 $SRoPO$ $per$ $HR$ $para$ $HR$ Banknote Authentication 5 6 160 2 2 291 2 3 326 8 154 1 % 6/10 2, 0.9 8/9 10 8 81 4 643 3 2 514 8 368 1.50 % 7/10 4, 0.9 8/9 15 7 217 4 485 3 1 962 8 89 2 % 8/10 5, 0.9 8/9 20 7 83 4 655 3 1 472 6 149 5 % 8/10 6, 0.9 8/9 Chess 5 1 324 2 1 860 1 10 542 5 170 1 % 3/10 2, 0.9 10/136 10 4 308 2 521 - 10 019 1 243 1.50 % 3/10 2.5, 0.9 10/136 15 4 626 3 401 - 9 350 1 301 2 % 4/10 3, 0.9 10/136 20 3 765 2 447 - 8 326 1 394 5 % 4/10 3.5, 0.9 10/136 WDBC 5 1 729 1 1 275 1 1 907 5 113 1 % 6/10 3, 0.9 5/6 10 6 76 4 378 1 1 673 5 145 1.50 % 6/10 4, 0.9 5/6 15 6 85 5 132 1 1 626 5 203 2 % 6/10 5, 0.9 5/6 20 5 91 6 112 3 1 459 5 233 5 % 6/10 6, 0.9 5/6 表 9 基于密度比的ReCon-DBSCAN与ReCon-OPTICS算法在三类数据集上的检测结果
Table 9 Detection results of density-ratio based ReCon-DBSCAN and ReCon-OPTICS on three real-world point sets
$Parameter$ 数据集1 数据集2 数据集3 $ToDR$ for RA-DBSCAN $ToDR$ for RA-OPTICS ReCon-DBSCAN ReCon-OPTICS ReCon-DBSCAN ReCon-OPTICS ReCon-DBSCAN ReCon-OPTICS 0.5 20 160 10 - 5 - - - 6 0.6 30 170 20 3/14 5 2/88 1 - 5 0.7 40 180 25 4/48 6 10/550 1 2/1 4 0.8 50 190 30 6/240 6 10/1 354 1 3/8 4 0.9 60 200 35 6/597 7 8/365 1 5/159 4 1 70 210 40 5/196 7 - error - 4 -
[1] 袁超, 柴毅.复杂网络的局部社团结构挖掘算法.自动化学报, 2014, 40(5):921-934 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18360.shtmlYuan Chao, Chai Yi. Method for local community mining in the complex networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(05):921-934 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18360.shtml [2] 原豪男, 郭戈.交通信息物理系统中的车辆协同运行优化调度.自动化学报, 2019, 45(1):143-152 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19423.shtmlYuan Hao-Nan, Guo Ge. Vehicle cooperative optimization scheduling in transportation cyber physical systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(1):143-152 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19423.shtml [3] 王立, 张蓉, 沙朝锋, 王晓玲, 周傲英.电子商务商品归一化方法研究.计算机学报, 2014, 37(2):312-325 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjxb201402005Wang Li, Zhang Rong, Sha Chao-Feng, Wang Xiao-Ling, Zhou Ao-Ying. A product normalization method for E-commerce. Journal of Computers, 2014, 37(2):312-325 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjxb201402005 [4] Hawkins D M. Identification of outliers. London:Chapman and Hall, 1980. 1 [5] Zhang Y, Hamm N A S, Meratnia N, Stein A, Voort M, Havinga P J M. Statistics-based outlier detection for wireless sensor networks. Int Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2012, 26(8):1373-1392 doi: 10.1080/13658816.2012.654493 [6] Rousseeuw P J, Hubert M. Robust statistics for outlier detection. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews:Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2011, 1(1):73-79 doi: 10.1002/widm.2 [7] Zhang K, Hutter M, Jin H. A new local distance-based outlier detection approach for scattered real-world data. Advances in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 2009:813-822 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_arXiv.org_0903.3257 [8] Wang B, Xiao G, Yu H, Yang X C. Distance-based outlier detection on uncertain data. In: Proceedings of the Ninth IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology. Xiamen, China: IEEE, 2009. 293-298 [9] Cassisi C, Ferro A, Giugno R, Pigola G, Pulvirenti A. Enhancing density-based clustering:Parameter reduction and outlier detection. Information Systems, 2013, 38(3):317-330 doi: 10.1016/j.is.2012.09.001 [10] Tao Y, Pi D. Unifying density-based clustering and outlier detection. In: Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Moscow, Russia: IEEE, 2009. 644-647 [11] Gupta M, Gao J, Aggarwal C C, Han J W. Outlier detection for temporal data:A survey. IEEE Trans on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2014, 26(9):2250-2267 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2013.184 [12] Aggarwal C C, Yu P S. Outlier detection for high dimensional data. In: Proceedings of the 2001 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data. New York, USA: ACM, 2001. 30(2): 37-46 [13] Jiang B, Pei J. Outlier detection on uncertain data: objects, instances, and inferences. In: Proceedings of the 27th IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering. Hannover, Germany: IEEE, 2011. 422-433 [14] 于彦伟, 王沁, 邝俊, 何杰.一种基于密度的空间数据流在线聚类算法.自动化学报, 2012, 38(6):1051-1059 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18085.shtmlYu Yan-Wei, Wang Qin, Kuang Jun, He Jie. An on-line density-based clustering algorithm for spatial data stream. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(6):1051-1059 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18085.shtml [15] Branch J W, Giannella C, Szymanski B, Wolff R, Kargupta H. In-network outlier detection in wireless sensor networks. Knowledge and Information Systems, 2013, 34(1):23-54 doi: 10.1007/s10115-011-0474-5 [16] Duan L, Xu L, Liu Y, Lee J. Cluster-based outlier detection. Annals of Operations Research, 2009, 168(1):151-168 doi: 10.1007/s10479-008-0371-9 [17] Du H Z, Zhao S J, Zhang D Q, WU J S. Novel clustering-based approach for local outlier detection. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops. CA, USA: IEEE, 2016. 802-811 [18] Maheshwari K, Singh M. Outlier detection using divide-and-conquer strategy in density based clustering. In: Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering. Jaipur, India: IEEE, 2016. 1-5 [19] Breunig M M, Kriegel H P, Ng R T, Sander J. LOF: identifying density-based local outliers. In: Proceeding of the 2000 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data. New York, USA: ACM, 2000. 93-104 [20] Kriegel H P, Schubert M, Zimek A. Angle-based outlier detection in high-dimensional data. In: Proceeding of the 14th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Las Vegas, USA: ACM, 2008. 444-452 [21] Rodriguez A, Laio A. Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks. Science, 2014, 344(6191):1492-1496 doi: 10.1126/science.1242072 [22] Wang X F, Xu Y. Fast clustering using adaptive density peak detection. Statistical methods in medical research, 2017, 26(6):2800-2811 doi: 10.1177/0962280215609948 [23] 褚睿鸿, 王红军, 杨燕, 李天瑞.基于密度峰值的聚类集成.自动化学报, 2016, 42(9):1401-1412 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18928.shtmlChu Rui-Hong, Wang Hong-jun, Yang Yan, Li Tian-Rui. Clustering ensemble based on density peaks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(9):1401-1412 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18928.shtml [24] Bie R, Mehmood R, Ruan S, Sun Y C, Dawood H. Adaptive fuzzy clustering by fast search and find of density peaks. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, 2016, 20(5):785-793 doi: 10.1007/s00779-016-0954-4 [25] Wang M, Zuo W, Wang Y. An improved density peaks-based clustering method for social circle discovery in social networks. Neurocomputing, 2016, 179:219-227 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.11.091 [26] Frey B J, Dueck D. Clustering by passing messages between data points. Science, 2007, 315(5814):972-976. doi: 10.1126/science.1136800 [27] Givoni I, Frey B. Semi-supervised affinity propagation with instance-level constraints. In: Proceeding of the 2009 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. Florida, USA: 2009. 161-168 [28] Inmar E, Givoni, Clement Chung, Brendan J. Frey. Hierarchical affinity propagation. In: Proceeding of the 27th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence. Barcelona, Spain: AUAI Press, 2011. 238-246 [29] Ankerst M, Breunig M M, Kriegel H P, Sander J. OPTICS: ordering points to identify the clustering structure. In: Proceedings of the 1999 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data. New York, USA: ACM, 1999. 49-60 [30] Zhu Y, Ting K M, Carman M J. Density-ratio based clustering for discovering clusters with varying densities. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 60:983-997 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.07.007 [31] Oh H K, Yoon S H, Kim S W. Hierarchical clustering and outlier detection for effective image data organization. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication. New York, USA: ACM, 2012. Article No. 18 [32] Kim K, Khabsa M, Giles C L. Inventor name disambiguation for a patent database using a random forest and dbscan. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/ACM Joint Conference on Digital Libraries. Newark, USA: IEEE, 2016. 269-270 [33] Abid A, Kachouri A, Mahfoudhi A. Outlier detection for wireless sensor networks using density-based clustering approach. IET Wireless Sensor Systems, 2017, 7(4):83-90 doi: 10.1049/iet-wss.2016.0044 -





 下载:
下载: